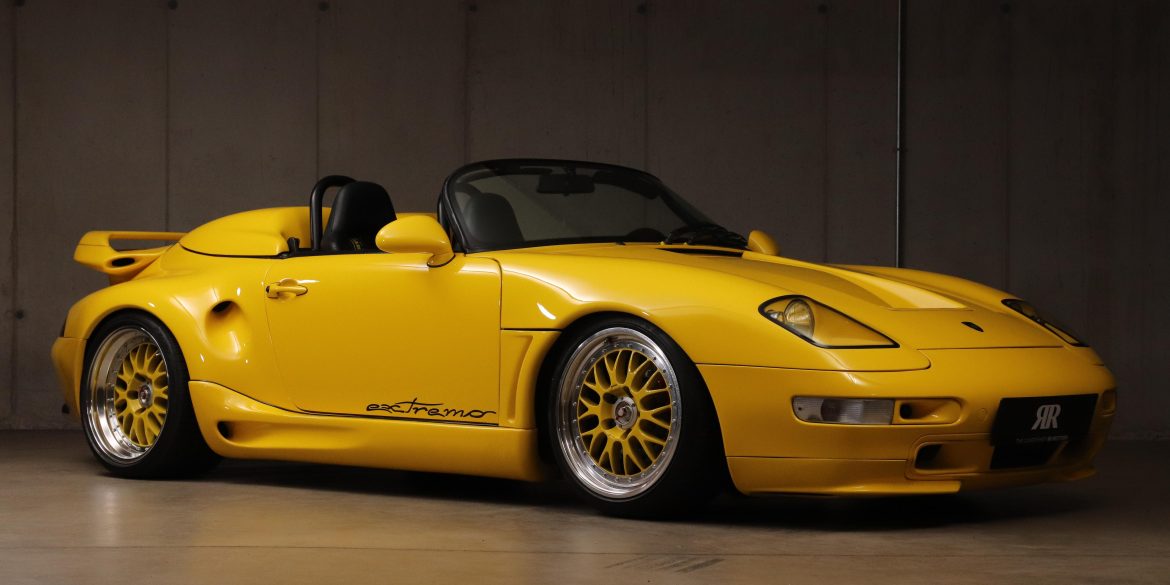
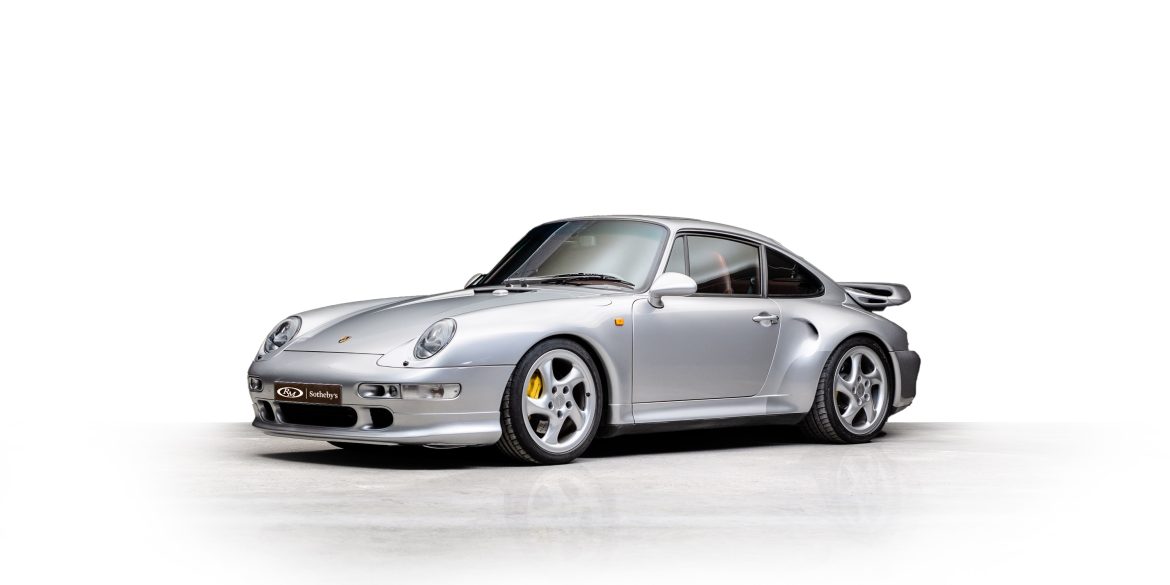
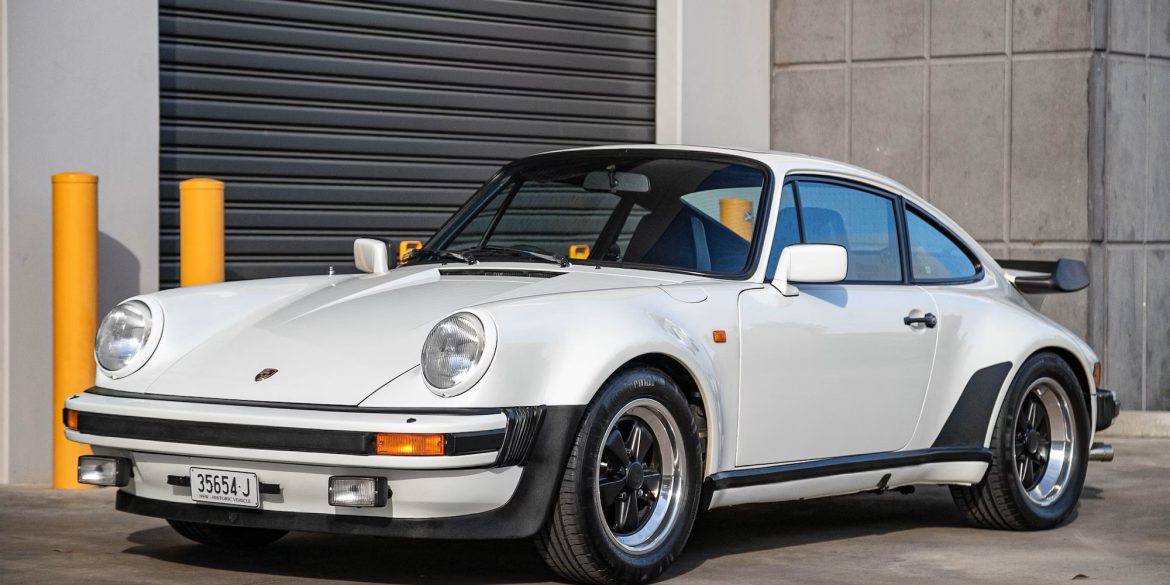
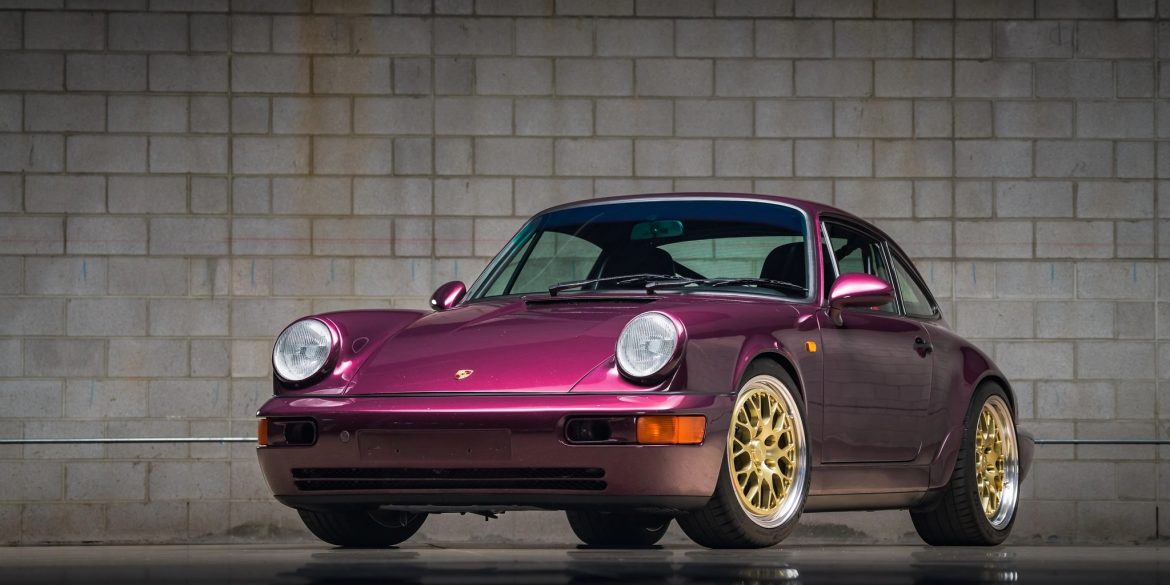
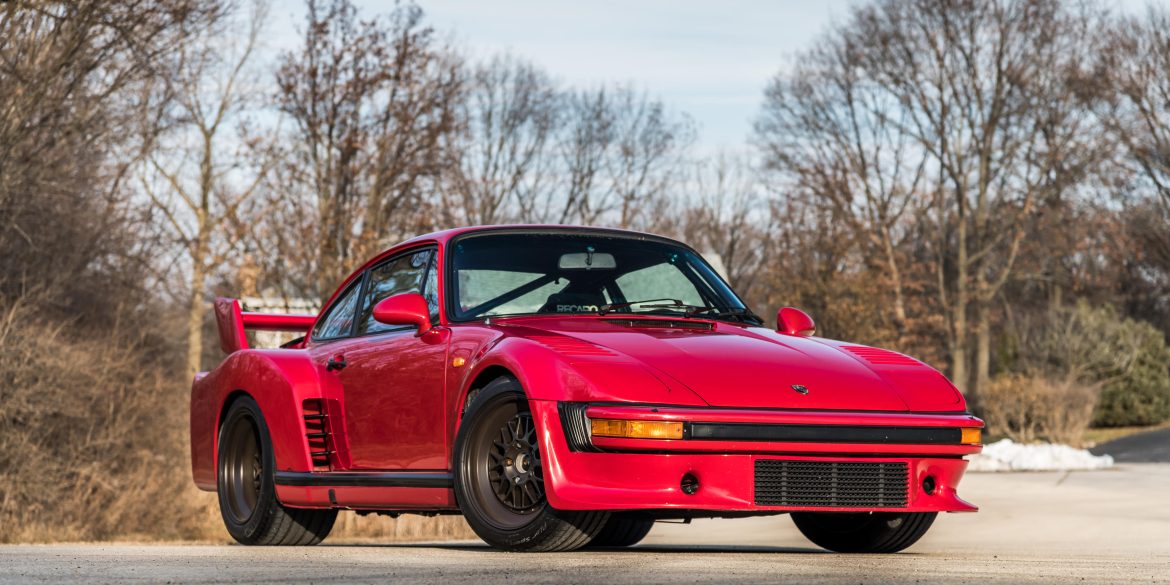
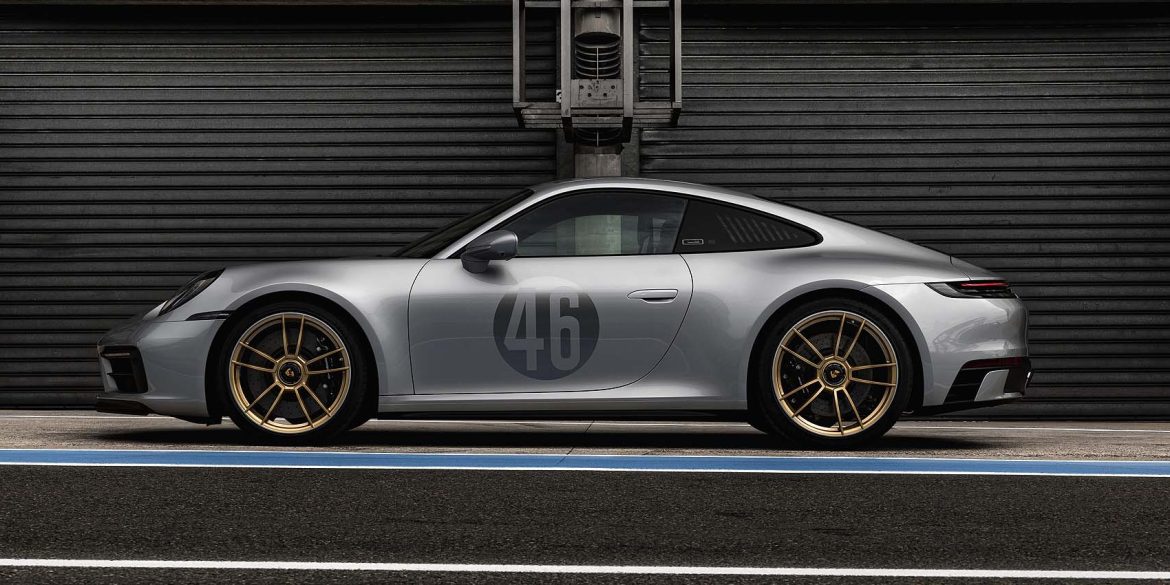
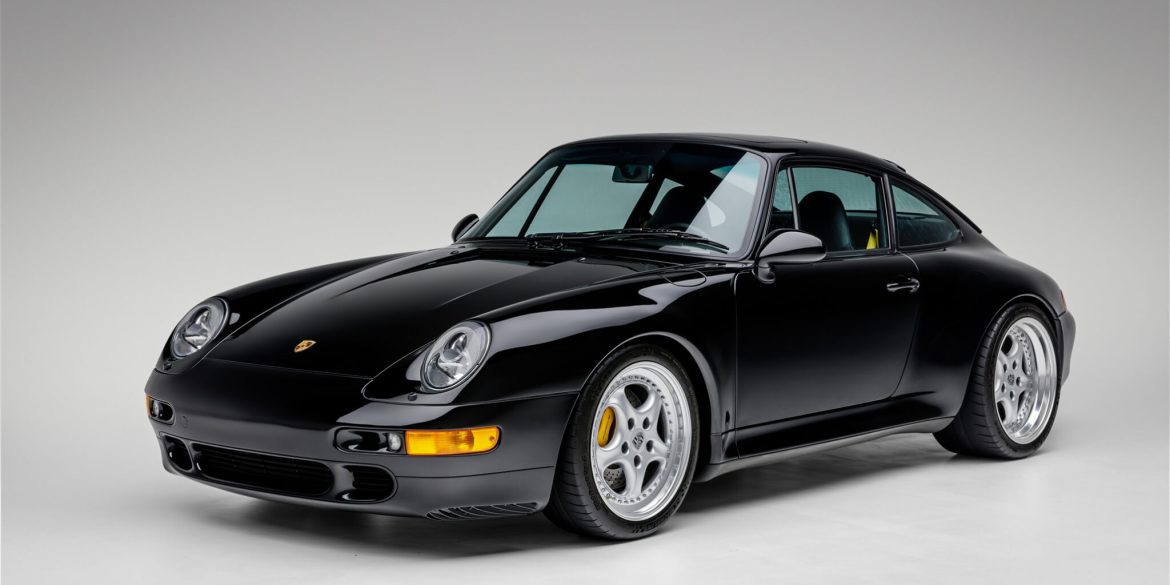
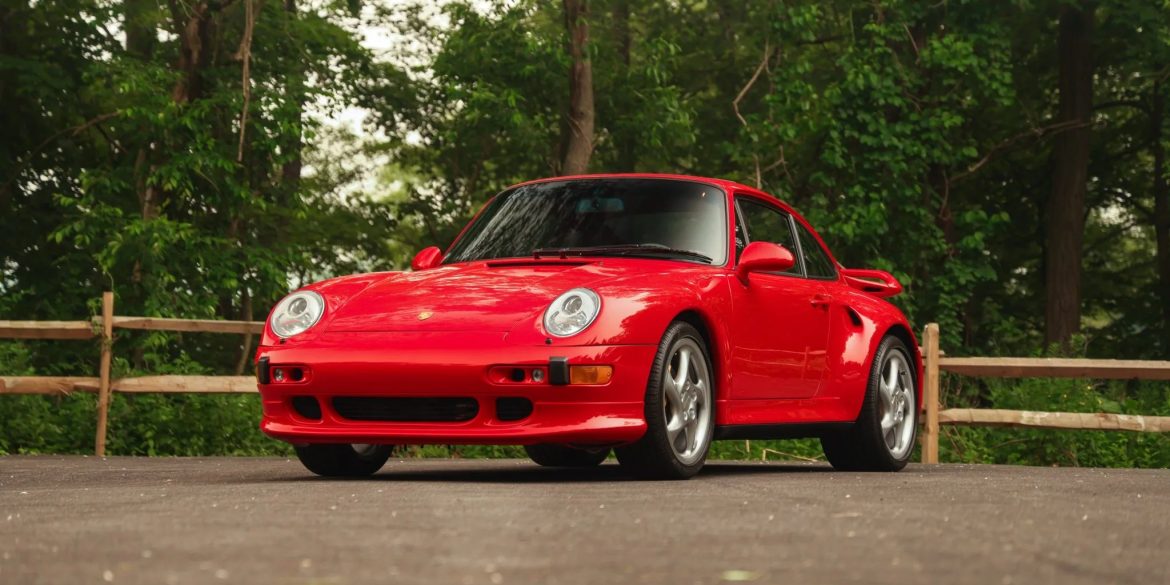
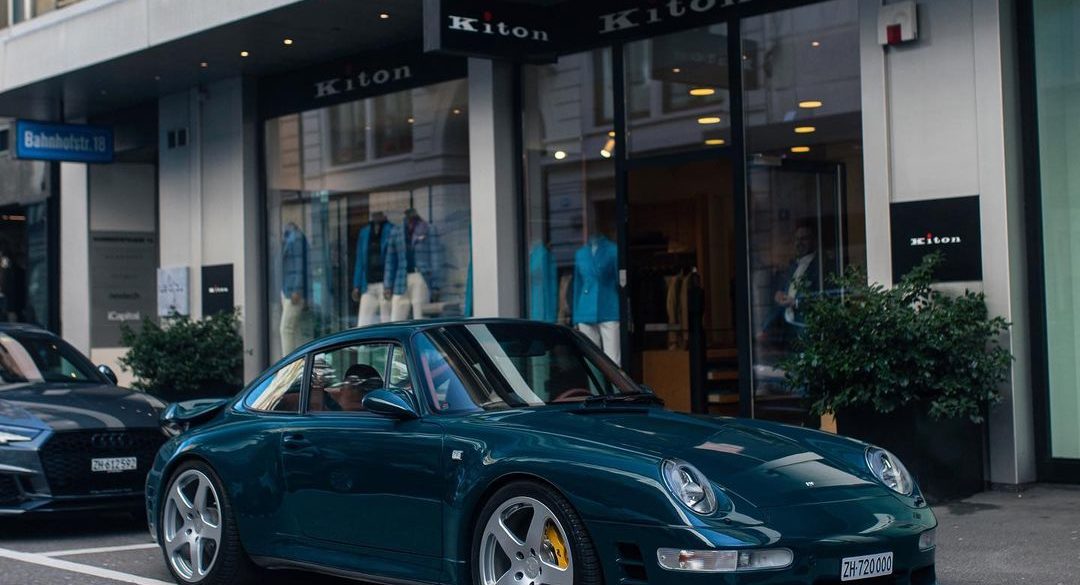
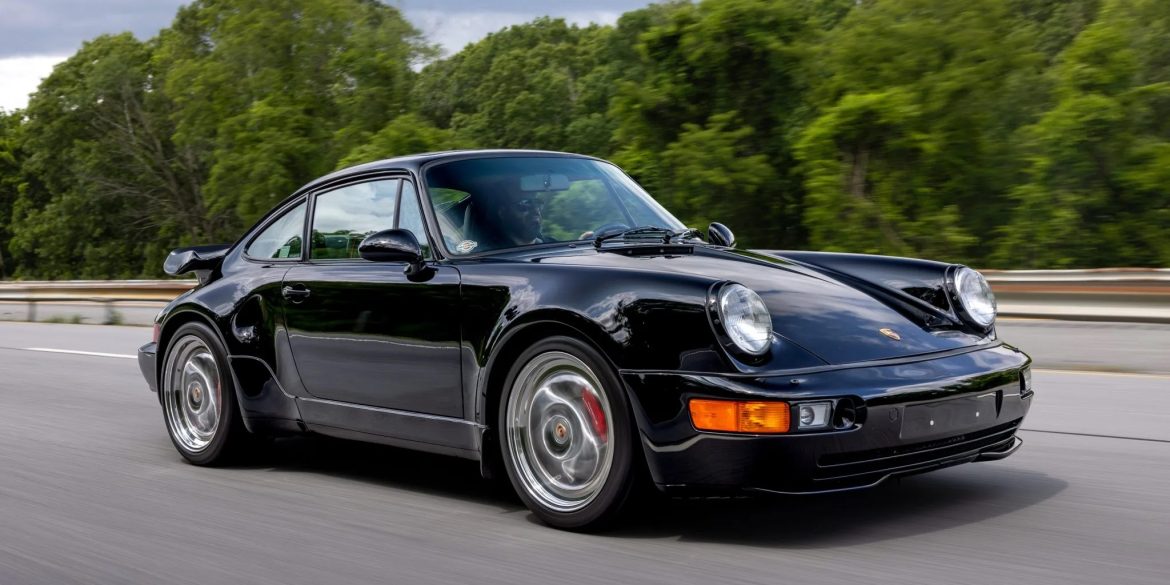
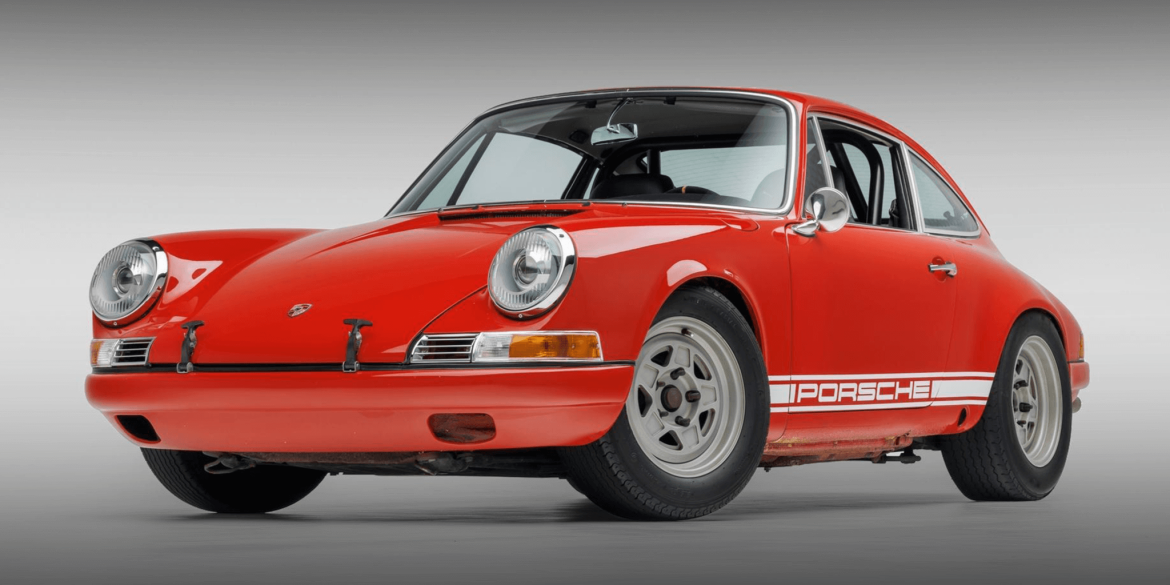
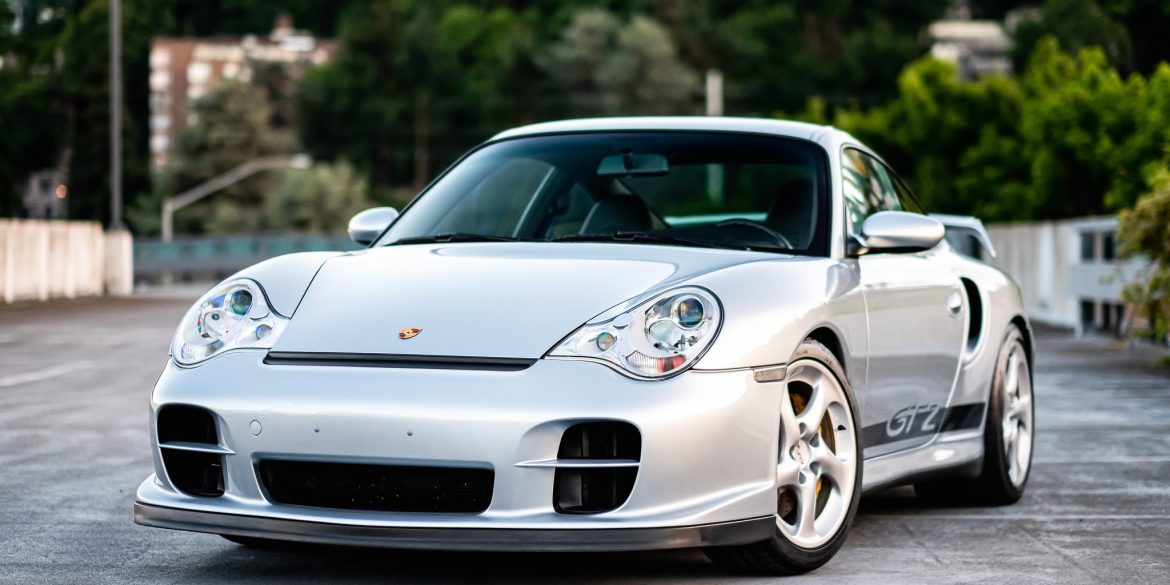
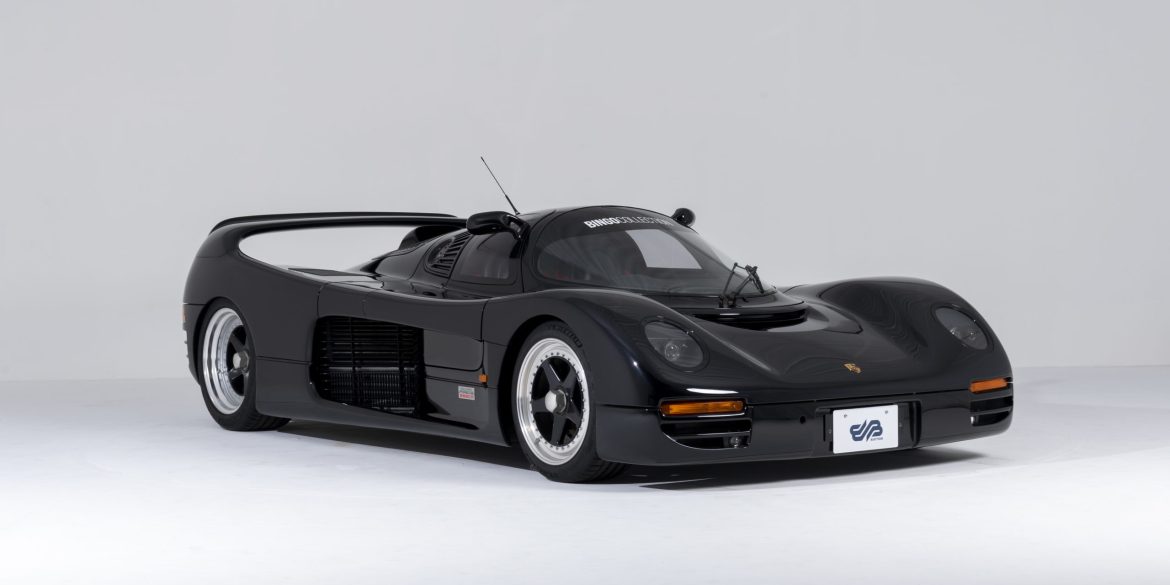
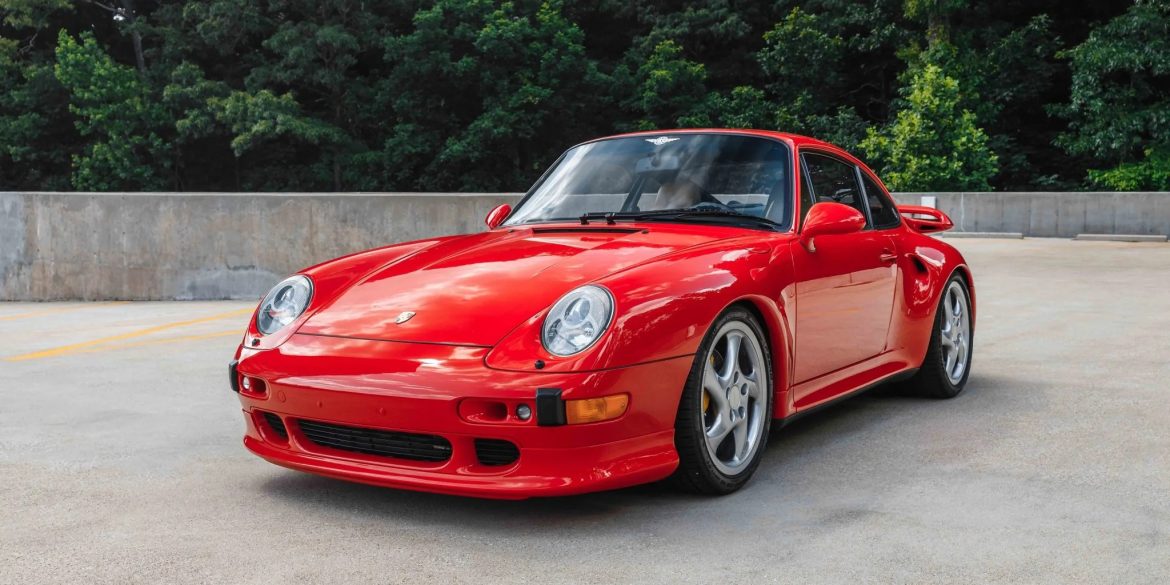
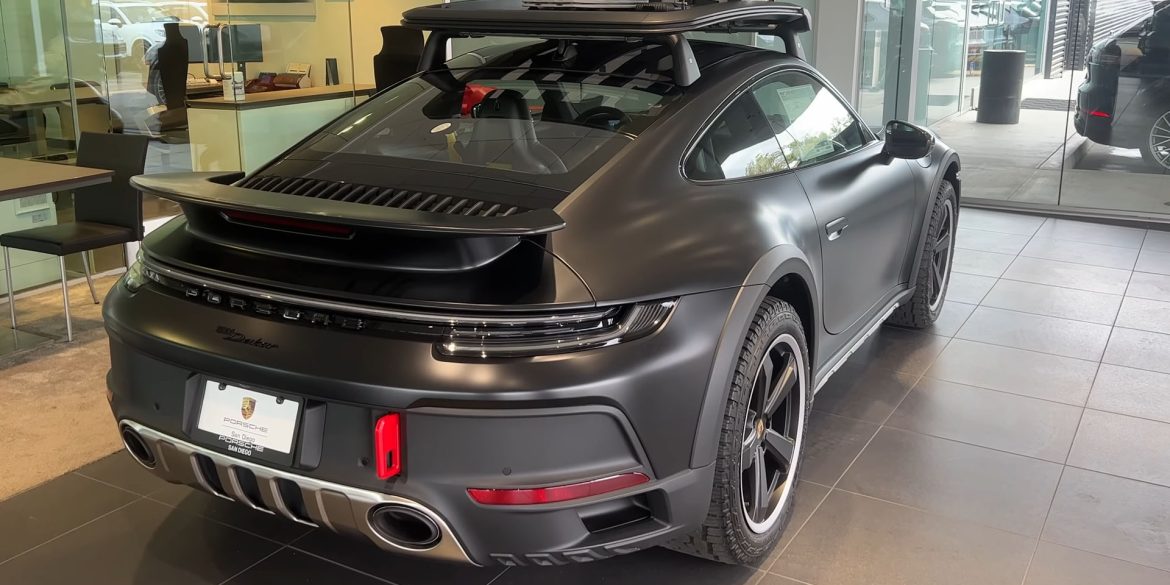
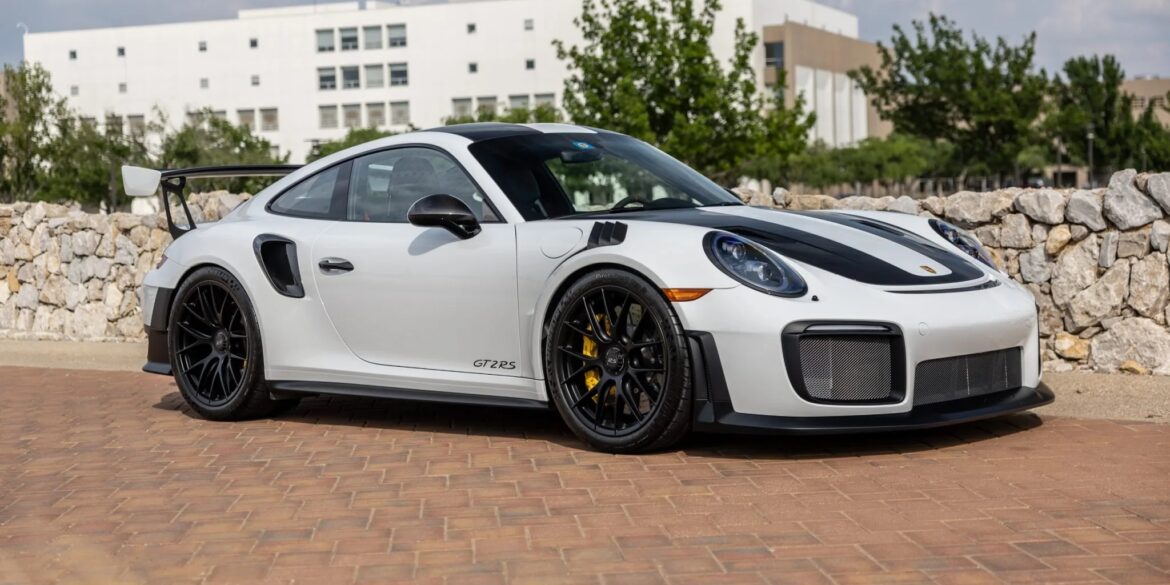
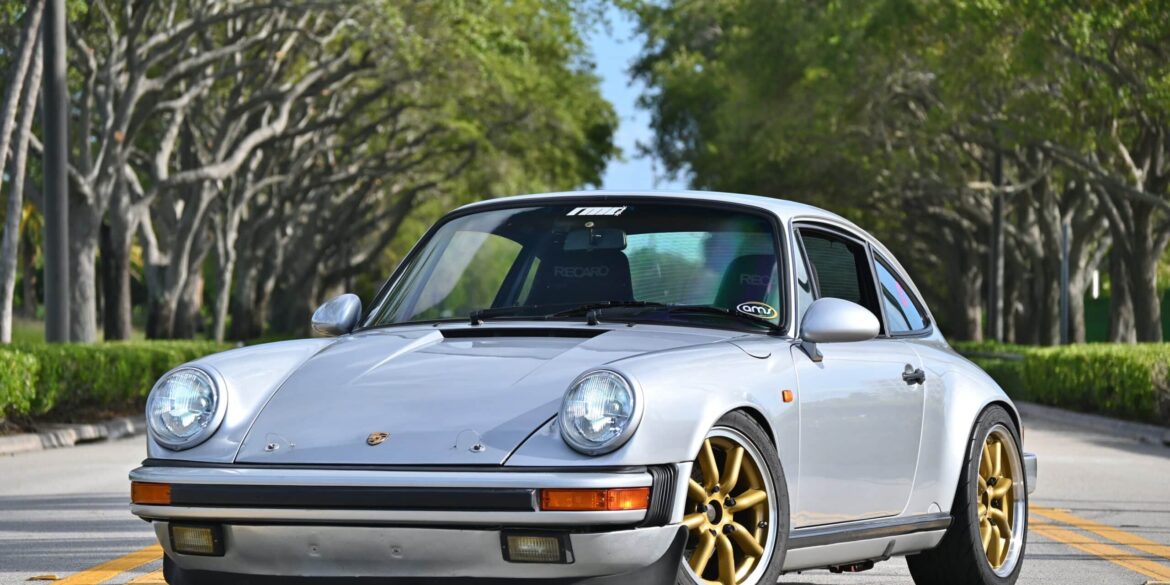
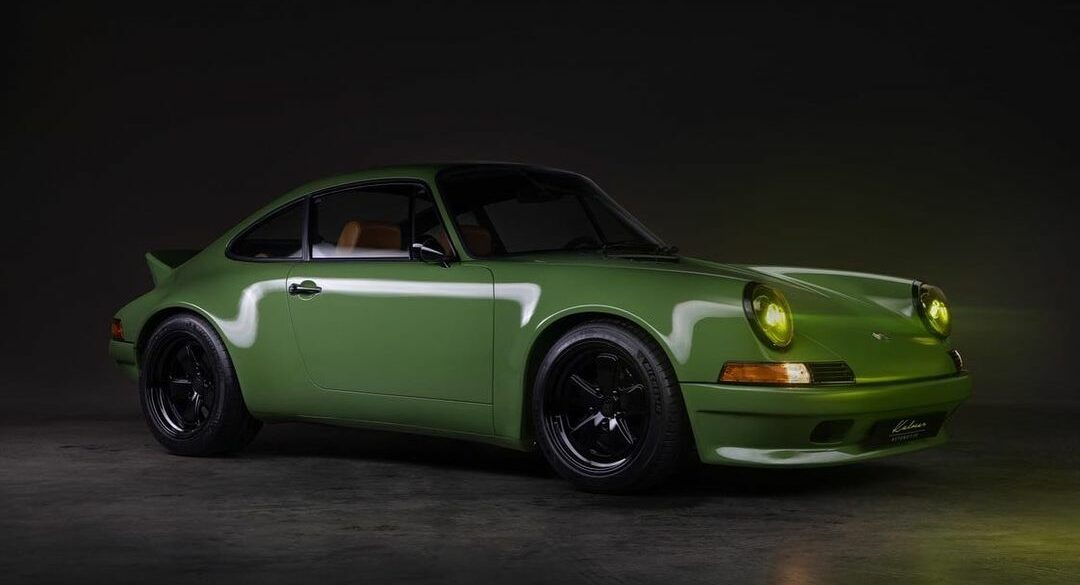
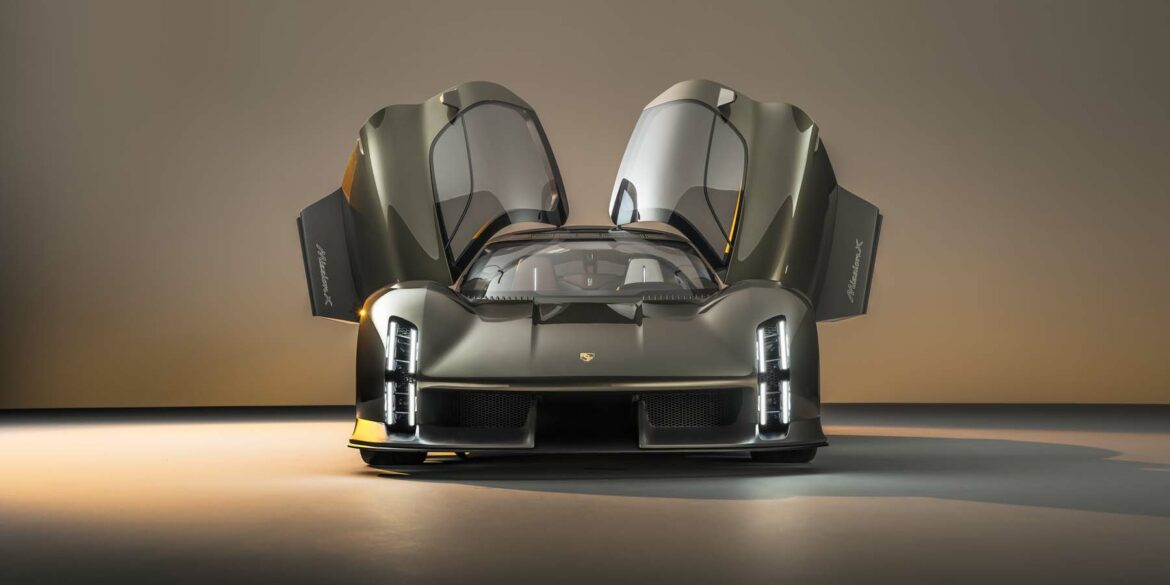
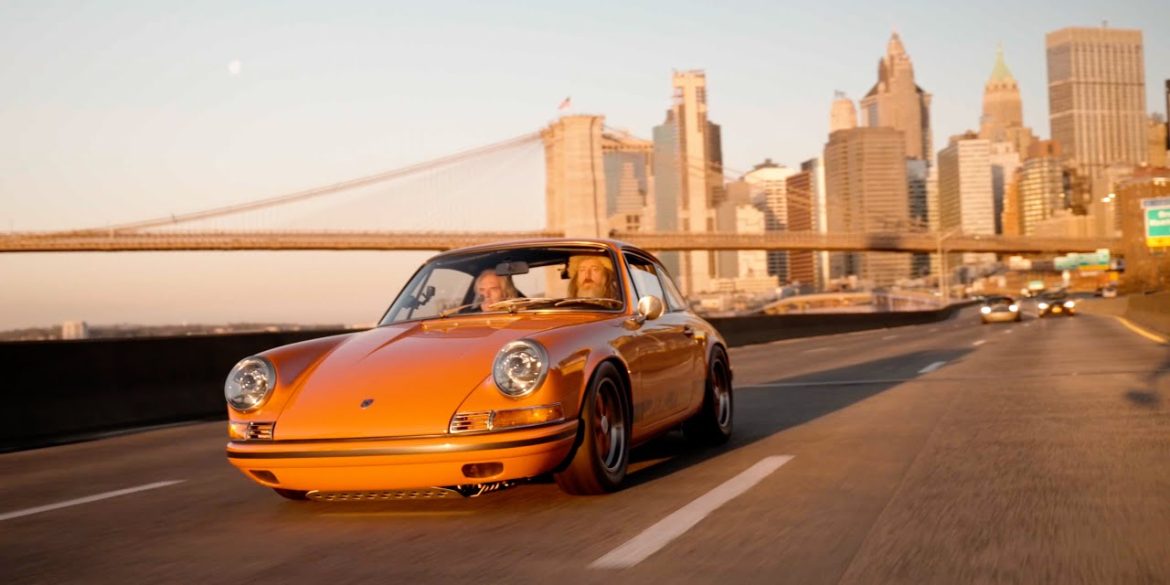
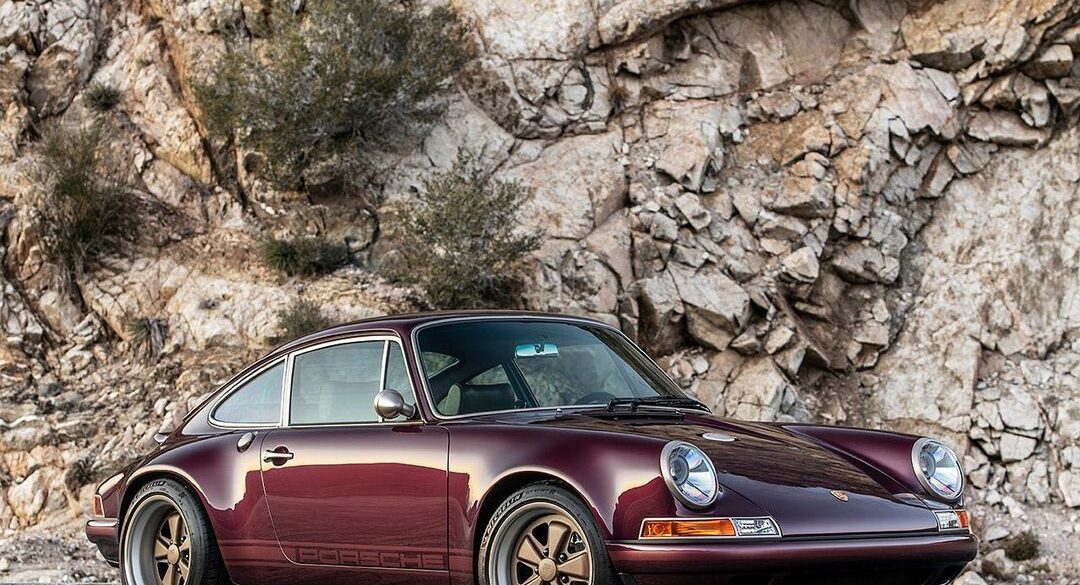
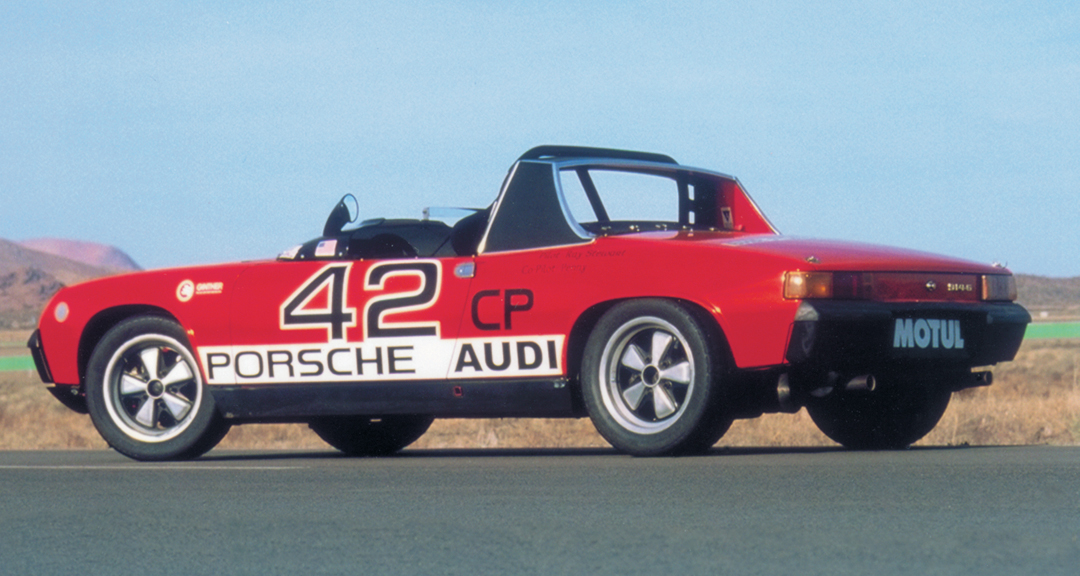
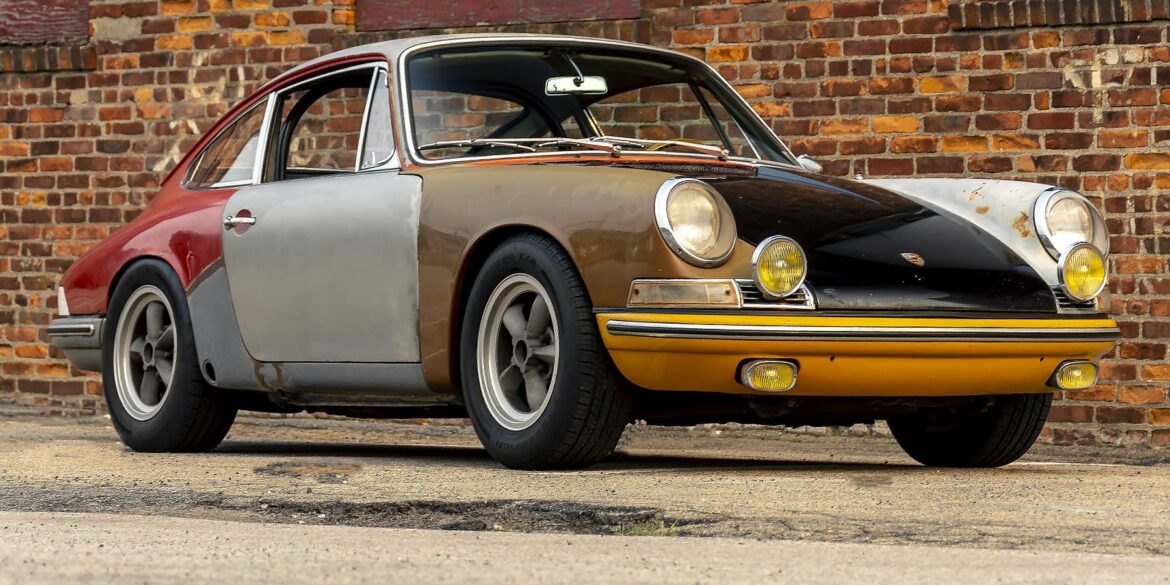
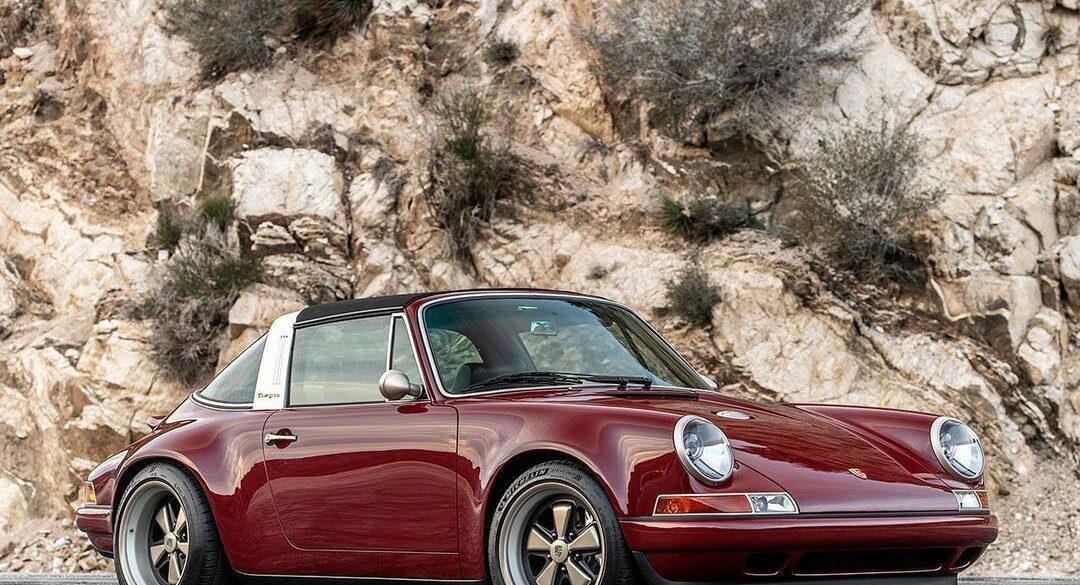
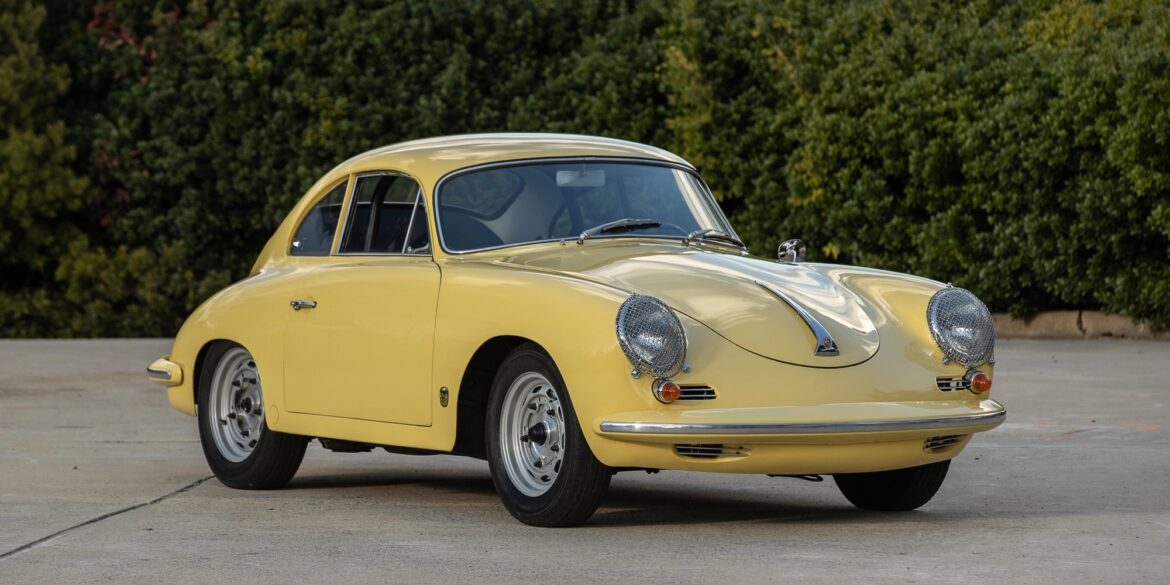
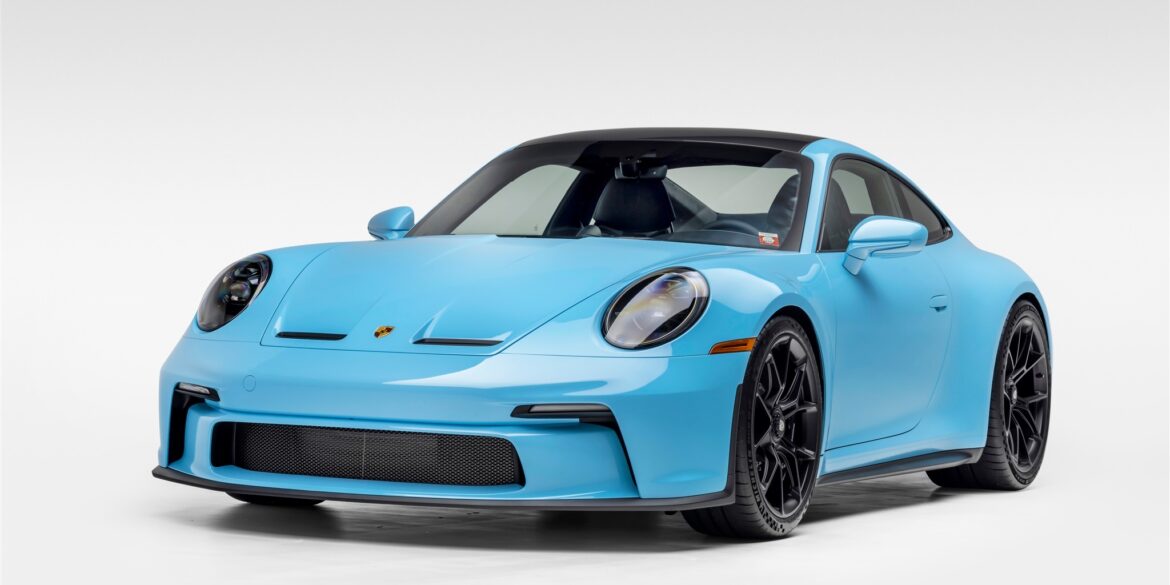
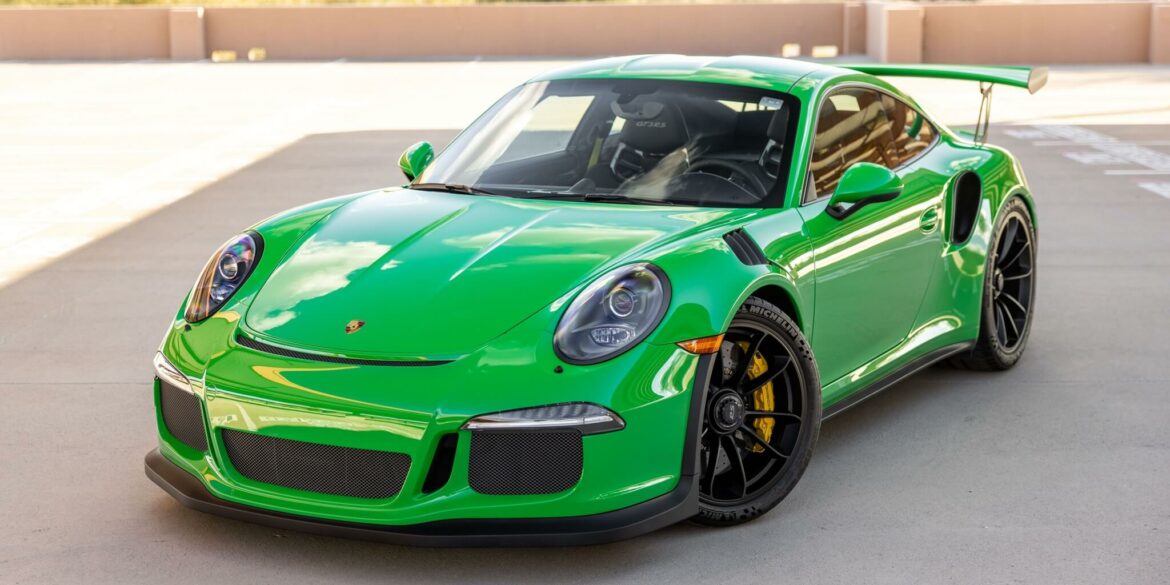
The Porsche you see here is an exceptionally beautiful car and one of just two ever created by Gemballa GmbH, the German car manufacturer and vehicle tuner located in Leonberg. It is based on the Porsche 911 Type 993 and was initially commissioned by the Fulda tire company, who desired...
Porsche Models
All
- Porsche 911
- Porsche 914
- Porsche 917K
- Porsche 918
- Porsche 924
- Porsche 928
- Porsche 944
- Porsche 959
- Porsche 962
- Porsche Boxster Concept
- Porsche Carrera GT
- Porsche Cayenne
- Porsche Cayenne 955/957 (1st Gen)
- Porsche Cayman 987 (2nd Gen)
- Porsche RS Spyder (9R6)
- Porsche Boxster 986 (1st Gen)
- Porsche Cayman 981 (3rd Gen)
- Porsche 356 Pre-A
- Porsche Boxster 987 (2nd Gen)
- Porsche Cayenne 958 (2nd Gen)
- Porsche 718 Cayman 982 (4th Gen)
- Porsche 356 A
- Porsche Boxster 981 (3rd Gen)
- Porsche 356 B
- Porsche 718 Boxster 982 (4th Gen)
- Porsche 356 C
- Porsche 968
- Porsche Panamera
- Porsche Panamera 970 (1st Gen)
- Porsche Panamera 971 (2nd Gen)
- Porsche Boxster
- Porsche Cayman
- Porsche Macan
- Porsche Taycan
- Porsche 912
- Porsche 919
- Porsche 956
- Porsche 2708 Indy
- Porsche Type 64
- Porsche 918 RSR Concept
- Porsche 918 Spyder
- Porsche 918 Concept
- Porsche 918 Spyder Prototype
- Porsche 917
- Porsche Race Cars
- 911 Carrera RS 2.7
- Porsche 550
- Porsche 718
- Porsche 901 (911)
- Porsche Concept Cars
- Porsche 904
- Porsche 906
- Porsche 907
- Porsche 908
- Porsche 910
- Porsche 911 (F-Series)
- Porsche 911 (991)
- Porsche 911 (G-Series)
- Porsche 911 (964)
- Porsche 911 (993)
- Porsche 911 GT1 Race
- Porsche 911 GT1 Street
- Porsche 911 (996)
- Porsche 911 (997)
- Porsche 916
- Porsche 919 Hybrid
- Porsche 934
- Porsche 934/5
- Porsche 935
- Porsche 936
- Porsche Mission E
- Porsche 928 S
- Porsche 928 S4
- Porsche 928 GT
- 911 Speedster Concept
- Porsche 928 GTS
- Porsche 928 Specials
- Porsche 928 H50
- Porsche 928 CS/SE
- Porsche 935 Tribute
- Porsche 597
- Porsche 551
- Porsche Mission E Cross Turismo
- Porsche 911 (992)
- Porsche Concept 917
- Porsche Sport Tourer Electric
- Porsche Le Mans Living Legend
- Porsche 960 Turismo Concept
- Porsche 919 Street
- Porsche 904 Living Legend
- Porsche 906 Living Legend
- Porsche 911 Vision Safari Concept
- Porsche Bergspyder Concept
- Porsche 917 Living Legend
- Porsche Macan Vision Safari
- Porsche Vision 916
- Porsche Vision 918 RS
- Porsche Vision 920
- Porsche Vision E
- Porsche 917 16-Cylinder Prototype
- Porsche 959 Gruppe B
- Porsche Carrera GT Concept
- Porsche Tapiro Concept
- Porsche 718 Cayman GT4 Rallye
- Porsche Taycan 4S
- Porsche Taycan Turbo
- Porsche Taycan Turbo S
- Porsche Type 360
- Porsche 645 Spyder
- Porsche 550 Coupé (Prototype)
- Porsche 550 Spyder (Prototype)
- Porsche 550 Spyder
- Porsche 550 RS Spyder
- Porsche 550A RS Spyder
- Porsche 787 F1
- Porsche 804 F1
- Porsche 904 Carrera GTS
- Porsche 904/6 Carrera GTS
- Porsche 904/8 Carrera GTS
- Porsche 904 Bergspyder
- Porsche 906 Spyder
- Porsche 906 LH Coupé
- Porsche 965 (911)
- Porsche 906 E Carrera 6
- Porsche 942
- Porsche 906/8 Coupé
- Porsche 959 Prototype
- Porsche 906 Carrera 6
- Porsche 969
- Porsche 910 Bergspyder
- Porsche 989
- Porsche 910 Targa
- Porsche 909
- Porsche C88
- Porsche 718 RSK Spyder
- Porsche Panamericana
- Porsche 718 RS 60 Spyder
- Porsche 718 RS 61 Spyder
- Porsche 718 W-RS Spyder
- Porsche 718 GTR Coupe
- Porsche 718/2 F2
- Porsche 718 RS 61 LM Coupé
- Porsche 718 RSK Mittellenker
- Porsche 907 K
- Porsche 907 LH
- Porsche 908/01 LH Coupé
- Porsche 908/01 K Coupé
- Porsche 908/02 K Spyder
- Porsche 908 K Flunder Spyder
- Porsche 908 LH Flunder Spyder
- Porsche 908/03 Spyder
- Porsche 908/03 Spyder Turbo
- Porsche 919 Hybrid Evo
- Porsche 984
- Porsche LMP2000
- Porsche LMP1-98
- Porsche 917 LH-69
- Porsche 961
- Porsche WSC-95
- Porsche 917 K-69
- Porsche 917 ‘Interserie Spyder’
- Porsche 917 K-70
- Porsche 917 K-71
- Porsche 917 LH-70
- Porsche 917 LH-71
- Porsche 917/20
- Porsche 917/10-71
- Porsche 917/10-72
- Porsche 917/10 Turbo
- Porsche 917/20 Turbo
- Porsche 917/30
- Porsche 914/4 (1.7 L)
- Porsche 914/4 (2.0 L)
- Porsche 914/6 (2.0 L)
- Porsche 914 LE
- Porsche 914/4 (1.8 L)
- Porsche 914/8
- Porsche 914-6 GT
- Porsche 924 (Base)
- Porsche 924 Turbo
- Porsche 924 Carrera GT
- Porsche 924 Carrera GTR
- Porsche 924 Carrera GTS
- Porsche 924S
- Porsche 924 Rallye Turbo
- Porsche 924 Carrera GTP
- Porsche 924 SCCA
- Porsche 944 Coupe
- Porsche 944 S Coupe
- Porsche 944 S2 Coupe
- Porsche 944 S2 Cabriolet
- Porsche 944 Turbo Coupe
- Porsche 944 Turbo S Coupe
- Porsche 944 Turbo Cup
- Porsche 944 Turbo Cabriolet
- Porsche 944 GTP
- Porsche 944 Swiss Special
- Porsche 944 French Special
- Porsche 944 Celebration
- Porsche 944 S2SE
- Porsche 968 Coupe
- Porsche 968 Cabriolet
- Porsche 968 CS Coupe
- Porsche 968 Turbo S
- Porsche 968 Turbo RS
- Porsche 968 Sport
- Porsche 959 Rally
- Porsche 959 Komfort
- Porsche Cayenne 9YA/9YB/9YC (3rd Gen)
- Porsche 959 Sport
- Porsche Boxster (Base)
- Porsche Boxster S
- Porsche Boxster S Special Edition
- Porsche Boxster Spyder
- Porsche Boxster RS 60 Spyder
- Porsche Boxster GTS
- Porsche Boxster T
- Porsche Cayman (Base)
- Porsche Cayman S
- Porsche Cayman GTS
- Porsche Cayman GT4
- Porsche Cayman R
- Porsche Macan 95B (1st Gen)
- Porsche Cayman S Black Edition
- Porsche Macan (Base)
- Porsche Cayman S Sport
- Porsche Macan S
- Porsche Cayman S Design Edition 1
- Porsche Macan GTS
- Porsche Cayman T
- Porsche Macan Turbo
- Porsche Cayman GT4 Clubsport
- Porsche Taycan (Base)
- Porsche 718 Boxster 25
- Porsche Taycan 4
- 964 Carrera
- Porsche Formula E
- 964 Carrera 4
- ’30 Jahre’ Anniversary
- 964 Speedster
- 964 Turbo
- 964 Carrera RS
- 964 Carrera Cup
- 964 RSR
- 993 Carrera
- Porsche Cayman GT4 RS
- 992 Edition 50
- 993 Carrera 4
- 993 Carrera 4S
- 911 2.0 Bertone Roadster
- Porsche Macan T
- 993 Carrera S
- Porsche Mission R Electric
- 992 Sport Classic
- 993 Targa
- Porsche Vision Gran Turismo
- 993 Turbo
- 993 Carrera RS
- 996 Carrera
- 992 America Edition 911
- 993 GT2
- 996 Carrera 4
- 993 Carrera Cup
- 996 Targa
- 996 Carrera 4S
- 996 Turbo
- Porsche 963
- 996 Turbo S
- Porsche 718 Cayman GT4 ePerformance
- 996 GT3
- 996 GT3 RS
- 996 GT2
- 996 GT3 Cup
- 996 GT3 R
- 996 GT3 RSR
- 996 GT3 RS Race
- 997 Carrera
- 997 Carrera S
- 997 Carrera 4
- 997 Carrera 4S
- 997 Targa
- 997 Targa 4S
- 911 Carrera 3.0 Coupe (G-Series)
- 997 Turbo
- 997 Turbo S
- 992 Carrera T
- 997 GT2
- 997 GT2 RS
- 997 Speedster
- 992 Dakar
- 997 Carrera GTS
- 997 Carrera 4 GTS
- 997 GT3 Cup
- 997 GT3 R
- 997 GT3 RSR
- 997 GT3
- 997 GT3 RS
- 991 Carrera
- 997 GT3 R Hybrid
- 991 Carrera 4
- 991 Carrera S
- 991 Carrera 4S
- Porsche 981
- 991 Targa 4
- Porsche Vision 357
- 991 Targa 4S
- 991 Turbo
- 991 Turbo S
- 991 Carrera GTS
- 991 Carrera 4 GTS
- 991 Targa 4 GTS
- 991 911 R
- 991 GT3
- 991 GT3 RS
- 991 GT2 RS
- 991 Speedster
- 991 GT3 R
- 991 GT3 Cup
- 991 RSR
- 991 Carrera T
- 992 Carrera
- 992 Carrera 4
- Porsche Type 540 America Roadster
- 992 Carrera S
- Porsche 718 Spyder RS
- 992 Carrera 4S
- 992 RSR
- 992 Targa 4
- 992 Targa 4S
- Porsche Mission X
- 992 Carrera GTS
- 992 Carrera 4 GTS
- 992 Targa 4 GTS
- 992 Turbo
- Porsche RS60 Spyder
- 992 GT3 R
- 992 Turbo S
- 992 GT3
- 992 911 S/T
- 992 GT3 Touring
- 992 GT3 RS
- 911 (G-Series)
- 992 GT2 RS
- 992 GT3 Cup
- 911 Carrera 3.0 (G-Series)
- Porsche Taycan GTS
- Porsche 356 SC
- 911 S (G-Series)
- 992 GT3 R Rennsport
- 911 Carrera RSR 2.8
- 911 SC (G-Series)
- 911 S/T
- 911 (Base Model)
- 911 Carrera 3.2 (G-Series)
- 911 L
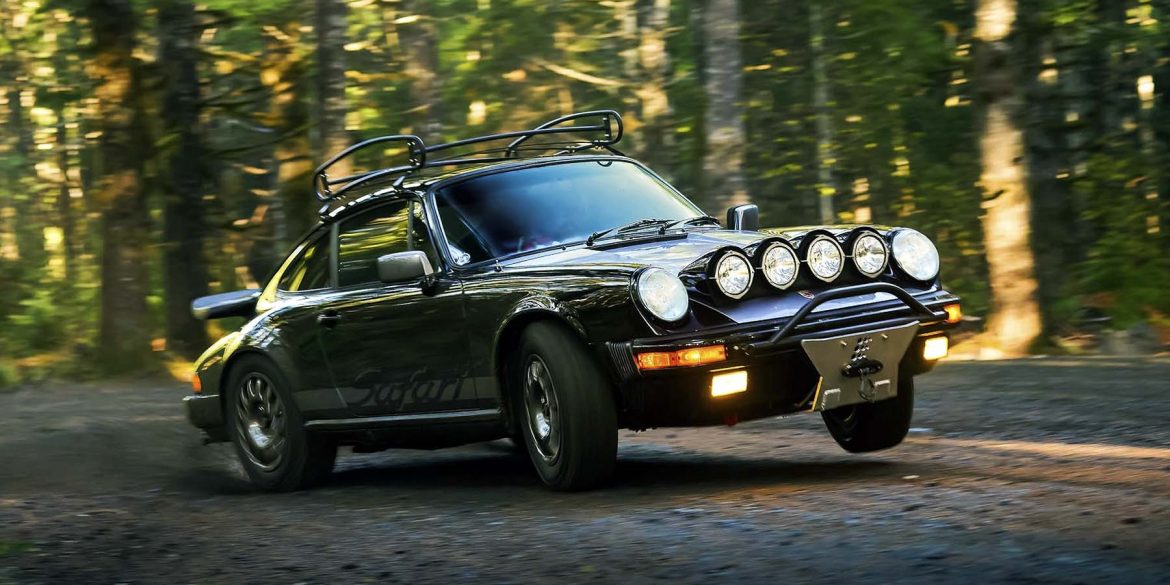
- 911 SC Safari
- 911 Turbo (930)
- 911 T
- 911 Carrera RSR Turbo 2.1
- 911 E
- 911 Carrera RSR 3.0
- 911 S
- 911 SC San Remo
- Porsche 356
- Pre-A Speedster
- 911 R
- 911 Carrera 3.2 Clubsport
- Porsche 953
- 911 T/R
- 911 Carrera 25th Anniversary
- 911 Carrera RS 3.0
- 911 SC RS
- 911 Turbo LE
- Beutler Coupe
- 911 3.2 Speedster
- 911 Carrera 2.7 (G-Series)
- 911 Carrera Commemorative
- 911 Turbo 2.7
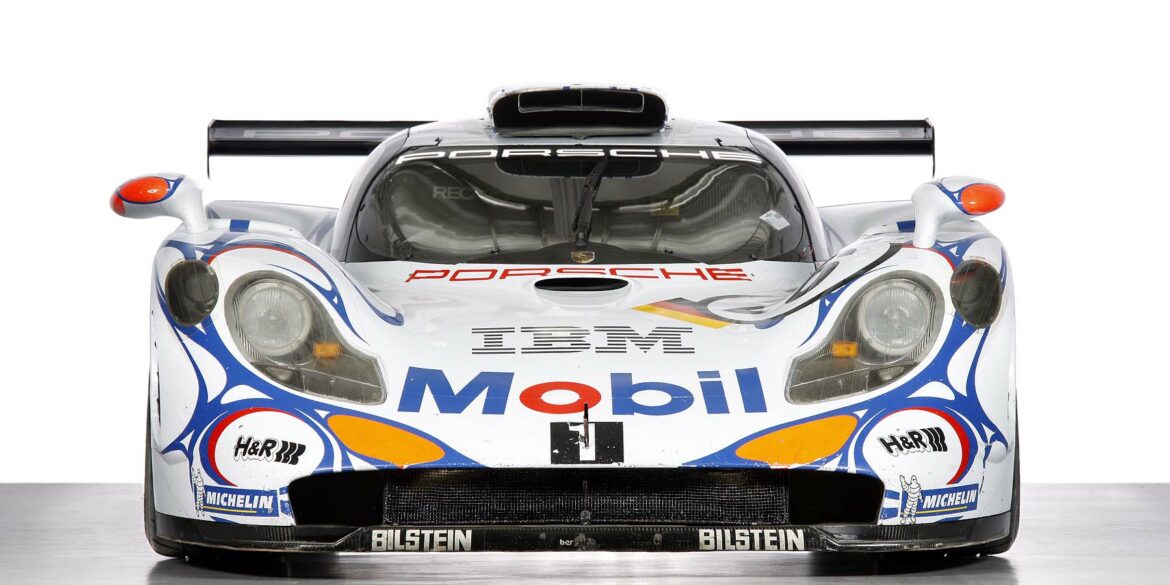
- Porsche 911 GT1
- Porsche 99X Electric
- 964 Turbo S
- Porsche Taycan Turbo GT
- Porsche Panamera 976 (3rd gen)
- Porsche Macan Electric (2nd Gen)
- Porsche 954
- Porsche Taycan Y1A/Y1B (1st Gen)
- Porsche Cayenne (4th Gen)
- Porsche Macan Turbo Electric
- Porsche Macan 4S Electric
- Porsche Macan 4 Electric
- Lohner-Porsche
- Porsche Macan Electric (Base)
- Porsche Taycan 9J1 (1st Gen)
- 992 “Turbo 50”
- Porsche Macan GTS Electric
- Porsche Type 940
- 992 Transfăgărășan Tribute
- Porsche 963 RSP
- 992 Carrera T Club Coupe
- 997 Sport Classic
- 992 GT3 90 F. A. Porsche
- Porsche Type 542
- Porsche Type 166
- Vision Renndienst Concept
- 991 50th Anniversary
- 997 Black Edition
- 993 Turbo S
- 992 Spirit 70
Sorry, but you do not have permission to view this content....
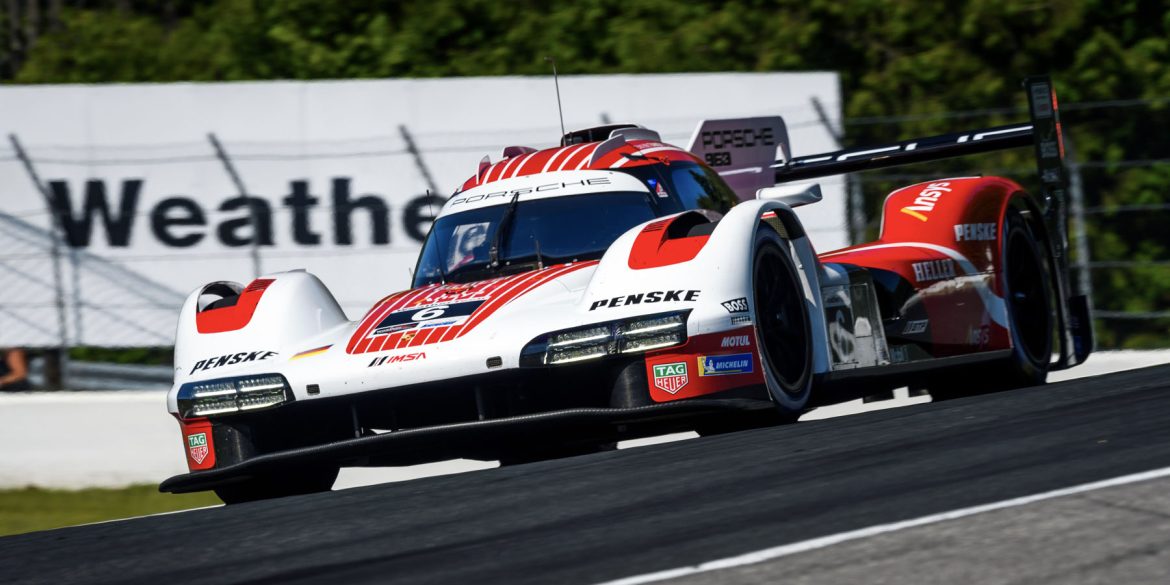
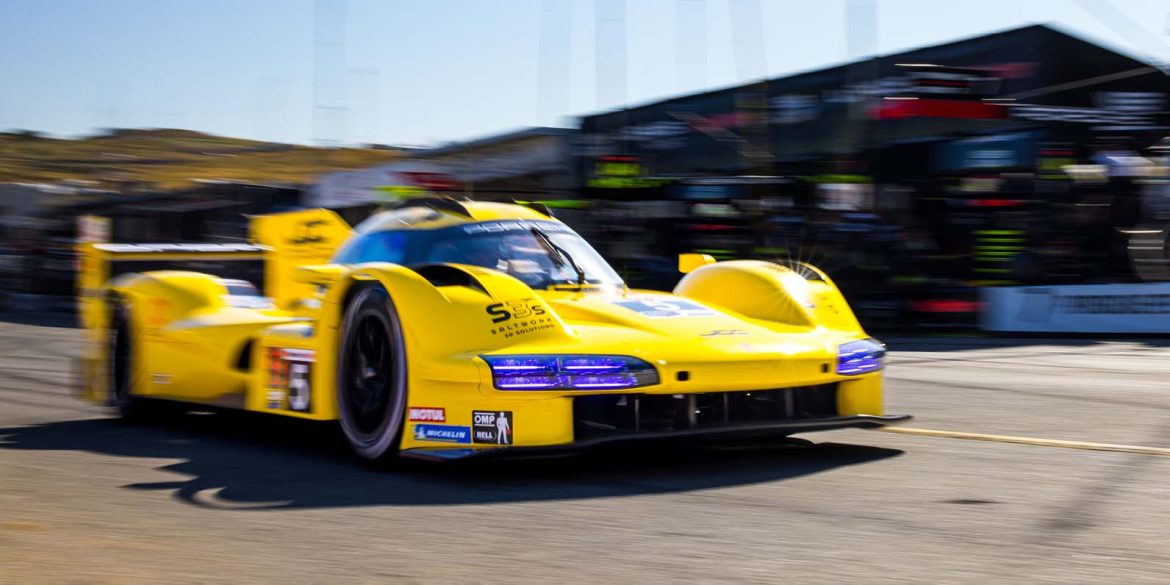
Lack of speed in Qualifying Works driver Felipe Nasr has qualified in fifth for round six of the IMSA WeatherTech SportsCar Championship. In the hunt for top times in Mosport, Canada, the Brazilian was the fastest driver at the wheel of a Porsche 963. The sister car fielded by the...
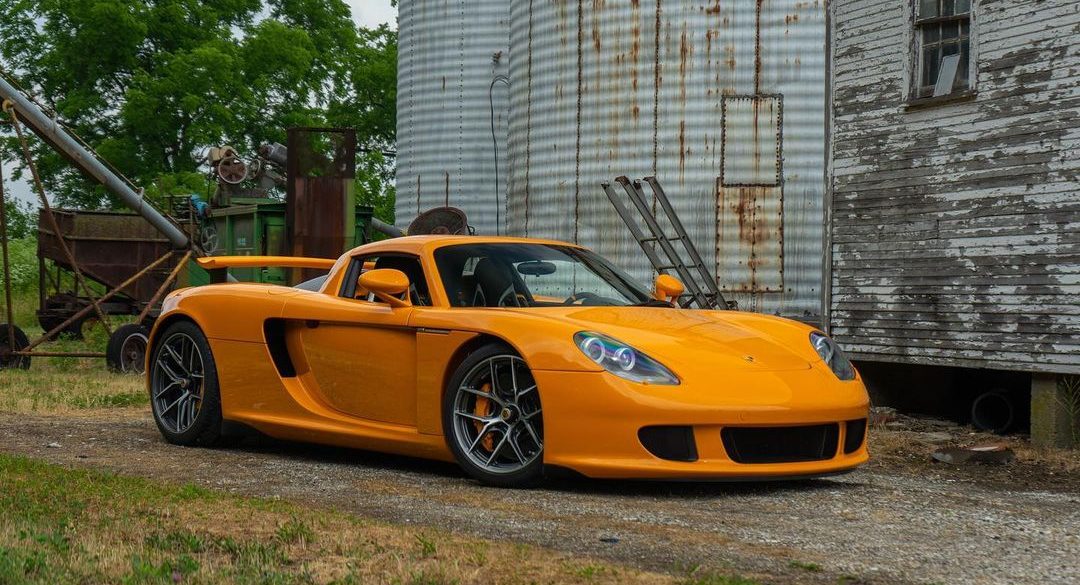
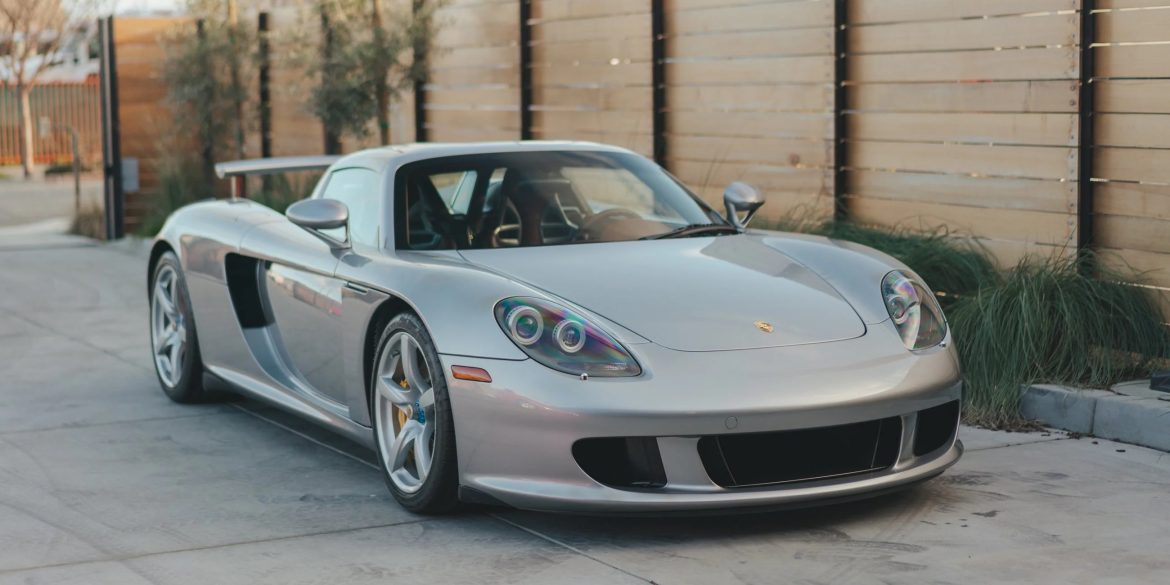
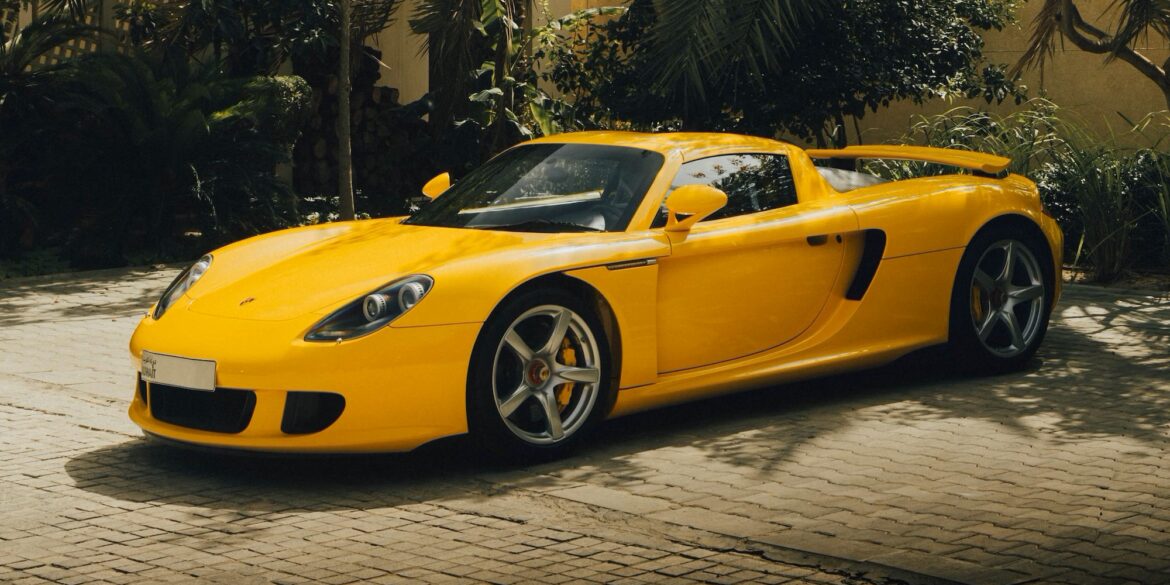
Porsche’s open-top, 603-hp, manually shifted Carrera GT makes other supercars seem quaint. It is arguably the best supercar ever made. Under the skin, the car used many modern hallmarks of motor sport engineering: a carbon fiber chassis, dry sump lubrication, inboard suspension and a mid-mounted engine that was engineered to...
The MR12 Force Rouge, created by Machine Revival, embodies the spirit of the cafe racer design and is built for maximum speed from point A to point B. Photo Source: Machine Revival...
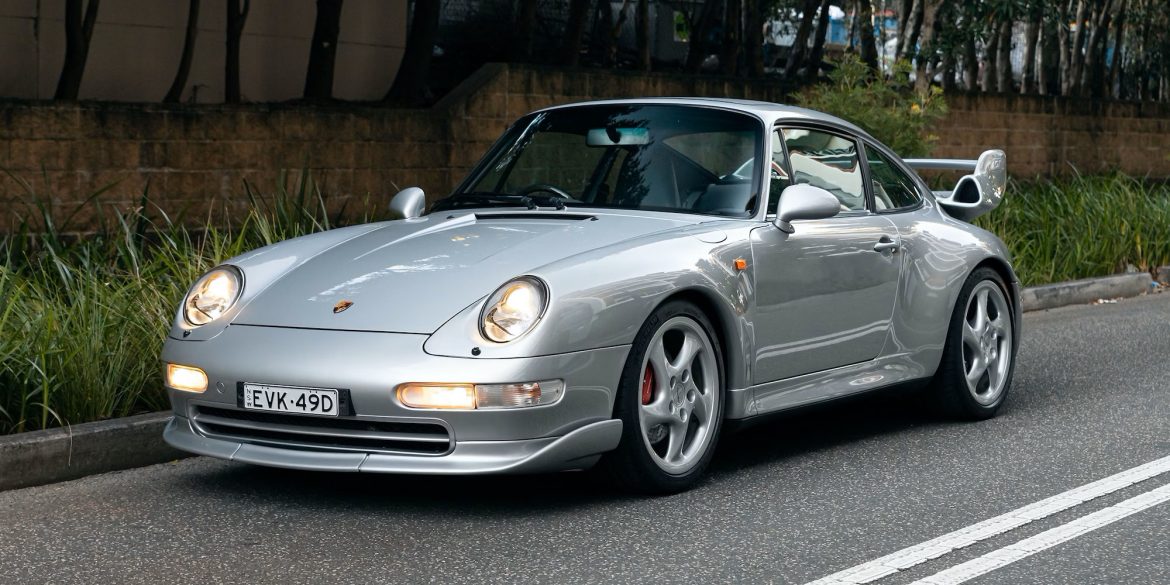
The Porsche 993 Turbo, introduced during the 993 generation of the 911, revolutionized the sports car landscape. With a 400 horsepower twin-turbo flat-6 engine, it achieved a 0-60 mph time of just over 4 seconds and a top speed exceeding 180 mph. This outstanding performance, combined with daily drivability and...
In 1997, Porsche produced a limited factory-production run of what is the last air-cooled 911 Turbo, the 993 Turbo S. Turbo S’s were fitted with most Turbo options as standard and also came standard with Aerokit II front and rear spoilers, unique side air ducts and front air inlets, and...
This custom Porsche 911 is a unique creation by CC Speedline of California, built for the owner of the company, utilizing a 1977 Carrera 3.0 Coupe as its base. The car showcases IROC-style bumpers and is finished in an eye-catching Montana Blue color. Inside, the vehicle boasts a bespoke tan...
Broad Arrow Auctions to offer Porsche rarity Chassis No. 9R6-705 is a Porsche RS Spyder, a sports racing prototype designed for the American Le Mans Series (ALMS) LMP2 class. The RS Spyder has a rich racing history, with notable victories and championships. In 2007, Dyson Racing, a long-time Porsche team,...
Lightweight racer is born During the 1960s, Ferdinand Piëch, the head of Porsche Research and Development, spearheaded the development of a new generation of lightweight race cars. By utilizing advanced materials and taking advantage of regulation changes, Piëch’s team created race cars with tubular frames and unstressed fiberglass bodies, offering...
Porsche and Mercedes-AMG have been engaged in a captivating rivalry over the past few years, each striving to create the ultimate well-rounded sports car capable of conquering the Nürburgring Nordschleife. We now have the opportunity to witness these two contenders face off on a drag strip, courtesy of Daniel Abt’s...
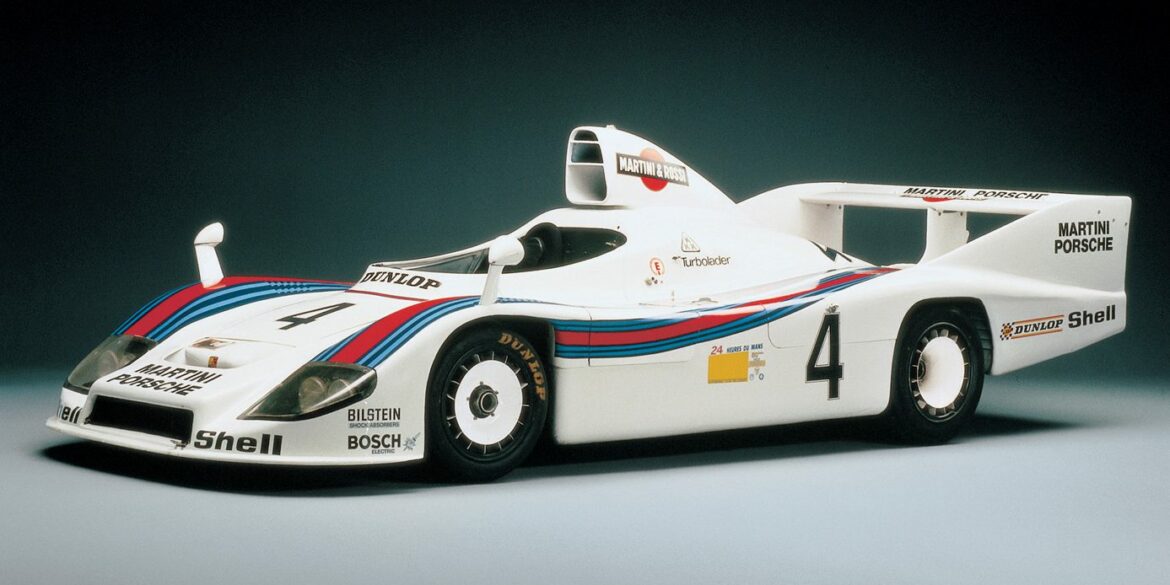
In 1977, Porsche’s “improvised” Type 936/77 took on the full-court press of four Renaults at Le Mans. Retirements and technical troubles suggested that winning was out of the question. But neither its drivers nor Porsche number 4 believed that. Against strong opposition from Alpine-Renault and Alfa Romeo, Porsche took the...
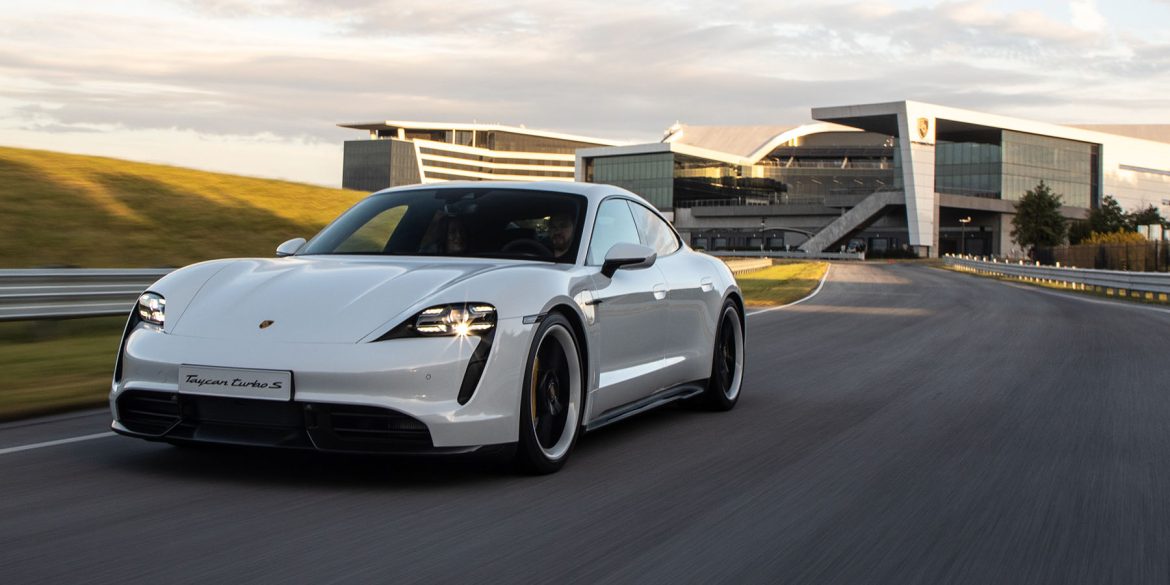
Used market by the numbers The Taycan is Porsche’s groundbreaking all-electric sports car success story, featuring an aerodynamic design that the automotive press lauded because of its combination of elegance and performance. Nevertheless, while early adapters benefited from driving Porsche’s newest technical wonder, they inevitably paid the price due to...
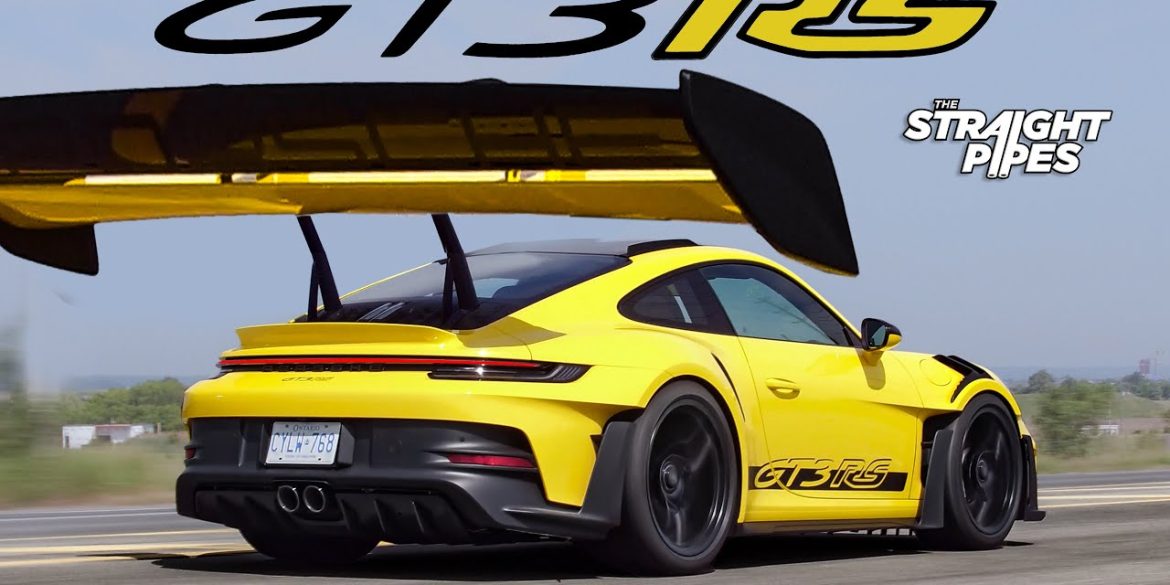
One simple look at the all-new 2023 Porsche 911 GT3 RS, and it’ll tell you right away that this car is meant for the track. Equipped with Porsche’s now-familiar 4.0-liter flat-six engine, the GT3 RS is capable of putting down 518 horsepower and 343 pound-feet of torque, allowing it to...
The unique restoration of this 1992 Porsche 964 Carrera 2 Coupe was exclusively commissioned to Olsen Motorsports, who carried out the project at their facility in Chicago dedicated to creating and restoring exceptional vehicles. To begin, the chassis underwent a complete strip-down process, followed by chemical stripping and modification, including...
The 930 was the most capable supercar of its time and catapulted Porsche’s brand worldwide, keeping up with the likes of Ferrari and Lamborghini while still being usable day to day. But Porsche never stands still so the 911 Turbo 3.3 is an updated variant of that original 911 Turbo...
Graham Rahal Performance, a team of dedicated professionals, is committed to preserving the Carrera GT through their bespoke recommissioning service. The GRP Porsche Carrera GT Recommission Project provides an excellent opportunity for owners to personalize their Carrera GTs however they want. Recently, Graham Rahal Performance introduced the GRP Project Recommission...
To compete in GT1 racing, Porsche produced a small batch of road-legal cars, resulting in the exclusive 993-based Porsche 911 GT1 Strassenversion. Alongside the likes of Mercedes-Benz CLK GTR and Maserati MC12, it utilized the 993’s chassis and front end, combined with the rear design of the iconic 962 race...
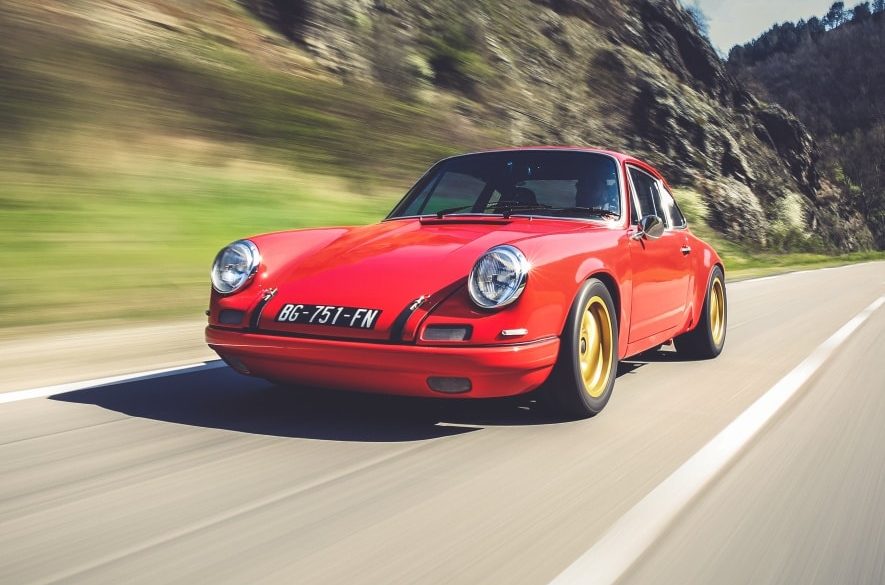
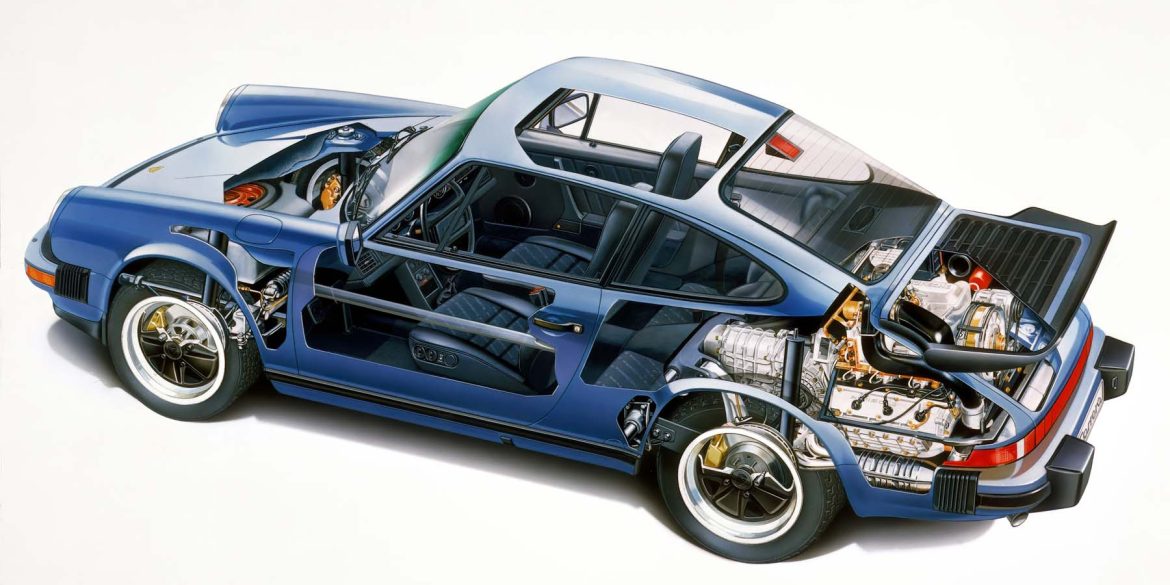
History Long regarded as the best entry-level air-cooled 911, the Carrera 3.2 remains highly desirable. It was the final evolution of the original torsion bar 911 built from 1964 to 1989. Visually the only significant change came in 1974 with the so-called ‘impact bumpers’ of the G series, but under...
The Porsche 962 arrived on scene in 1984 as essentially a Porsche 956 for the IMSA/US market. IMSA mandated that the driver’s feet had to be behind the front wheel centerline. Therefore Porsche needed to change the 956 to accommodate this difference and ultimately that meant redesigning the monocoque and giving...
The 964 Carrera RS was introduced by Porsche for model year 1992 specifically for the European market as a lightweight, high performance version of the 964 Carrera 2. It featured a revised version of the standard 3.6 liter engine, titled M64/03 internally, with an increased power output of 260 bhp...
In 1984, a Porsche was purchased in Illinois and upgraded to RUF BTR specification. The modifications included increasing the engine displacement, adding a turbocharger, and customizing the bodywork. The car gained recognition as the RUF RSR and was featured in “The World’s Fastest Cars” in 1989. After completing the project,...
“…Dan Gurney’s Porsche had flat caps on all wheels, secured with a few small bolts. Contrary to expectations, Gurney said the caps had no effect on the car’s handling, even in a crosswind…” The Motor, September 19, 1962...
In 2023 Porsche unveiled the 911 Carrera GTS Le Mans Centenaire Edition, a special version of the iconic 911 . This exclusive model celebrates the 100th anniversary of the 24 Hours of Le Mans race and pays tribute to Porsche’s history at the renowned Circuit de la Sarthe. The 911 Carrera GTS Le Mans Centenaire Edition draws inspiration from two winning cars, the Porsche 356 SL and the 911 GT1 '98.
This 1997 Porsche 993 Carrera S finished in sleek Black with a black leather interior, underwent an extensive custom rebuild spanning four years. No expense was spared in transforming this classic beauty into a one-of-a-kind masterpiece. The meticulous restoration included a full glass-out repaint in its original color, an enhanced Rothsport...
The final air-cooled 911 Turbo from Porsche was the Type 993 Turbo S, offering a remarkable conclusion to that era. Only 176 example were made for North America, with each of them being meticulously designed and built by the Exclusive Department with custom features and numerous engine and chassis upgrades....
Watch this thrilling onboard video featuring a Porsche 962 in action during Group C qualifying at Spa Francorchamps. This turbocharged flat-six racer could be tuned to deliver over 600bhp, producing one of the most magnificent turbocharged soundtracks you’ll ever hear! ...
All Images by: Virtual Motorpix/Glen Smale and Corporate Archives Porsche AG In the 2023 Le Mans 24 Hour race, the Iron Dames team of Sarah Bovy, Rahel Frey and Michelle Gatting driving the No. 85 Porsche 911 RSR, was the only all-female squad in the centennial race. This was the...
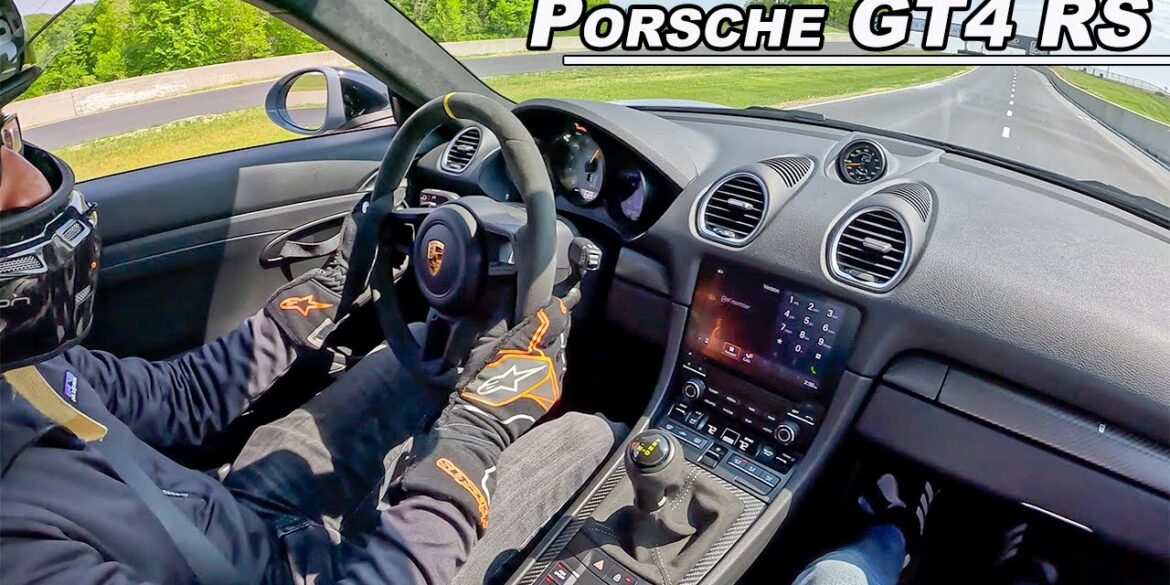
The 2022 718 Cayman GT4 RS is the most thrilling Cayman model to date. Powered by the same impressive flat-six engine found in the 911 GT3, it boasts a 4.0-liter unit delivering 493 horsepower and 331 lb-ft of torque. With a 0-62 mph time of 3.9 seconds and a top...
Ruf released the Turbo R Limited in 2016, paying homage to the original Turbo R. Only seven units were produced, all of which were sold. With prices starting just below US$600,000, the car is based on the 993-generation Porsche 911 Turbo, offering exceptional performance combined with meticulous craftsmanship. The twin-turbo...
This 1994 Porsche 911 Turbo S 3.6 Package is a stunning example of one of the 17 “Package” models produced with standard Turbo bodywork for the North American market. It is a gorgeous example despite showing over 41k miles on the odometer. Designed as an exclusive swan-song offering for the...
DLS Turbo restoration services are imagined with each owner to celebrate the victorious 934/5 endurance racers of the 1970s. In the year that Singer is going racing with the latest turbocharged Porsche endurance racecar, the Type 963, this celebration of racing DNA links past and present. The Porsche 911 began...
The McLaren Artura, a recently unveiled British supercar, has entered production in 2023, showcasing a cutting-edge hybrid propulsion system that harnesses the power of an electric motor. Unlike some hybrids focused on efficiency, the Artura’s electric motor contributes to its robust and instantaneous performance. With 680 HP at its disposal,...
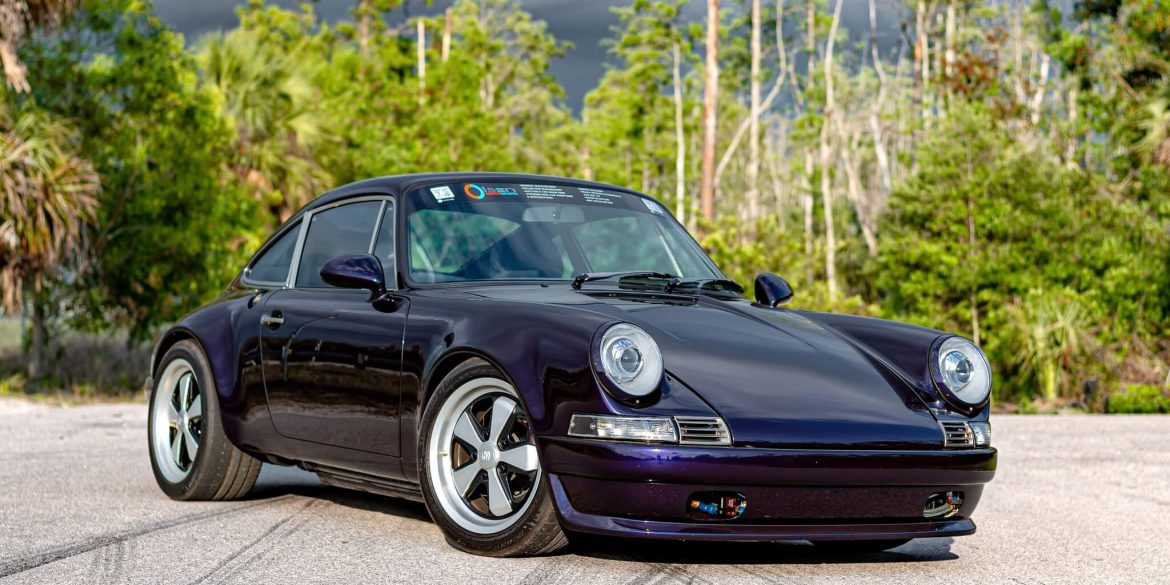
Originally from California, this 1975 Porsche 911S underwent a remarkable transformation. Acquired in 2014, it was customized into a backdate 911 with classic long hood styling. The modifications include steel RS fender flares, the removal of the sunroof, custom wheels, and an upgraded interior featuring a bolt-in roll bar, leather...
The Porsche 911 GT2 combines the sporting character of the 996 911 GT3 with the power and straight line performance of the 911 Turbo. The fastest member of the 911 family, the 911 GT2 gets power of 462 bhp @ 5700 rpm and torque of 457 ft lbs @ 3500 rpm. It accelerates to...
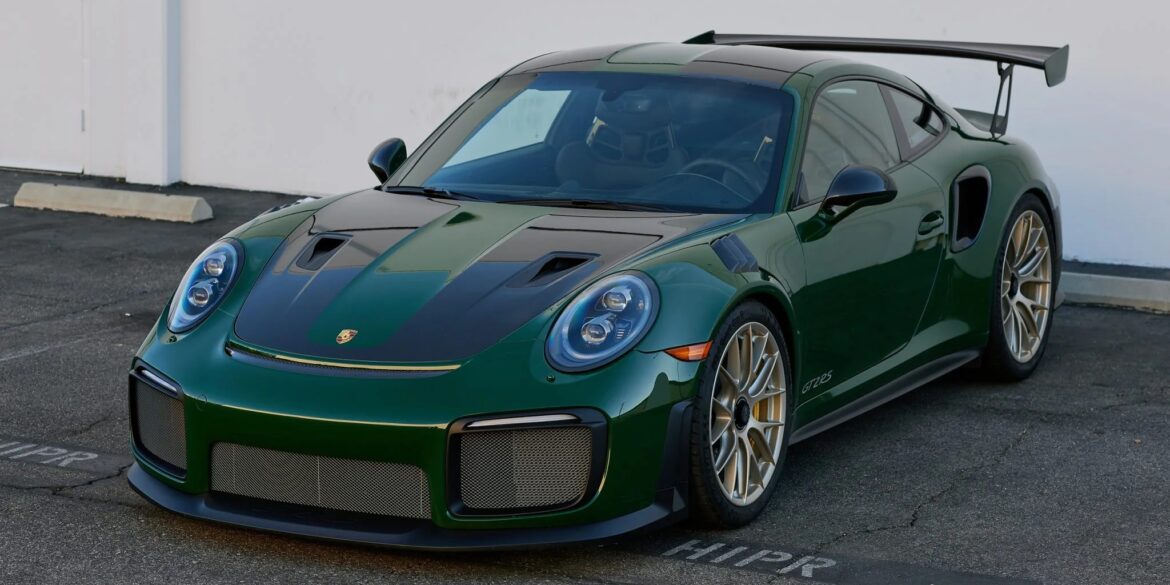
The rear-engine, rear-wheel drive GT2 RS celebrated its official world premiere at the Goodwood Festival of Speed in the UK which took place from June 30th to July 2nd, 2017. It was here that the world was first introduced to Porsche’s fastest and most powerful street-legal 911 ever made. A...
The 2022 Porsche Targa 4 GTS adds more grunt, packs less weight, has sharper handling, and packages it up in the sexiest bodystyle that Porsche sells. The Targa 4 GTS gives us the best of all worlds, providing all-wheel-drive traction, an open-top experience, and a fixed-roof feeling in the same...
Designed to surpass all other supercars of its time in terms of technological advancements, the Porsche Carrera GT was meticulously engineered to push boundaries and redefine automotive innovation. Its foundation was built upon a powerful V10 engine, tracing its origins back to the legendary 10-cylinder race engine developed for the...
This is a one-of-a-kind 1979 Porsche 911SC Targa featuring a Stone Grey exterior complemented by a bespoke interior featuring brand-new brown leather upholstery and early-style German square weave carpeting. Meticulously restored over the course of a year by a renowned Porsche specialist, this one-of-a-kind 911SC Targa exemplifies unrivaled craftsmanship and...
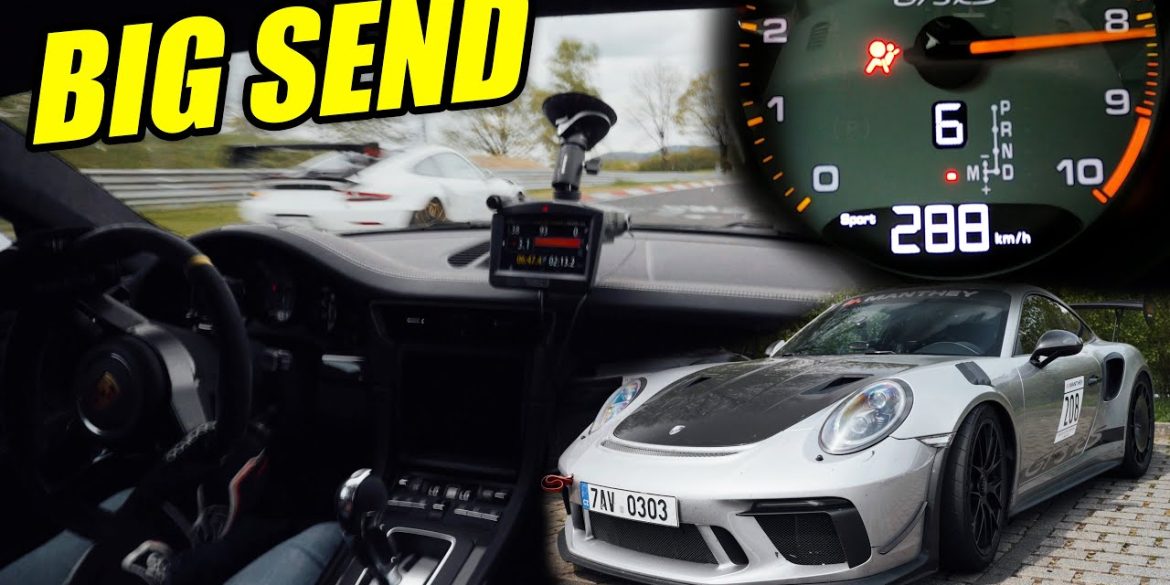
Here’s what happens when you let a rally driver slide behind the wheel of a Porsche GT3 RS by Manthey Racing with Misha Charoudin riding shotgun!...
Proven in the dirt Porsche has a rich history of competing in various rally events, particularly during the 1960s and 1970s. Some highlights include: 1. Monte Carlo Rally: Porsche succeeded considerably at the prestigious Monte Carlo Rally. In 1968, the Porsche 911 T driven by Vic Elford won the event...
Magnus Walker’s popular YouTube series, “Other Peoples Porsche,” explores unique and fascinating Porsche cars across the country. From a 1969 Porsche 911T in New York to a 1982 Porsche 930 Turbo in Miami, Magnus has already seen some remarkable examples from the German brand. In the newest episode of his...
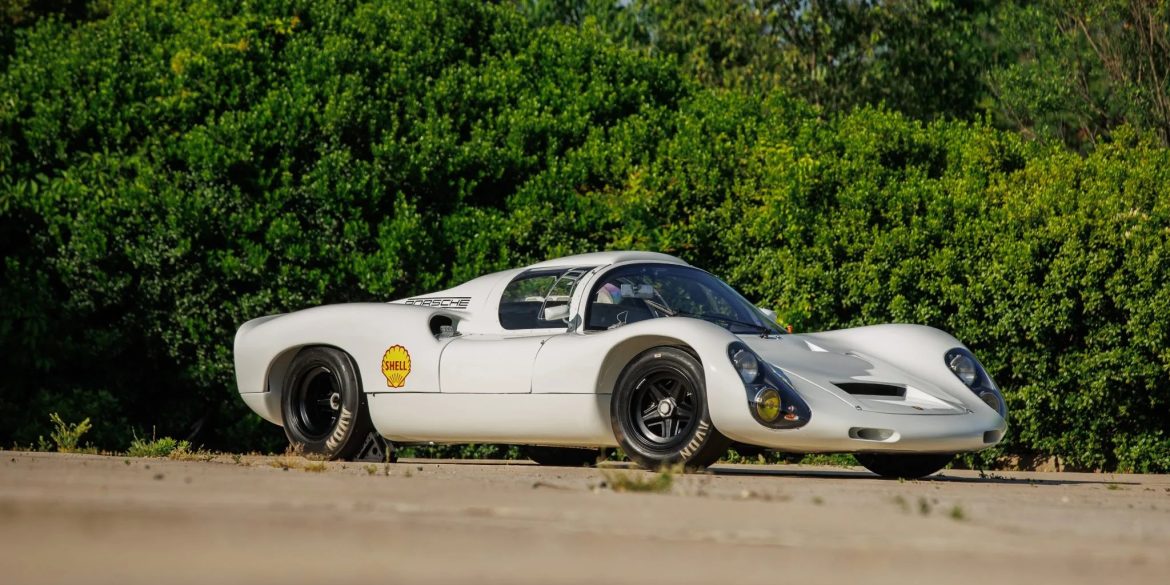
The Porsche 910, also known as the Carrera 10, was introduced during the summer of 1966 and raced through 1967, continuing the company’s assault on international competition. It was similar to the preceding 906, including the spaceframe chassis, but with suspension, changes to accommodate the smaller 13-inch magnesium wheels. The...
From 1983 onwards, the Porsche 956 and its 962 IMSA spec version dominated motorsports for a decade. Porsche produced around 150 956/962s, selling many to private teams and providing comprehensive customer support. This success at Le Mans not only made Porsche the most successful marque but also enabled other companies...
Back in the States The Le Mans debacle is over, and now it’s time for Porsche Penske Motorsport to head to round five of the IMSA WeatherTech SportsCar Championship as the leader of the team classification. In the 6 Hours of Watkins Glen in the US state of New York,...
The Kaege Retro Turbo is based on a Porsche 993 Turbo. It offers all-wheel drive and more than 450 hp! It has that awesome tough, planted look. Open the carbon-fiber engine cover with its classic ducktail spoiler, and you are confronted by an eyeful of 993 Turbo S intercooler, which...
Doug DeMuro recently fulfilled his dream of owning a Porsche Carrera GT and shared an update on his YouTube channel. However, he quickly realized that owning this car comes at a high price. With average auction prices around $1.2 million and ranging up to $2 million, the Carrera GT is...
Akira Nakai and Daniel Arsham are renowned figures in the realm of automotive artistry, especially when it comes to Porsche customization. Combining their talents, the Japanese car tuner and American artist have crafted an exceptional work of art called the “RWBA” – the world’s first slant nose Porsche 964 RWB....
AutoTopNL, an automotive YouTube channel, recently released a video featuring a Porsche 992 Carrera being pushed to its limits on the German Autobahn. Equipped with a 3.0-litre flat six engine producing 385 horsepower, the 992 Carrera boasts an impressive top speed of 183 mph (295 km/h) and accelerates from zero...
The 992 GT3 becomes the seventh iteration of one of Porsche’s most established and beloved automobiles and it continues to embody the spirit of previous GT3 models by amalgamating all that is awesome about the 911 – and the Porsche brand – in a single road car. It is perfect....
Created for its first Italian customer, a discerning collector from Milan, ITA001 is transformed with a featherweight all-carbon body, semi-active suspension and a snarling, 4.0-liter naturally aspirated flat-six. ITA001 is the realization of a client’s Porsche 911 fantasy. It is a fully-restored and enhanced machine that – as with all...
Unlike its Boxster brother, the S version of the mid-engined Porsche roadster offered a 3.4-liter unit from its predecessor, but with some improvements and a lower vehicle mass. It offered 311 hp and enough torque to push the car to 100 kph (62 mph) in 4.8 seconds if the car...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
911 2.7 RS Carrera highlights One of the most iconic sports cars of all time Delivered new in Germany Present ownership for more than 15 years An older restoration Recently checked by Porsche specialists Garage Moderne in Geneva Registered in Switzerland Background Porsche revived the Carrera name for its top-of-the-range...
Mat Watson and racing driver Sam have embarked on an exciting journey, driving a Porsche 911 GT3 and a Porsche Cayman GT4 RS all the way from the UK to Spa Francorchamps. Their mission is to thoroughly test these track-focused Porsches and push them to their limits. Both of these...
In 1997, Porsche manufactured a limited run of the 993 Turbo S, which marked the final air-cooled 911 Turbo. These Turbo S models came equipped with most of the Turbo options as standard, including Aerokit II front and rear spoilers, distinctive side air ducts and front air inlets, and yellow...
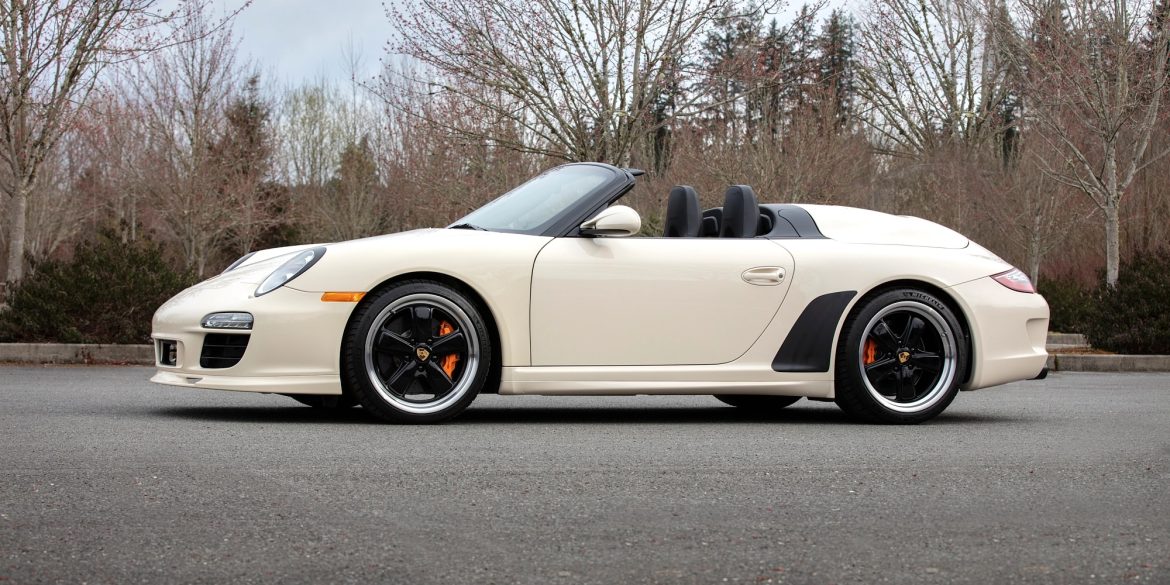
The 2011 Porsche 911 Speedster is a unique blend of classic features from the original Speedster model, the 356 Speedster, and enhanced performance of the contemporary 911 generation. Equipped with a 3.8-liter flat-six engine, it delivers 408 horsepower (300 kW), surpassing the 911 Carrera S by 23 horsepower. Only 356...
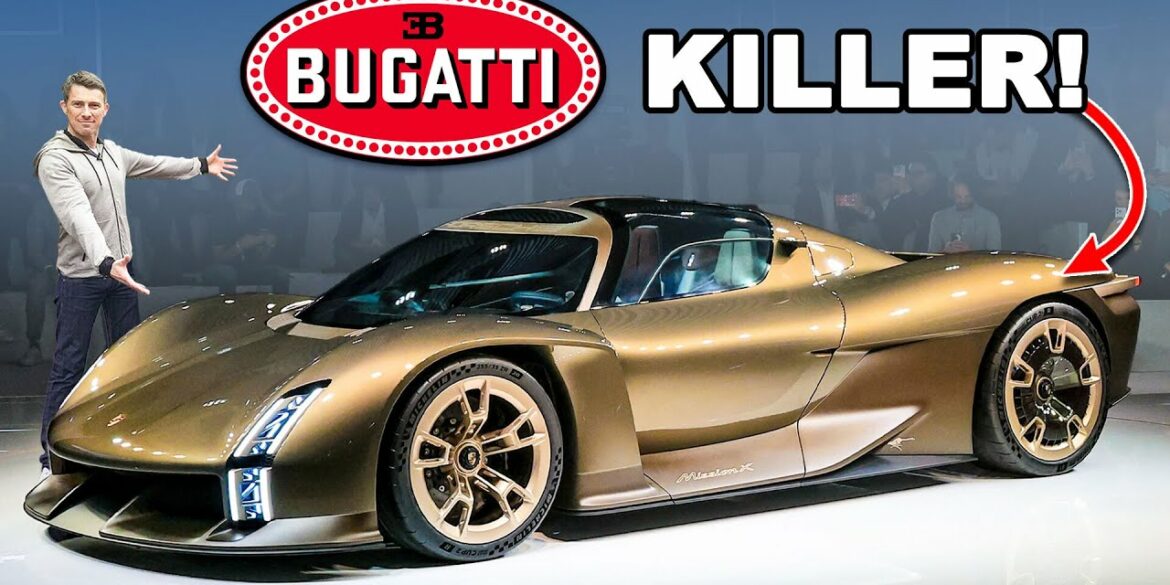
Introducing Porsche’s latest all-electric hypercar, the Mission X! This remarkable vehicle marks Porsche’s return to the hypercar segment following the 918 Spyder, and it has set its sights on an impressive goal – to claim the record for the fastest road-legal car to complete a lap on the renowned Nürburgring...
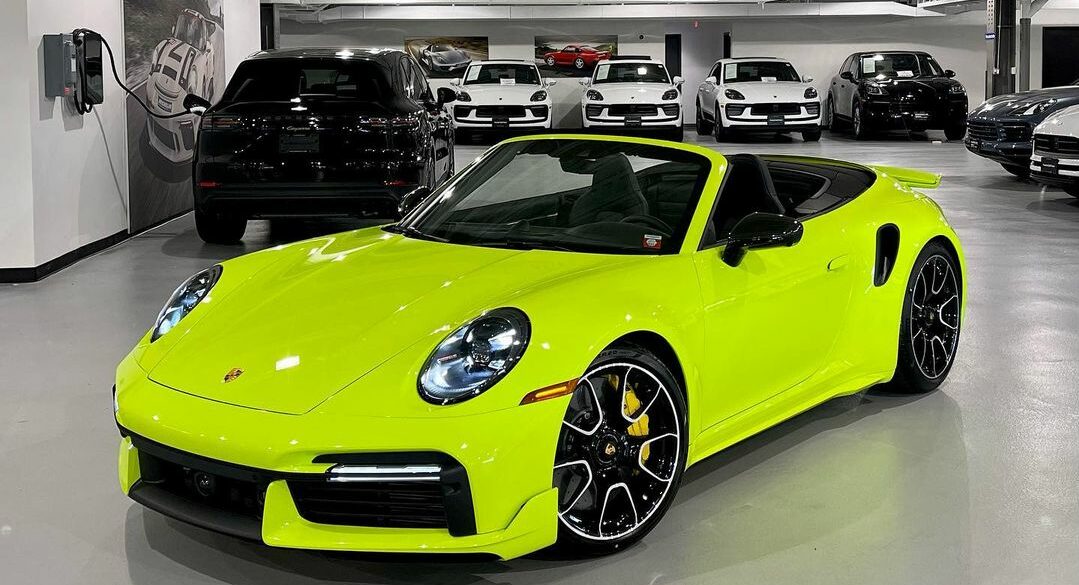
The 2022 Porsche 911 Turbo S Cabriolet is a formidable beast. The new Turbo S comes with an all-new, 3.8 liter boxer six with two variable turbine geometry (VTG) turbochargers. The power output is a staggering 640 hp and 590 lbs-ft of torque. In keeping with previous Turbo models, the...
Director sells Turbo for $60K, later auctioned for $1.3M Amazingly, Bad Boys director Michael Bay was involved in a bombshell not of his own making, following the sale of a car the filmmaker once owned. That car being the gorgeous Porsche 964 Turbo you see here. Taking to Instagram following the...
A Brief History Of Electric Performance At Porsche Porsche, ever since the first 356 rolled out of the factory doors 75 years ago, has always sought to push the boundaries of what is possible in automotive engineering. They were told time and again that placing the engine beyond the back...
Porsche 356A Modern automobile manufacturers would tell you – if you ran the Porsche history past them without putting a name to it – that it couldn’t possibly be true. A father and son leave allied prisons after WWII and set up a small design firm. One of their projects...
The 2023 911 Carrera T is Porsche’s model for those that want nothing more than a sports car that wants, needs, begs to be driven. No distractions, just hands on the wheel, feet on the pedals, feeling the way the tires bite into the pavement as you enter a turn, then...
Dubbed the “Lautrec Commission,” this custom Porsche 911 reimagined by Singer showcases an extraordinary and meticulously planned specification. Similar to the renowned French Impressionist painter Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, after whom it is named, this car stands as an unparalleled work of art. Dressed in a striking Paint-to-Sample Magnetic Silver exterior,...
We’ve even seen it from Lamborghini with their Huracán Sterrato, a raised, off-road version of their supercar, and that is precisely what Porsche created with the new 2023 Porsche 911 Dakar, taking the classic beauty of the 911 model and adding wheel arches to protect the paint from rock chips,...
The Porsche 718 Cayman GT4 RS is equipped with the same scintillating flat-six engine that powers the 911 GT3. It’s a 4.0-liter unit that makes 493 hp and 331 lb-ft of torque in the GT4 RS. Porschephiles will notice that those figures are not quite as high as in the...
Intended to surpass all other supercars of its era in terms of technological advancements, the Porsche Carrera GT was engineered to push boundaries. Its powerful V10 engine traces its lineage back to the 10-cylinder race engine developed for the 2000 Le Mans 24-hours. Notably, the Carrera GT pioneered the utilization...
The 2019 Porsche 911 GT2 RS is painted in custom-ordered, non-metallic Irish Green and comes with the Weissach Package, featuring exposed carbon fiber on the hood and roof panel. The car is powered by a twin-turbocharged 3.8L flat-six engine that was factory rated at 700 horsepower and 553 lb-ft of...
The debut of the Porsche 911 GT2 RS took place during the 997 generation in 2010 and received exceptional acclaim. In 2018, the 991-generation GT2 RS was introduced, surpassing its predecessor with an additional 80 horsepower and 37 pound-feet of torque. These enhancements enable the car to achieve an astonishing...
This lightweight hotrod, based on a Euro 911, is built for high-performance driving. With tasteful modifications, including a carbon fiber hood, RUF rear bumper, and Watanabe Minilight style wheels, it boasts an aggressive look. Inside, Recaro SPG seats, a Bridge Moto steering wheel, and racing-inspired upgrades create a lightweight and...
In 2020, Porsche answered our prayers and gave us the 718 Cayman GTS 4.0. Porsche already had a 718 Cayman GTS with a potent 2.5 liter turbo four cylinder. The new 718 Cayman GTS 4.0 featured the 4.0-litre flat-6 from the Cayman GT4 and Boxster Spyder, albeit slightly detuned to 294 kW (394 hp; 400 PS)....
Watch as the folks from Sam CarLegion YouTube channel pits a Ford Mustang GT500, a 2018 Ford Roush Mustang GT, and a 991 Porsche GT3 RS in a drag race. Porsche’s 991 GT3 RS, weighing 3,296 lbs, boasts a 7-speed dual-clutch transmission and a 4.0-liter 6-cylinder boxer engine, delivering 493...
Commissioned for ‘Mr. Le Mans’ Tom Kristensen, the Kalmar 7-97 is an homage to the Danish driver’s inaugural Le Mans triumph in 1997 and it is also available for sale to interested clients. Its name derives from Kristensen’s victorious feat in that renowned endurance ace while driving a Joest Porsche...
Porsche Mission X: yet another dream takes shape At Porsche, innovative concept cars have always laid the groundwork for the future. The sports car manufacturer is continuing this tradition with this latest concept study. Mission X is a spectacular reinterpretation of a hypercar, with Le Mans-style doors that open upwards...
In a new video, Magnus Walker interviews Charles Lennon, a dentist from New Jersey, who is also the proud owner of the “Creative Chaos Six Nine,” a modified 1969 Porsche 911T finished in burnt orange. The car is powered by a rebuilt 3.4-liter engine that was originally a 80s-era 3.2-liter...
The Berkshire Commission is a 4.0L, left-hand drive (LHD), rear-wheel-drive beauty presented in Amethyst Metallic with delicate ghosted stripes and lettering, accompanied by bronze wheel centers. Each Porsche 911 reimagined by Singer is tailored to the unique preferences of its owner. In the case of this car, the owner has...
For better, and sometimes for worse, corporate culture and business strategy have historically played a significant role in motorsport. Over the years, racecars and racing programs have been created and eliminated for no other reason than to satisfy marketing strategies and brand positioning. While many of us tend to view...
First air-cooled adventure Ryan Polson’s first word was car. Not Mama or Dada. Car. It seems that Ryan’s trajectory was set from the beginning. It also might have had something to do with his dad’s 1939 Ford Street rod that Ryan rode shotgun to car shows and the like. As...
In a recent video, CarWow lined up three super sports cars in a drag race, two of which feature electrified hybrid drive systems: the Porsche Panamera Turbo S e-hybrid and Mercedes-AMG GT 63 S e-hybrid, and the ICE powered BMW M5 Competition. Among the competitors, the Porsche Panamera Turbo S...
The Glasgow Commission, reimagined by Singer, is based on a right-hand drive 964 Targa. The car showcases carbon fiber bodywork in Blood Red – Dark and is equipped with a centrally mounted, external fuel filler. The wheels feature closed lug nuts and are adorned with Michelin Pilot Sport 4S tires....
For decades, Porsche has established itself as a renowned car manufacturer, celebrated for its adaptability and agility. It has consistently catered to the desires of racing enthusiasts and discerning clients by creating special versions of their beloved cars. During the early 1960s, the 356s were no exception to this tradition....
I recently completed a back-to-back track day event at Area 27 Motorsports Park a couple of weeks ago. There was a fine sampling of Porsche sports cars being purposefully piloted by some amazing drivers on the circuit over both days. It has been a good 3 years since I’ve visited...
A 2023 Porsche 911 GT3 Touring finished in paint-to-sample Olympic Blue. It also features the optional Touring Package in Black, which introduces stylish black window trim and rear Porsche lettering. Notably, the Touring Package also brings forth a revised decklid with a mesh grille and a retractable rear spoiler, offering...
The Porsche 991 GT3 RS is a track-focused variant that was unveiled at the 2015 Geneva Motor Show. It introduced several enhancements such as lightweight bodywork, aggressive aerodynamics, full bucket seats, and a powerful naturally aspirated 4.0-liter flat-six engine producing 500 horsepower. This specific example was originally ordered by a...
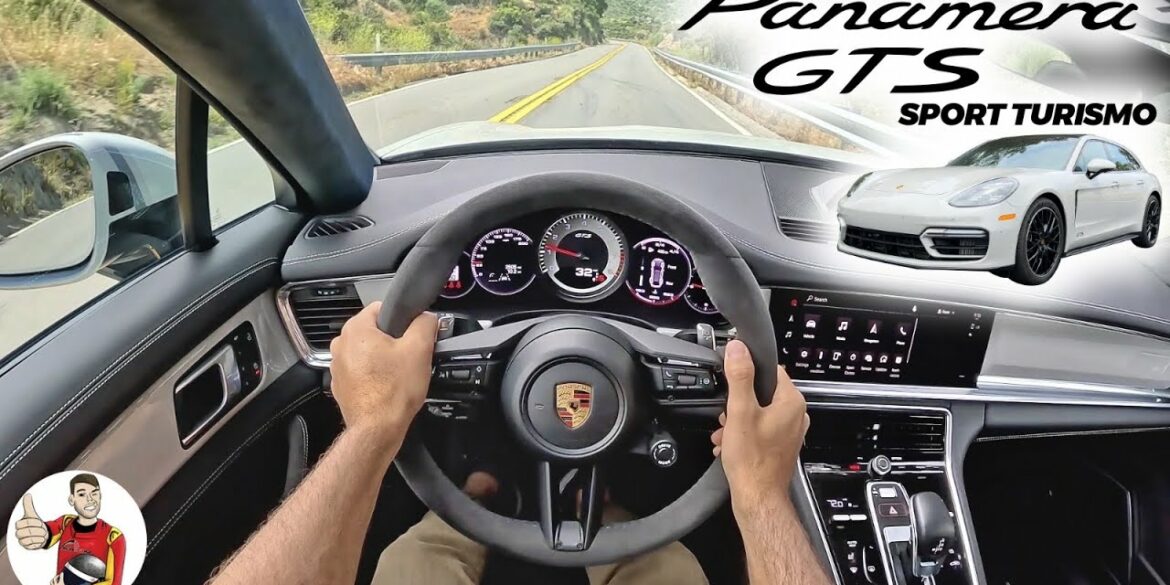
The Panamera GTS Sport Turismo costs only $6,900 more than the sedan variant in base trim. With the same powertrain and better practicality, this performance wagon may just be the most significant direct threat to the Panamera GTS sedan. The extra boot space, up to 49 cubic feet, with the...
With Stuttgart neighbor Mercedes on the rampage, Porsche had trouble on the track in the late 1990s GT1 era. But when it was essential to pull out a win at Le Mans to celebrate Porsche’s 50 years of making cars, the GT1/98 had what it took. Planning for Le Mans...
Porsche & Le Mans Newly released “Racing with Giants” video features archival footage of Le Mans past and present, along with interviews with multiple drivers and Porsche team principals, including Allan McNish, Patrick Long, Jacky Ickx and Nick Tandy. Porsche has long competed at Le Mans, though recently solely in...
For years, the Porsche Cayman GT4 has established itself as an exceptional sports car, offering incredible performance for those willing to invest. However, it has often lived in the shadow of the recently introduced 911 GT3 RS. With the introduction of the new Cayman GT4 RS, equipped with a powerful...
A rare Emory Motorsports restomod 1958 Porsche 356A is currently up for auction on Bring A Trailer and is said to be the fifth Emory Special built. Emory Motorsports is a company that makes the best Porsche “Outlaw” cars. The attention to detail is stunning and there are few more...
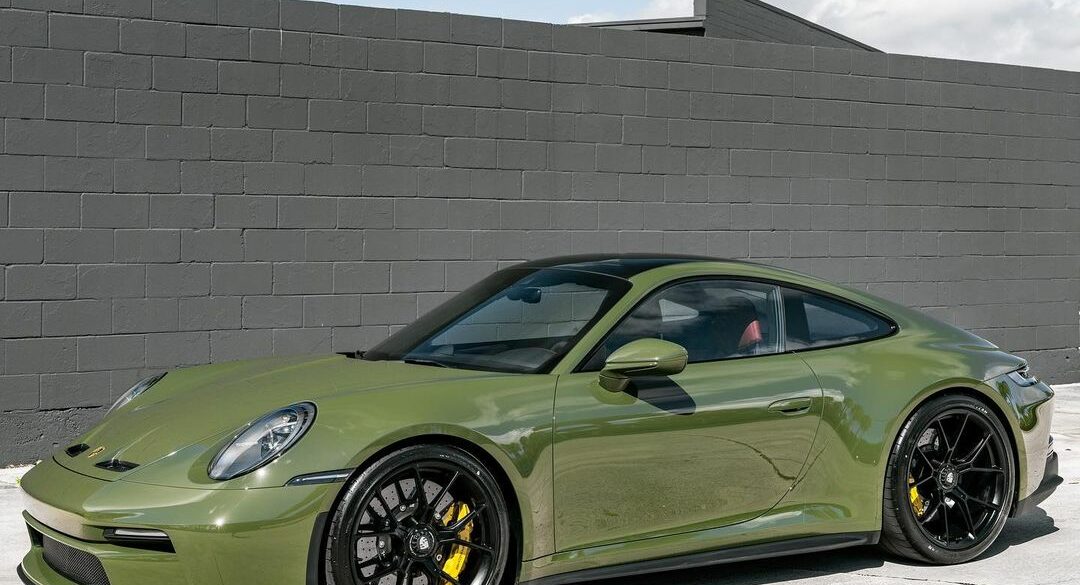
A Porsche 911 (992) GT3 Touring finished in paint to sample Nato Olive. Nato Olive is one of the 4 “olive” colors currently approved for PTS on the 992 and 718. As the name implies, Nato Olive closely resembles the iconic “military green” that has gained popularity in recent times. Photo...
A new video from the Throttle House YouTube channel allows us to witness a head-to-head matchup between three rival German car manufacturers that are known for their superior engineering. They organized a series of drag and rolling races, pitting the 2023 BMW M2, the 2023 Porsche Cayman GTS 4.0, and...
The “Indy Commission” by Singer Vehicle Design was built for IndyCar legend Dario Franchitti. Powering the Indy commission is a 4.0L, naturally-aspirated, air-cooled flat-six. The engine is specified with a ceramic plenum finish and drives the rear wheels through a 6-speed manual gearbox. Photo Credit: Singer Vehicle Design ...
The 718 Porsche Cayman GT4 is everything you could possibly want in a sports car. The sublime combination of a legendary chassis and naturally aspirated 6-cylinder Porsche engine is accentuated by the emphasis that less is more when done right – and nobody does this better than Porsche’s GT division. No...