Porsche Race Cars
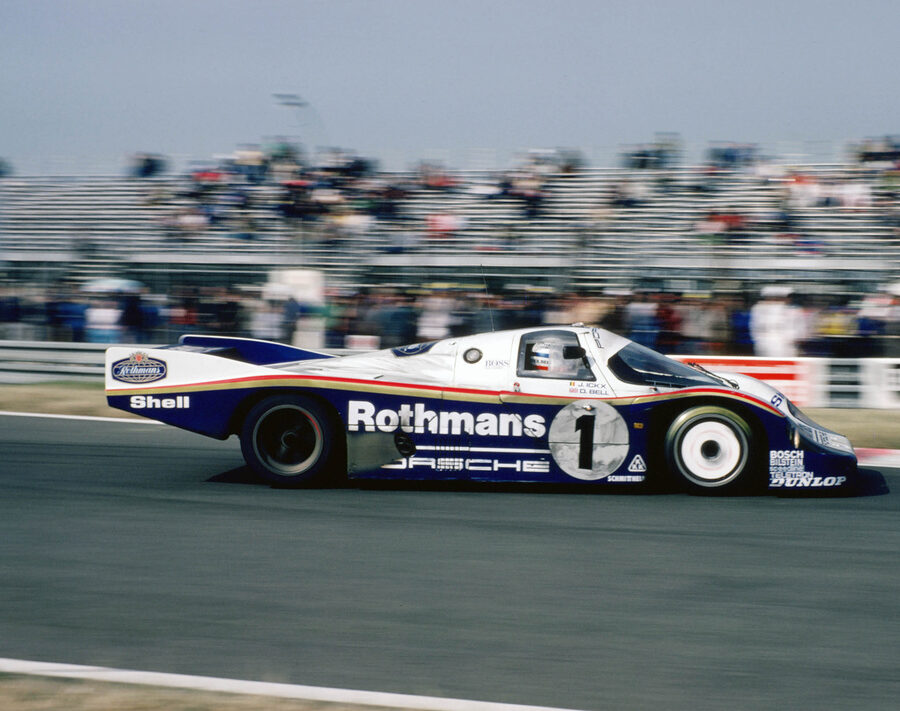
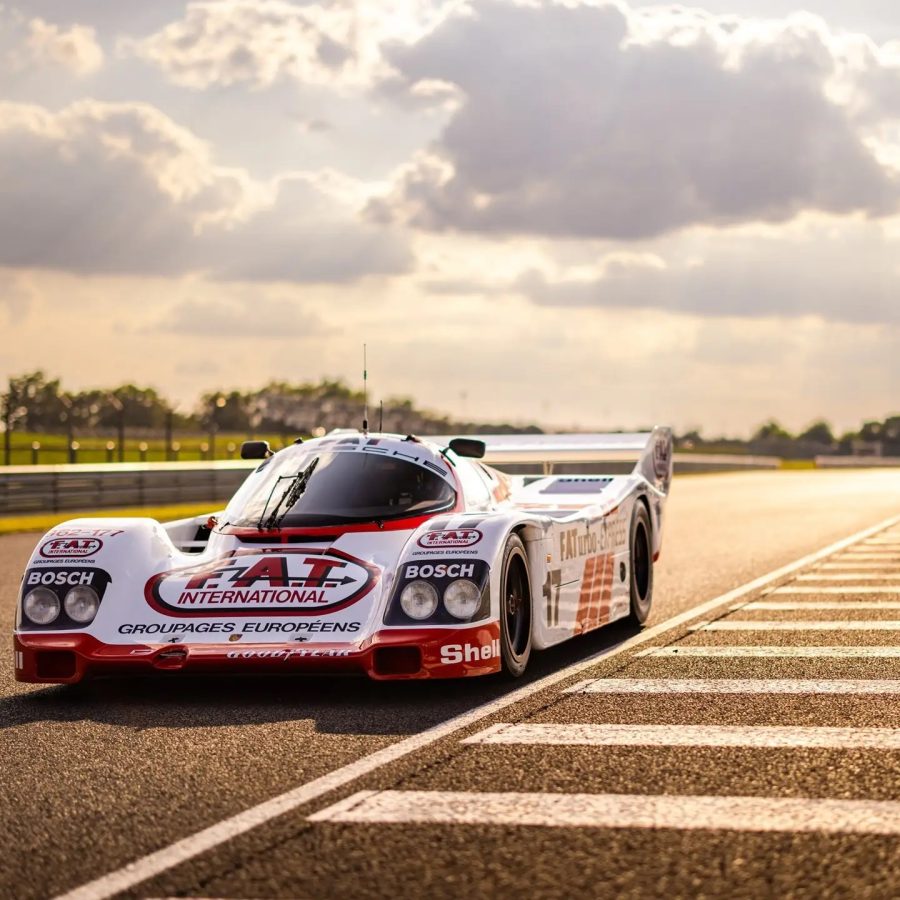
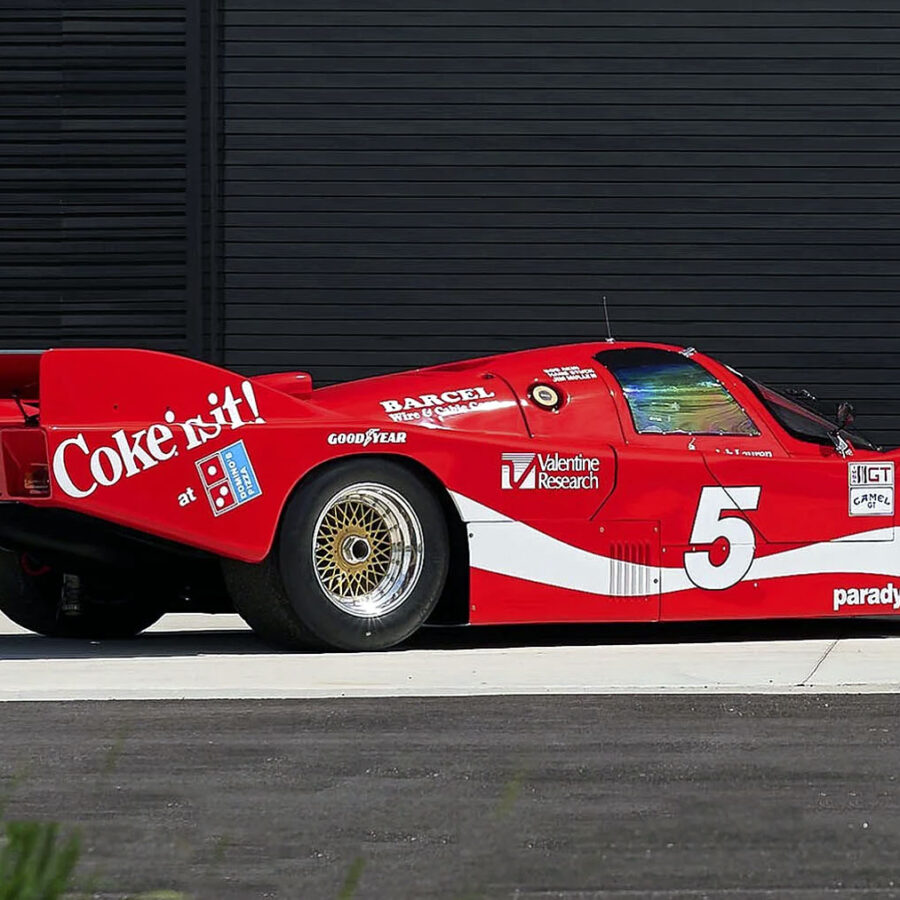
Market Place: 1984 Porsche 962
Porsche 75th Anniversary Auction | Estimate: $1,000,000 - $1,300,000
Porsche 911 SC “San Reno” (1981)
Röhrl's one-off drive at the 1981 San Remo Rally is regarded as one of the greatest drives ever
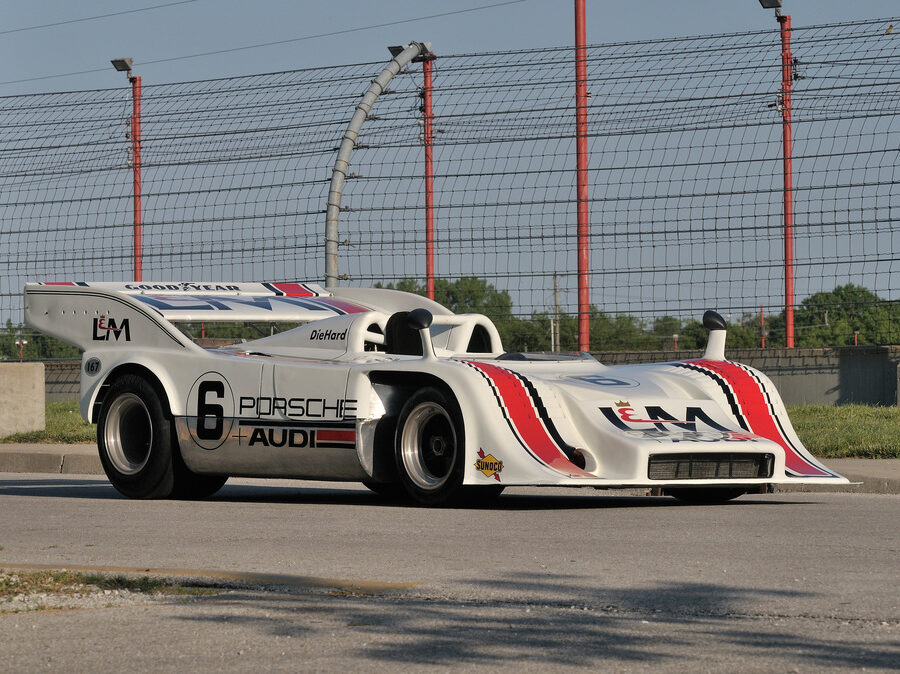
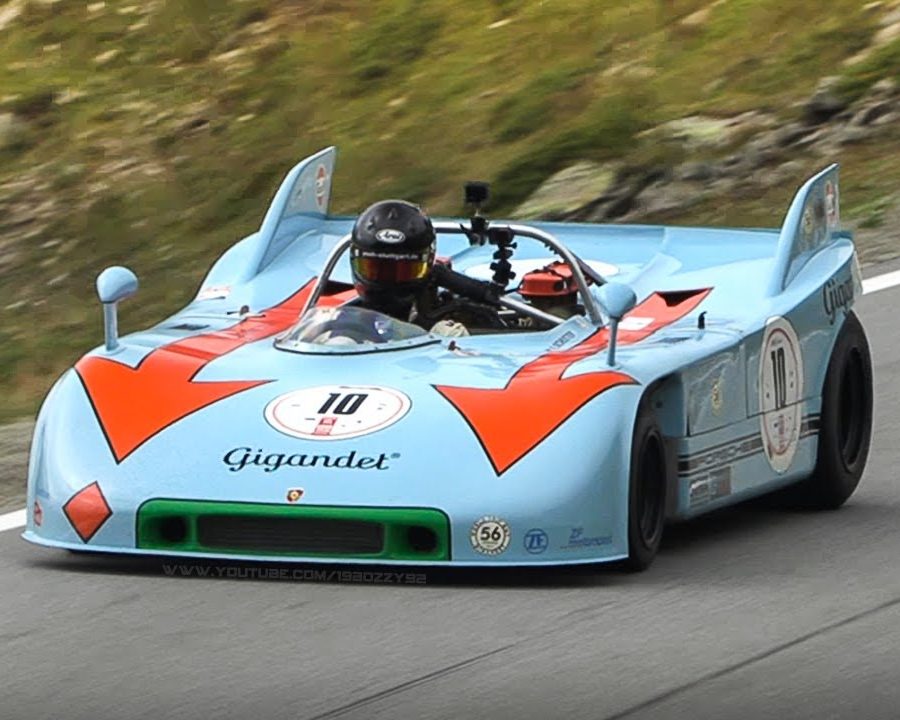
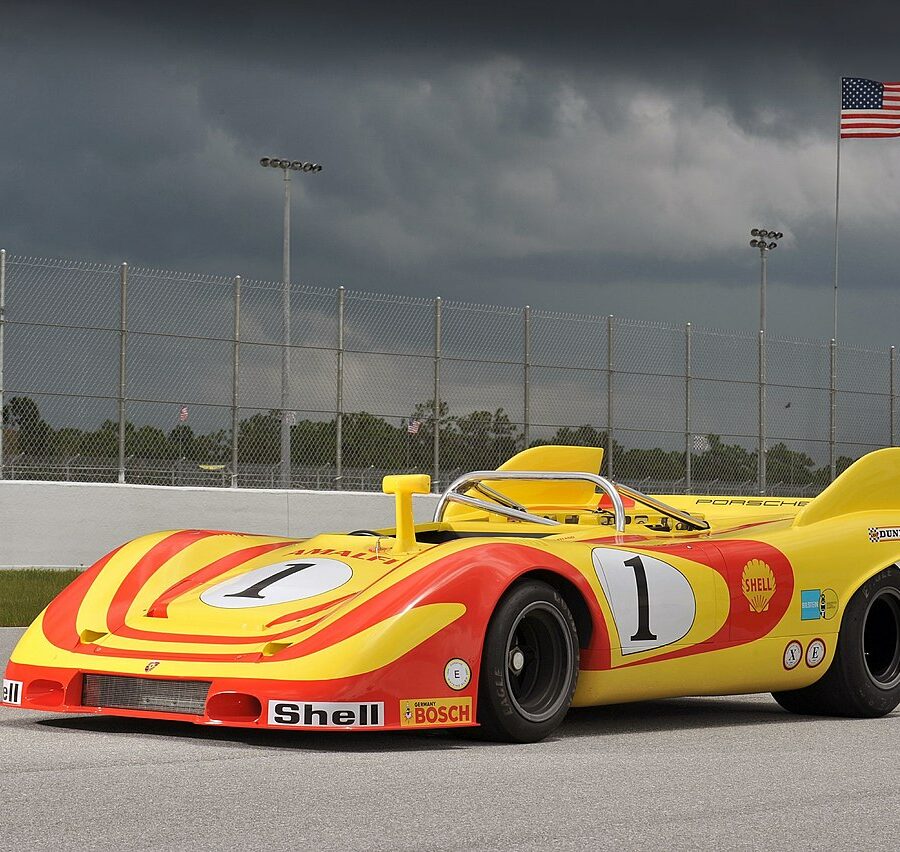
Porsche 917/10-72 (1972)
The 1972 917/10 was similar to the 908/03, but had the 12-cylinder engine instead of the 3-litre flat-8.
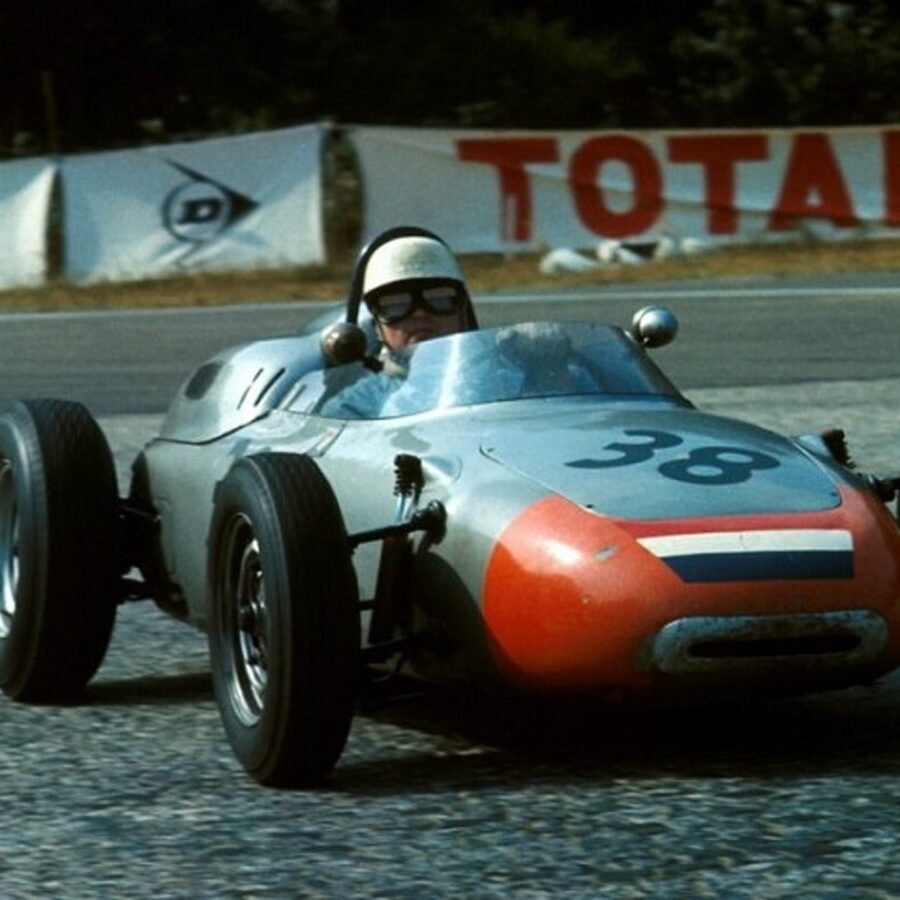
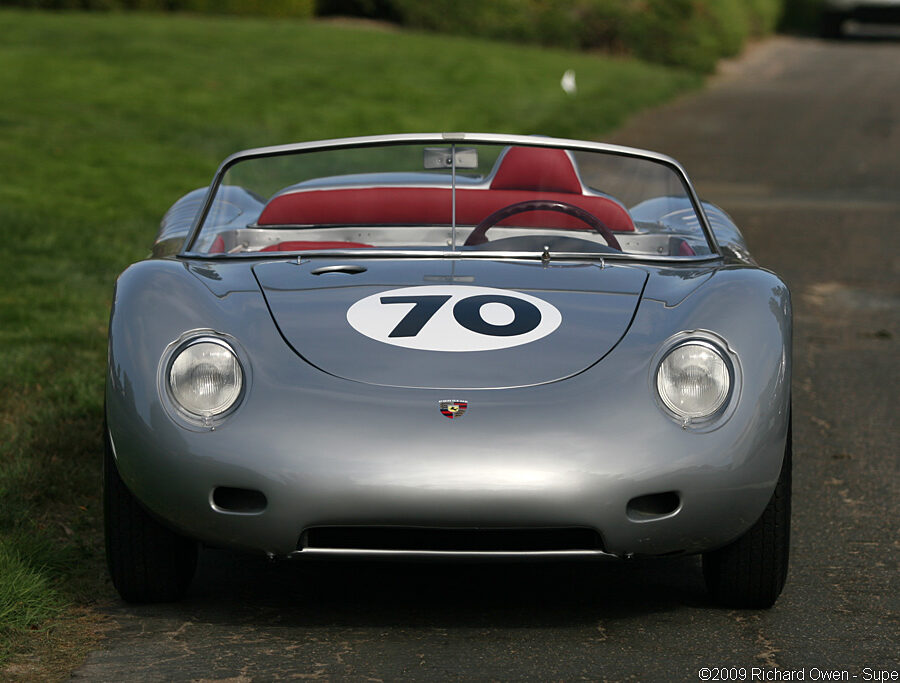
Porsche 718 RSK Mittellenker (1958)
For 1958, the 718 RSK Spyder was modified to compete in FIA Formula racing events. Gone was the conventional two-seat layout now replaced with a single seat in the middle.
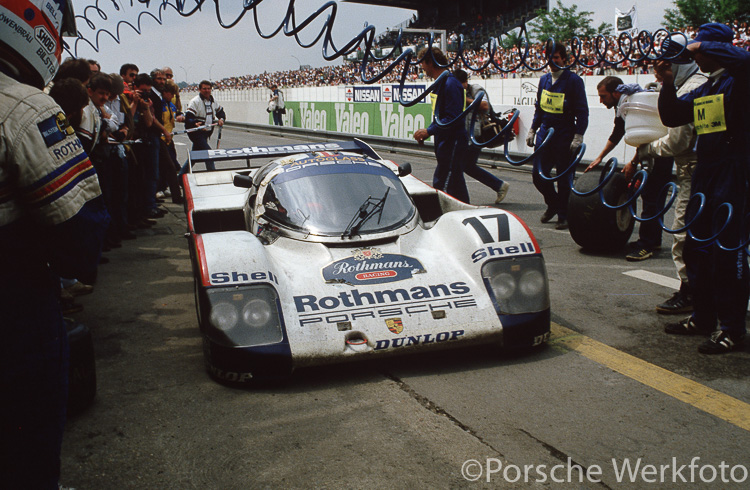
Porsche 956 (1982 – 1983)
Built by Porsche in 1982 for the FIA World Sportscar Championship. In 1983, driven by Stefan Bellof, this car established a record that would stand for 35 year
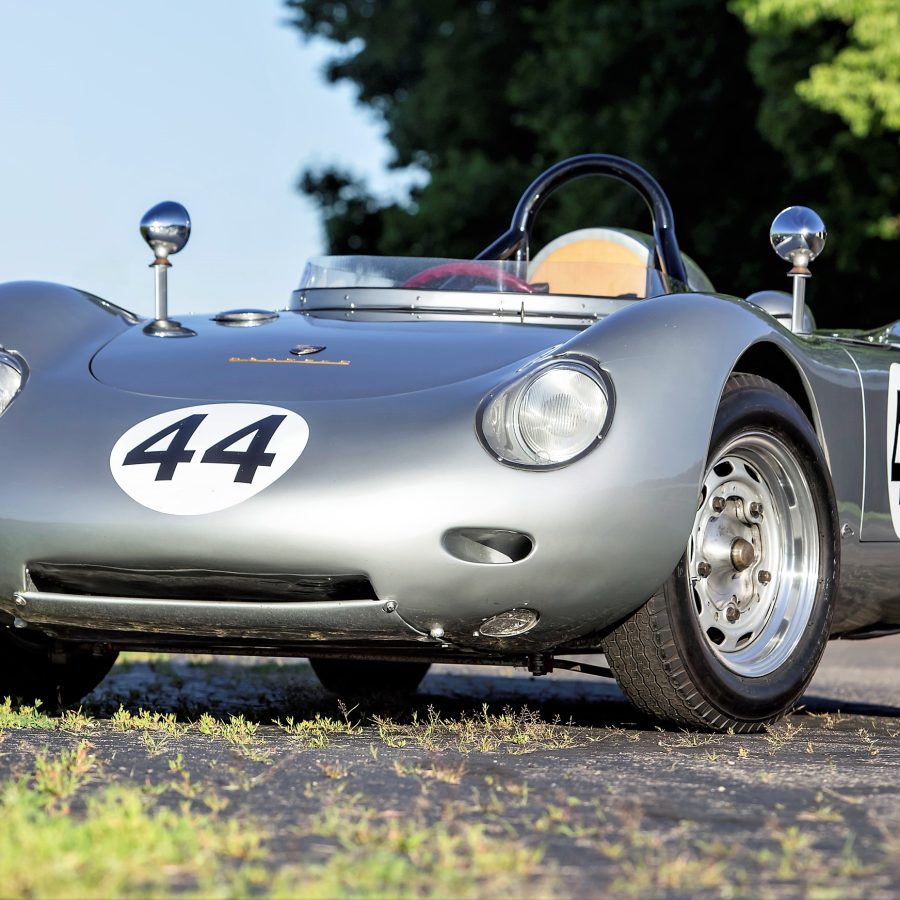
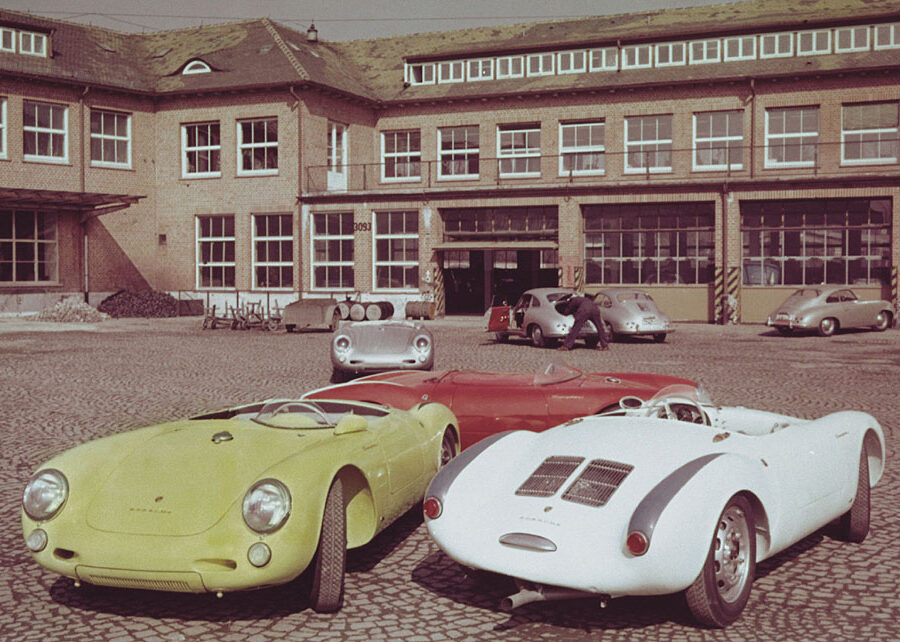
Porsche 550A RS Spyder (1956 – 1957)
The 550A was based on Porsche’s first purpose-built racing car, the mid-engined RS 550 Spyder.
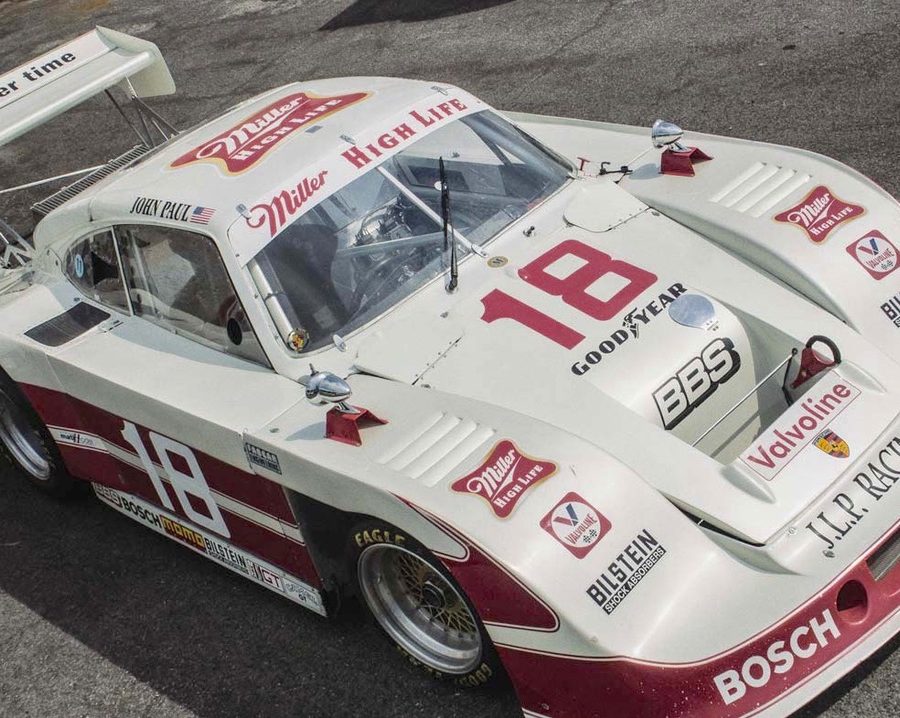
A Brief History of JLP-4
There are 935s, and then there are 935s…
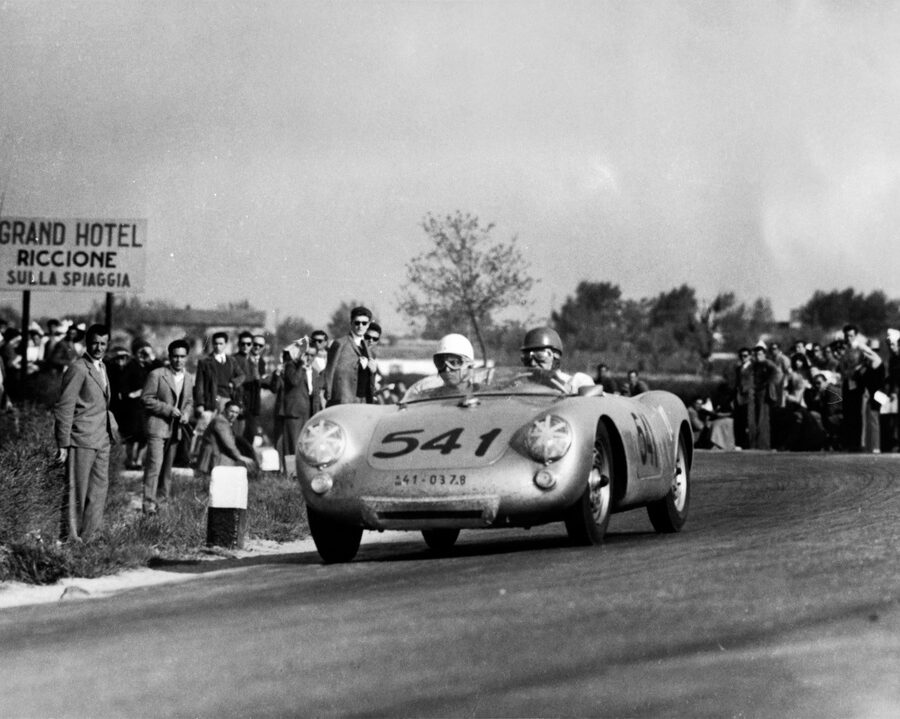
Porsche 550 – The Story
By the early fifties Porsche found that modified production cars would no longer win races. The 550 was the answer. The original giant killer had arrived.
Porsche 787 F1 (1961)
For the 1961 F1 season Porsche created a new car called 787.
Porsche Museum turns 15
A monumental undertaking continues to thrive
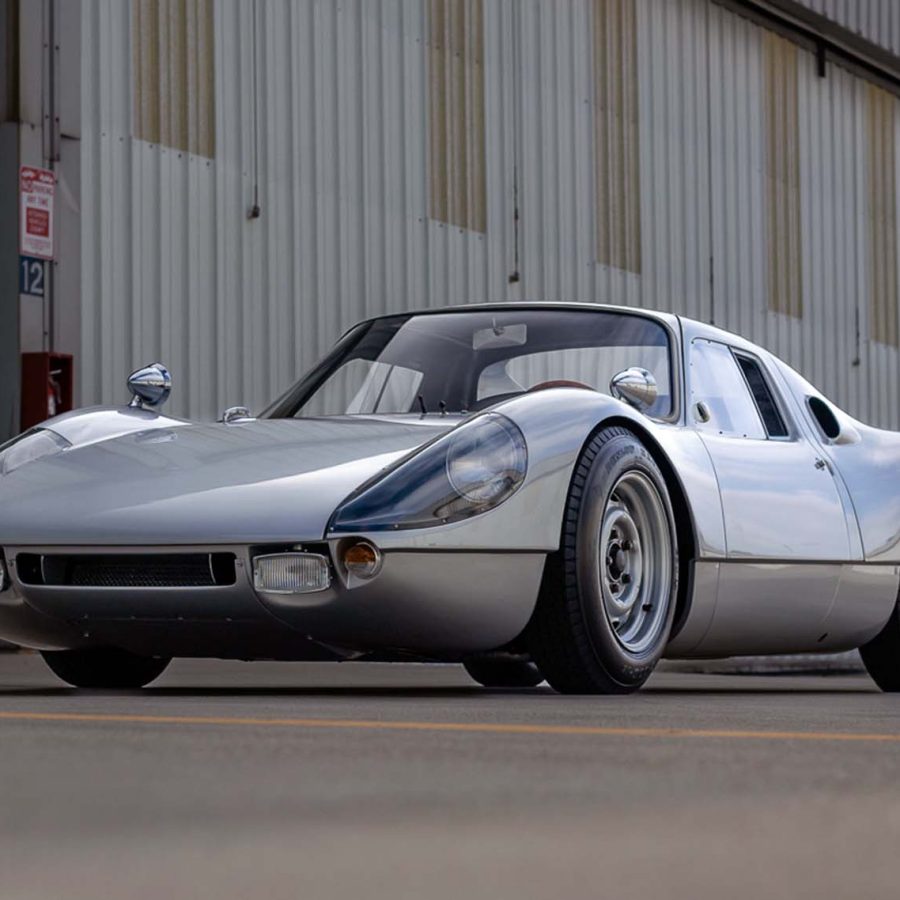
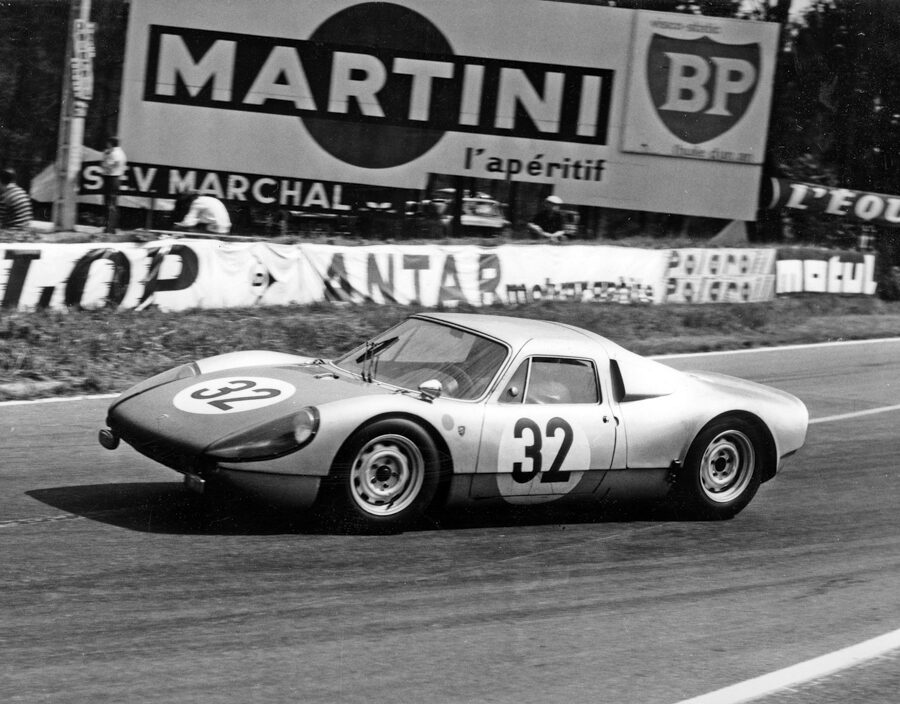
Porsche 904/6 Carrera GTS (1964 – 1965)
In 1965, the 904’s second and final production year, some examples received a version of the 911’s 2.0-liter flat-six. This version was dubbed the 904/6.
Air | Water’s SoCal debut makes a splash
The second iteration reflects a dedicated and growing following
Porsche 718 RS 61 Spyder (1961)
The 1961 Porsche RS was one of the last Spyders made by Porsche that used the potent 4-cam engine. It was a successor to the 1960 RS60
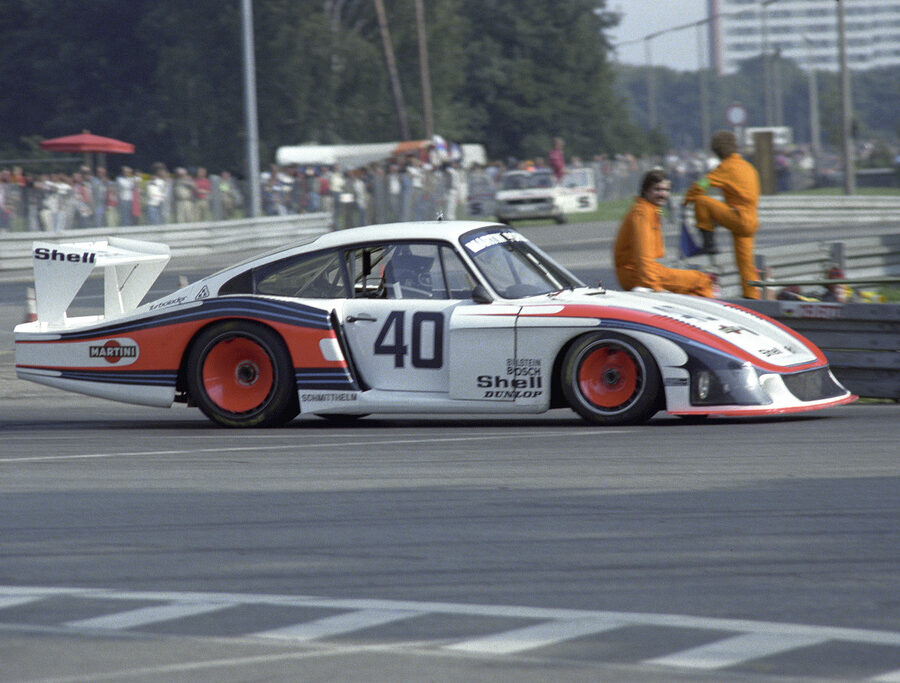
Porsche 935/78 ‘Moby Dick’ (1978)
The 935/78 was the ultimate expression of the 911 factory race car before Porsche officially withdrew from motor sport.
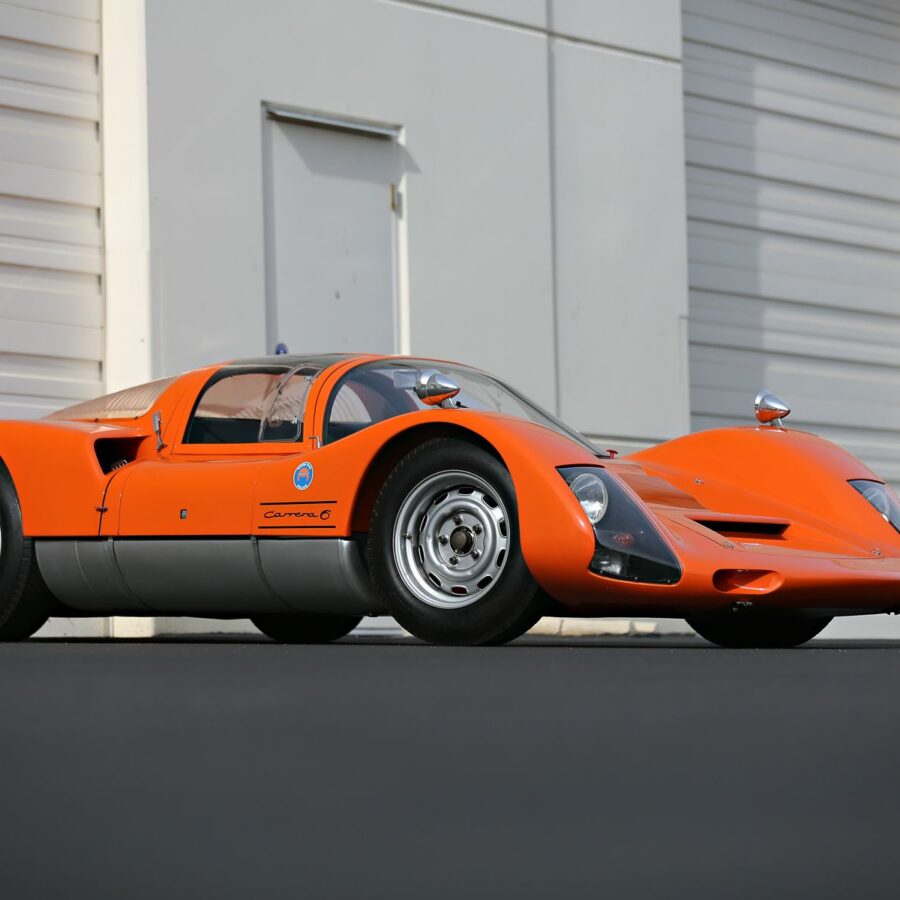
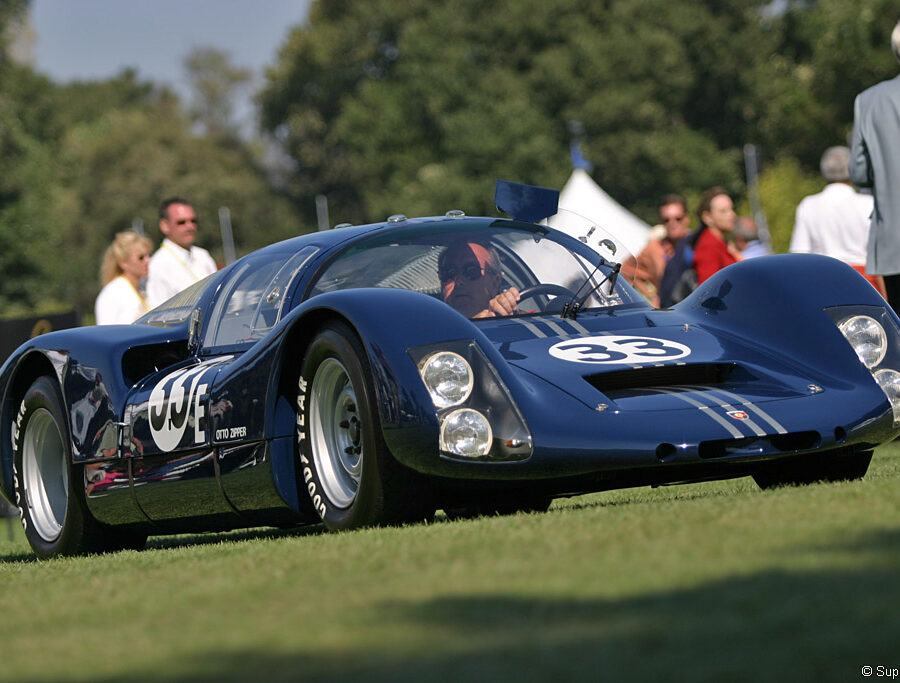
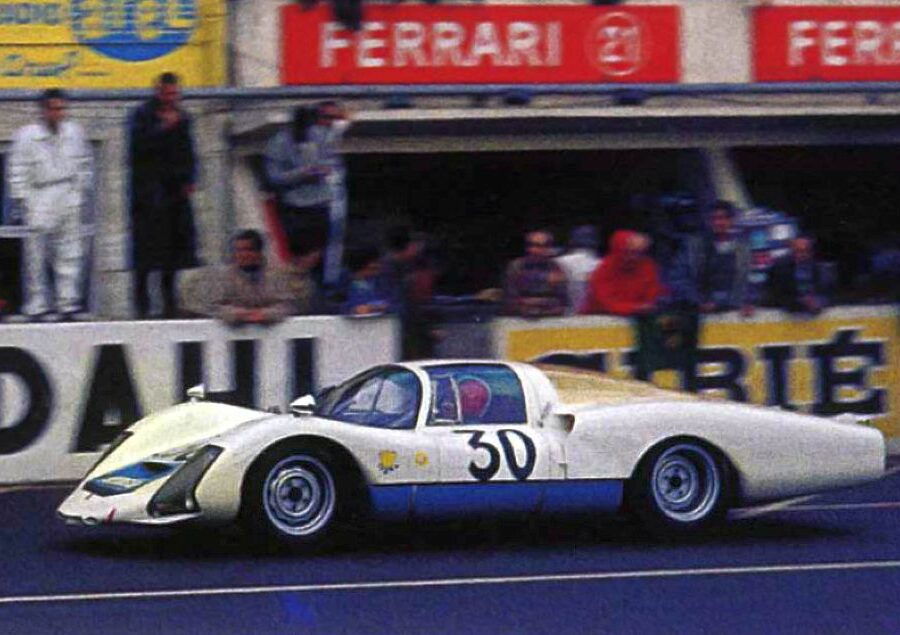
Porsche 906 Carrera 6 (K Coupé) (1966)
Developed for endurance sports car racing, the 906 was a street-legal racing car that raced in the FIA's Group 4 class
Porsche 804 F1 (1962)
The Porsche 804 competed in Formula One (F1) in 1962. Porsche developed an 8-cylinder engine for it.
Porsche 961 (1986 – 1987)
The Porsche 961 was the racing version of the 959 supercar.
Porsche 718 Cayman GT4 Clubsport (2019 – Present)
The 718 Cayman Race Car
Historic 935 and 904 Porsche duo arrives in Monterey
Gooding & Co to auction significant chapters in Porsche's history
Porsche Penske Motorsport dominates Road America
Spectacular double victory in the thrilling IMSA race at Road America
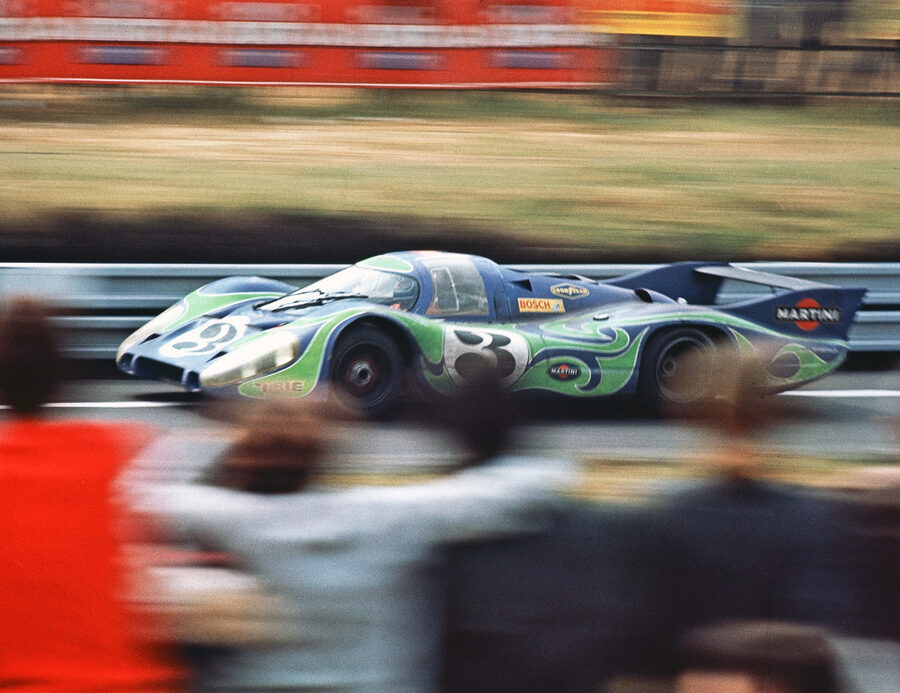
Porsche 917 K-69 (1969)
The short tail 917 K ("Kurz" in German for short) was raced first. The only engine available in 1969 was the 4.5-litre flat 12.
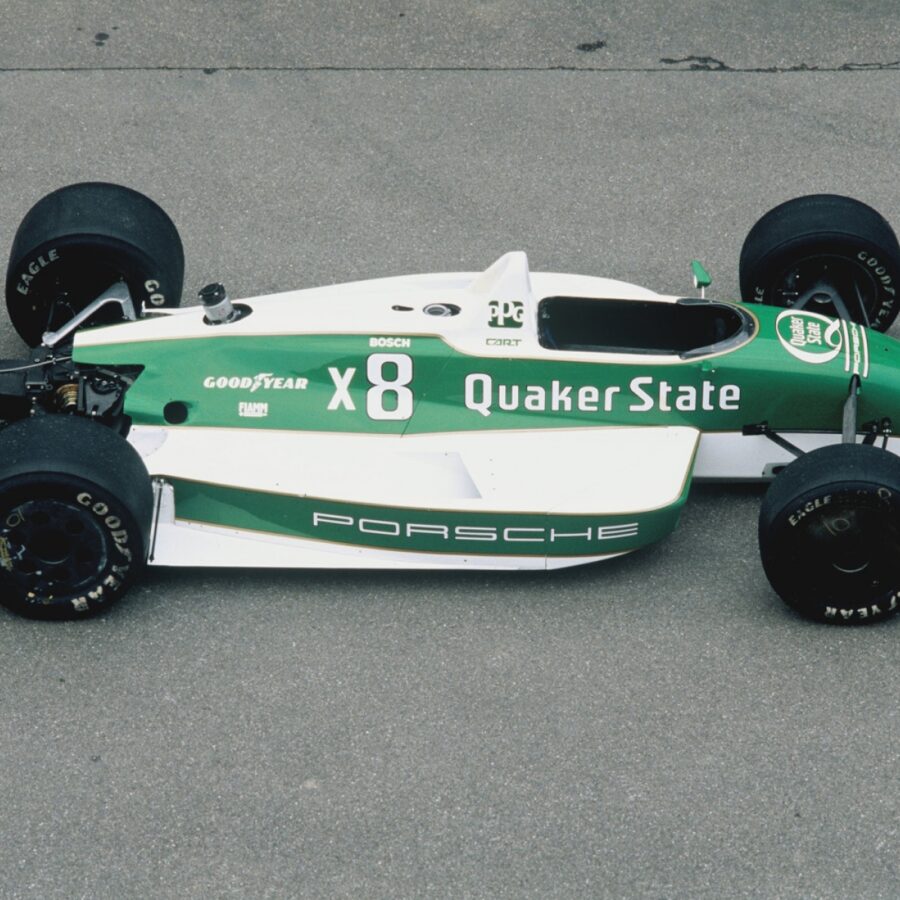
Porsche 2708 Indy (1987 – 1988)
1987 - 1988. Unlucky and Unprepared Porsche CART Race Car
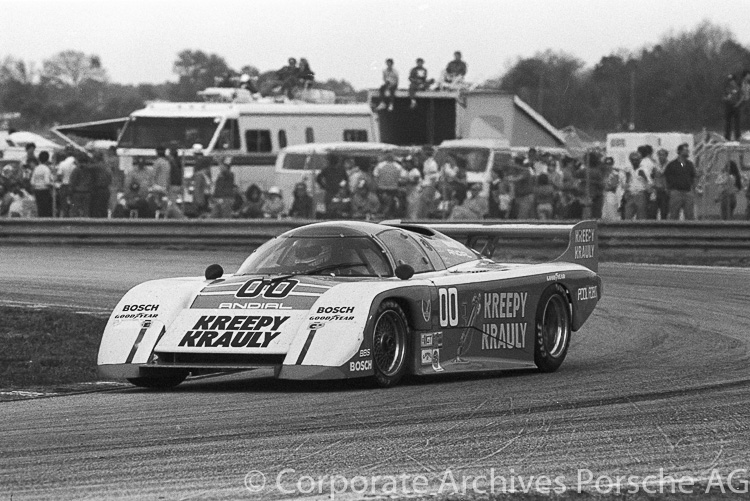
The Final Production Schuppan 962CR Hits the Auction Block
The second and final production Schuppan-Porsche 962CR
Luftgekühlt spin-off Air-Water show comes to SoCal
Tickets now available for Air | Water, April 27, 2024
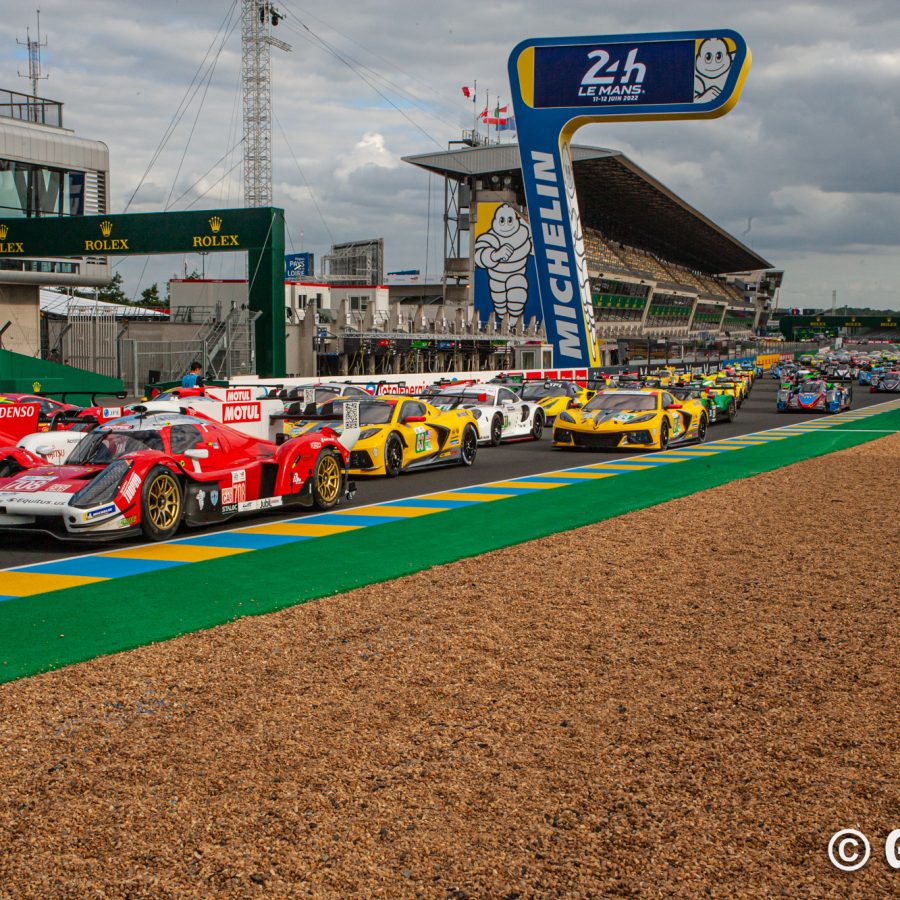
Le Mans 24 Hours Race Week
A pre-race teaser of the exciting weekend to come.
2024 Icons of Porsche Festival
Estimated 50,000 attendance
2019 Porsche 935
Porsche track-day 935 on BaT
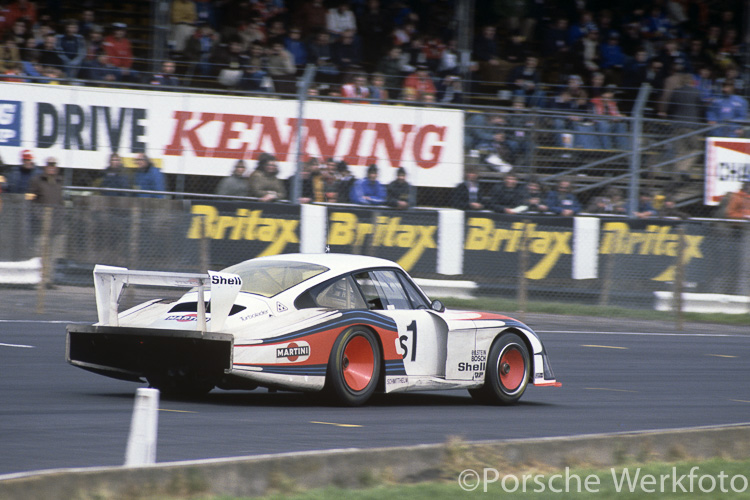
Porsche 917/20 Turbo (1973 – 1974)
The 917/20 Turbo is a confusing car - its chassis number reads 917/30-001, but it is not the real 917/30
Porsche 906 E Carrera 6 (1967)
Nine factory vehicles received the 2-liter, six-cylinder boxer engine with an injection system
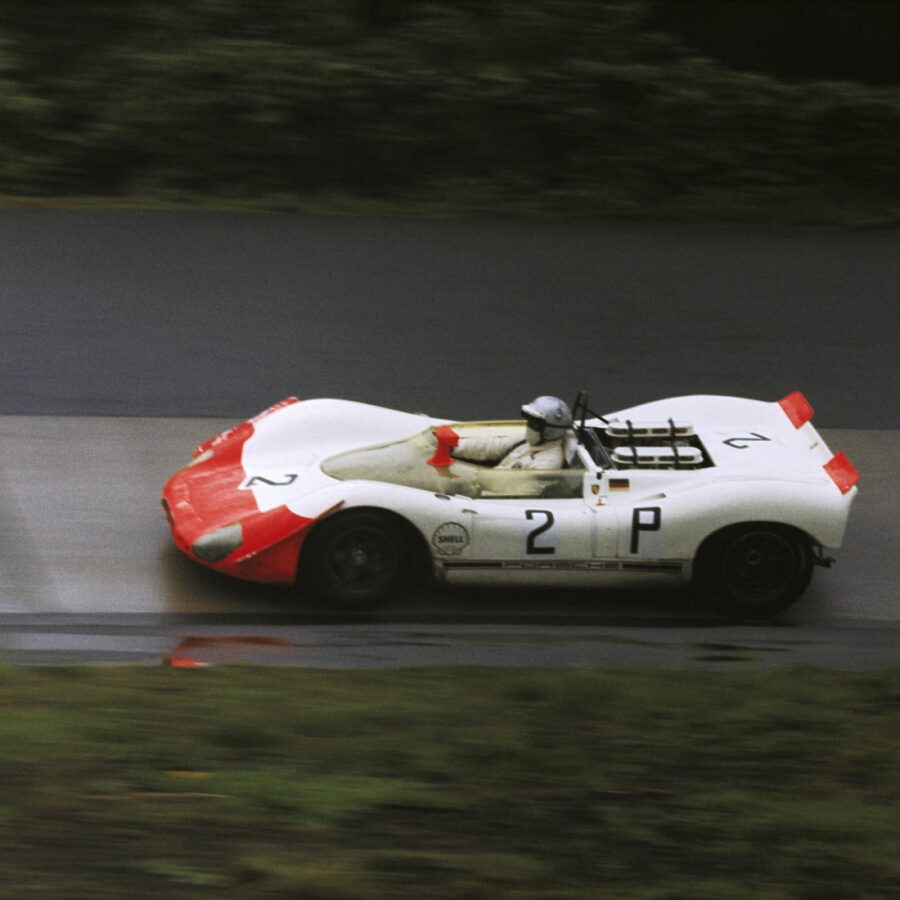
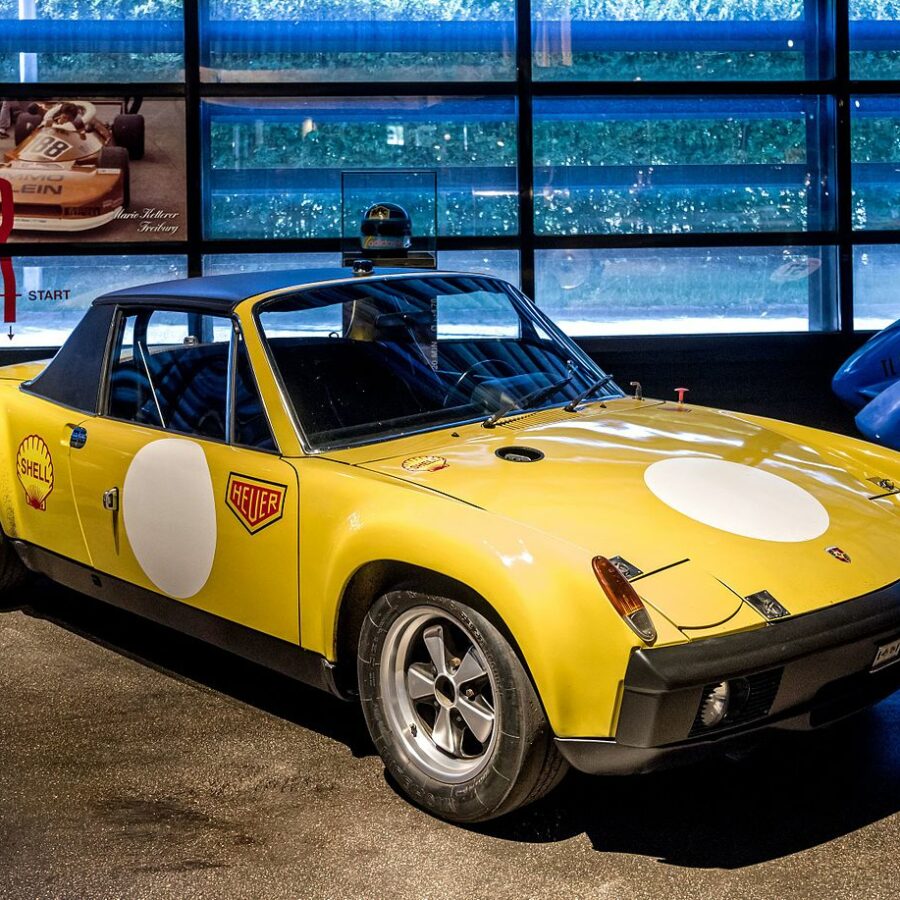
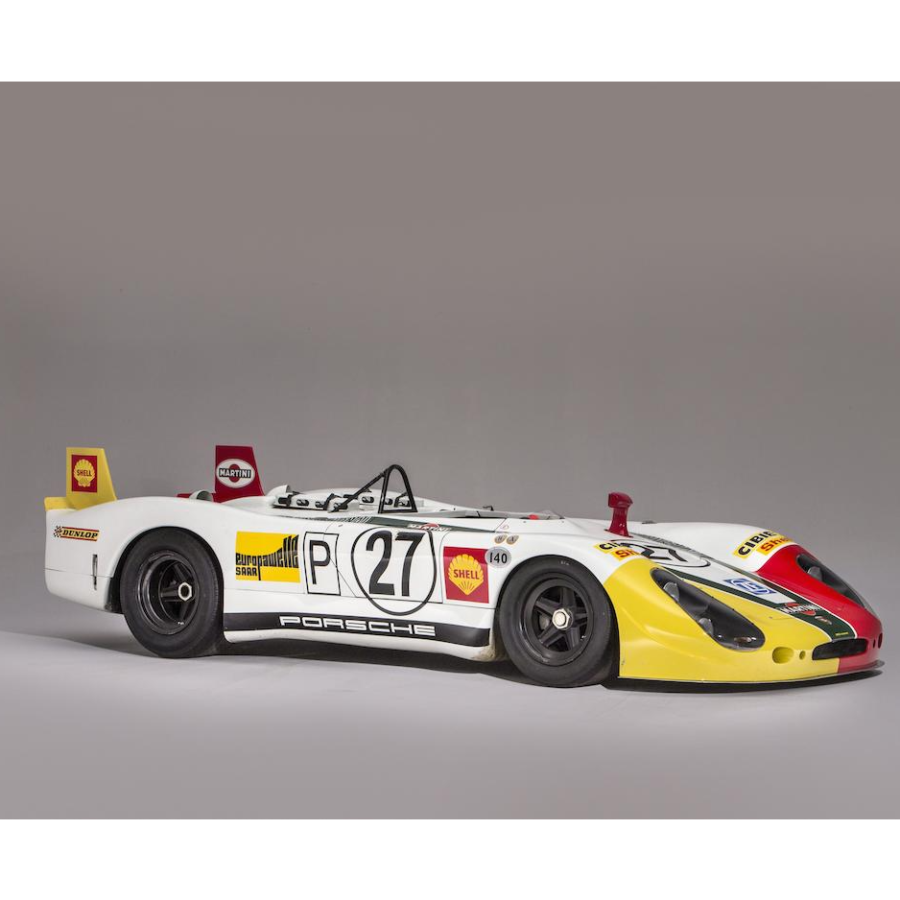
Porsche 908/02 K Spyder (1969 – 1972)
Notching up over 50 major victories and more than 100 podium results, the 908/02 Spyder is one of the most successful Porsche race cars
Porsche 910 Targa (1967 – 1968)
Porsche 910 was the evolution of the 906 with Ferdinand Piëch as its main driving force and Hans Mezger
Porsche 907 K (1967 – 1968)
The 907 was conceived and built as a way to win the 1967 Le Mans race.
Rennsport Reunion 7
For the love of Porsche
Luftgekühlt goes to Europe!
Summer shows in Wroclaw, Poland, and Copenhagen, Denmark
Porsche 917 ‘Interserie Spyder’ (1969 – 1970)
Of all the 917 variants, the ‘Interserie Spyder’ was one of the most successful. It won the Interserie championship outright for two years in a row before the model was replaced by the 917/10 of 1972
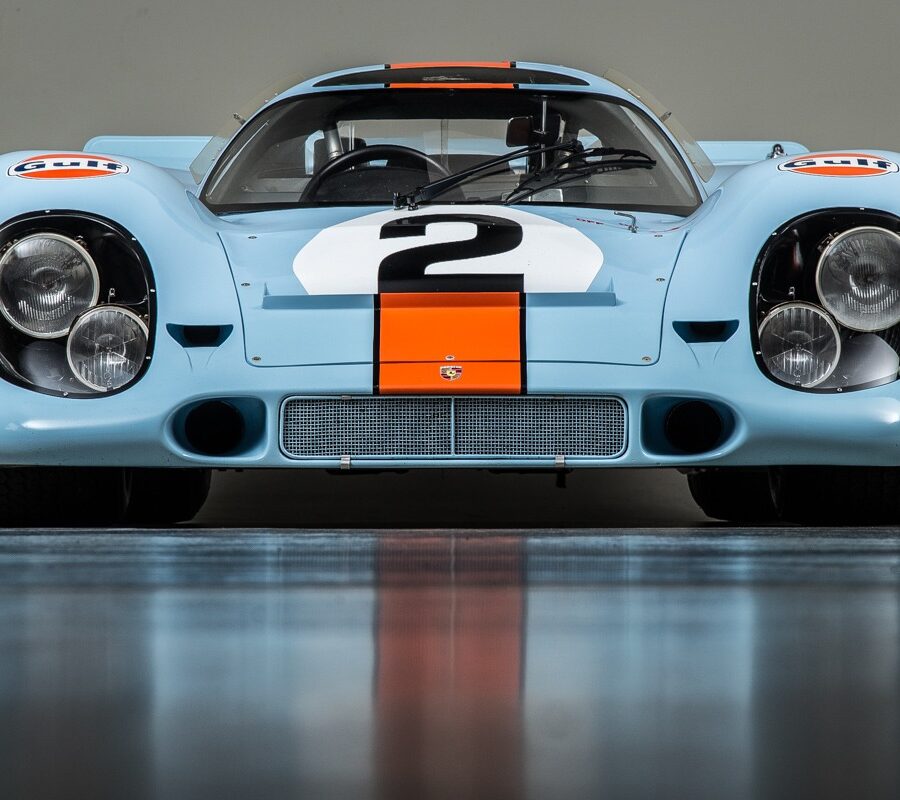
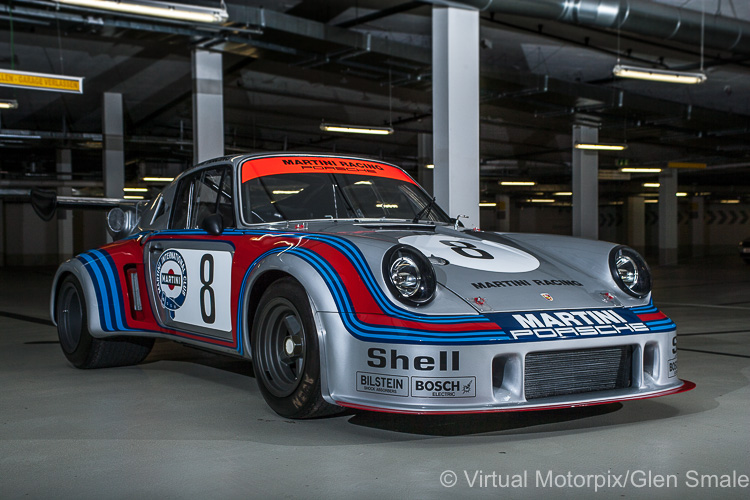
IROC Porsches: The 935 & the International Race of Champions
The made-for-TV IROC series was a remarkable innovation and the genesis of the all-conquering 935.
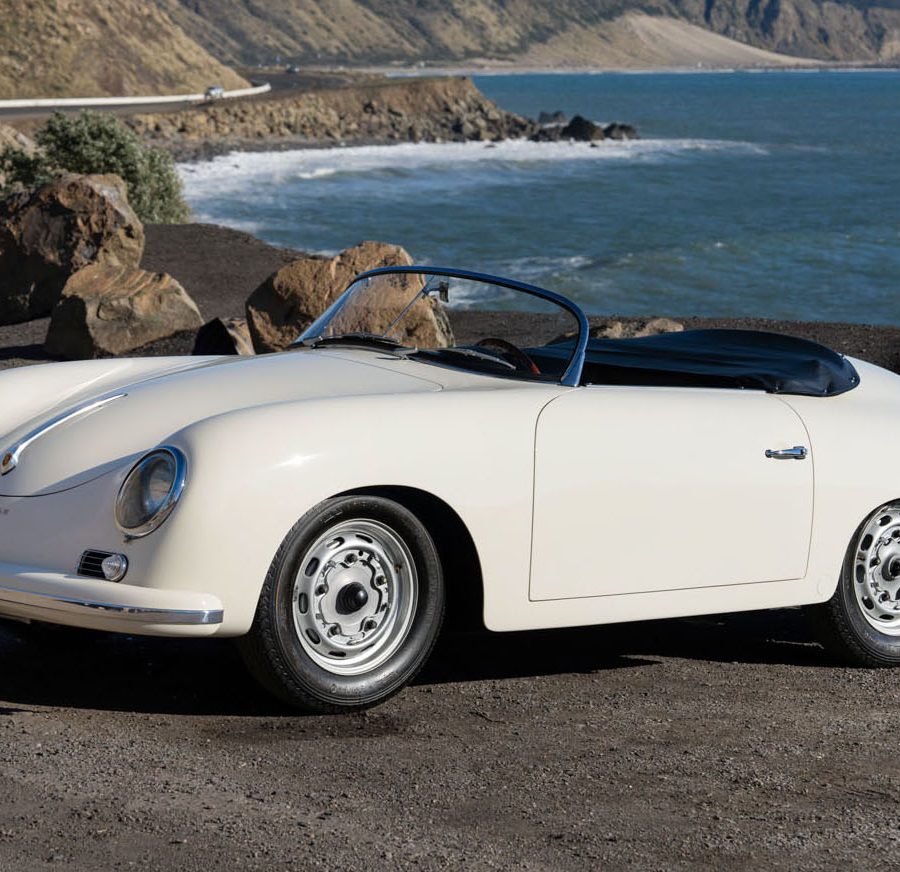
1957 Porsche 356A 1500 GS/GT Carrera Speedster
The ultimate GT Speedster comes to light?
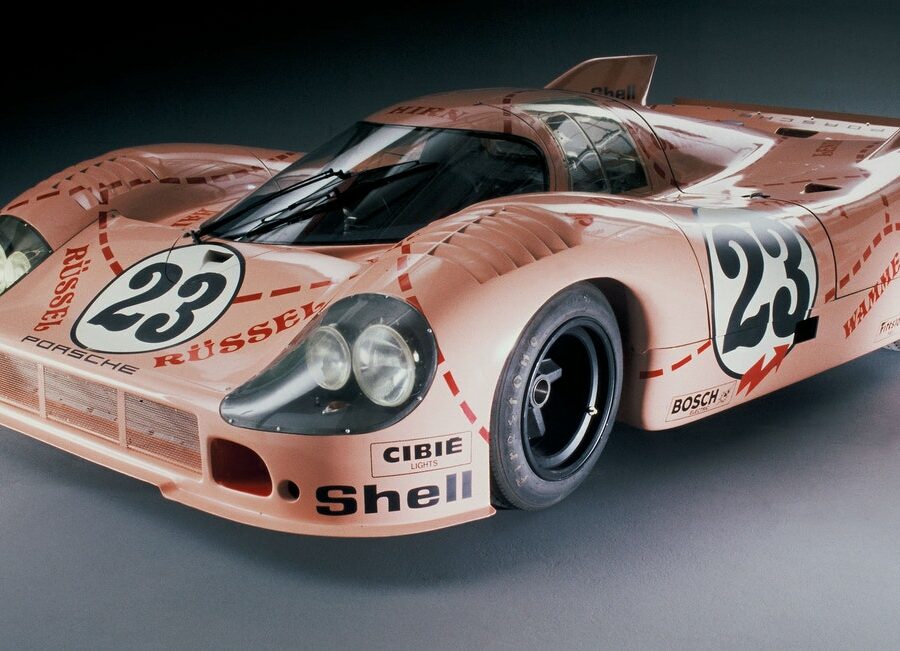
Porsche 917/20 Le Mans (1971)
The Pink Pig
Porsche 934 (1976 – 1977)
Using the 930 Turbo as a basis, Porsche built the 934 for Group 4 GT racing.
FOR SALE: 1966 Porsche 906 Carrera 6
Successful Italian period racing history
Porsche 550 RS Spyder (1954 – 1956)
The giant killer
Porsche 917K with unique history
Racing milestone comes to market
Porsche 917 LH-71 (1971)
Like the 917 LH of 1969 and 1970, the 1971 version was also made for one race only - the 24 hours of Le Mans.
Porsche 906 LH Coupé (1966)
For the 1966 Le Mans 24h race, long-tail LH ("Langheck") versions were made and now the standard 906 were called as 906 K ("Kurz", short in German)
Porsche 908 LH Flunder Spyder (1969 – 1975)
There was a belief that longer bodies are more aerodynamic and are therefore better for faster tracks, so a 908 Flunder Spyder with a longer tail was created
Porsche Heritage and Museum at Solitude Revival
A high-octane journey back in time!
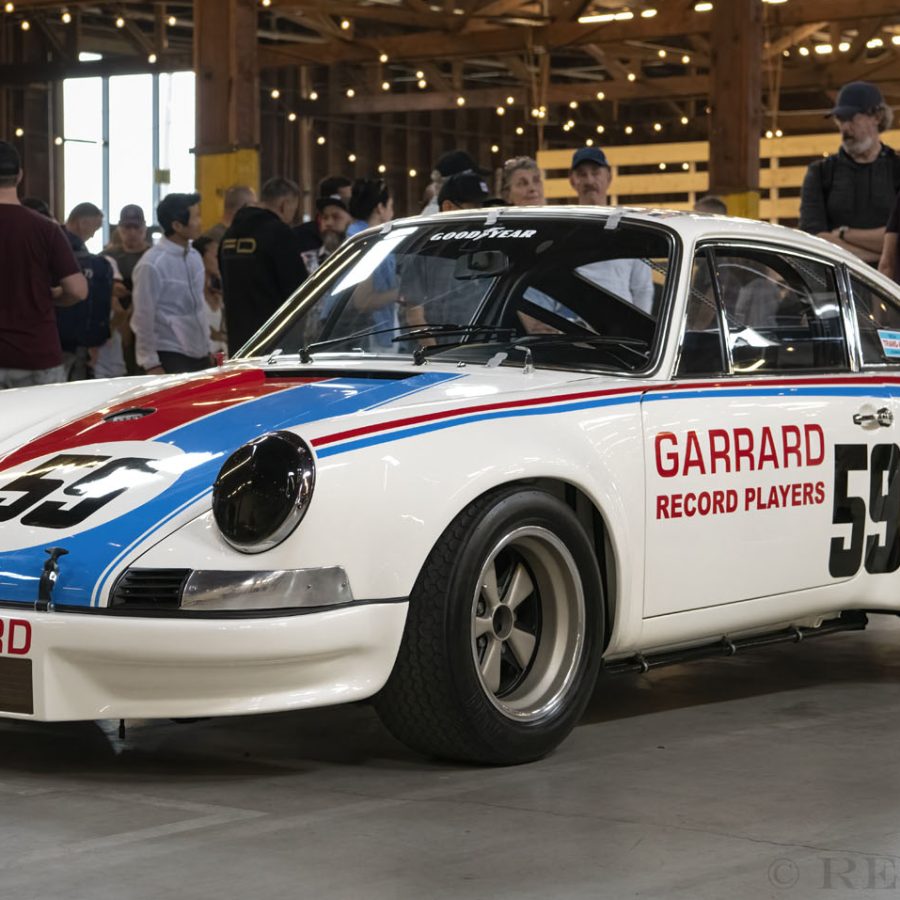
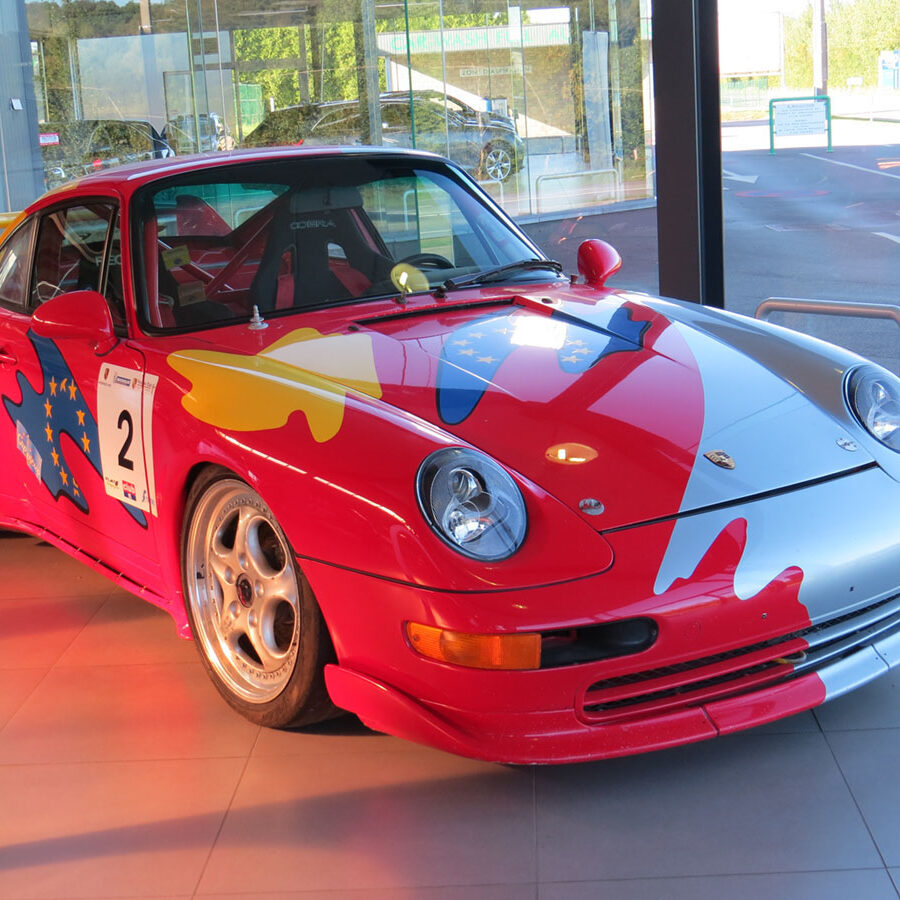
Porsche 911 Cup 3.8 (993) (1994 – 1998)
Developed at Porsche’s race department using the platform of their new 993 Carrera 2
2024 Targa California Rally
Successful 15th iteration includes IROC group