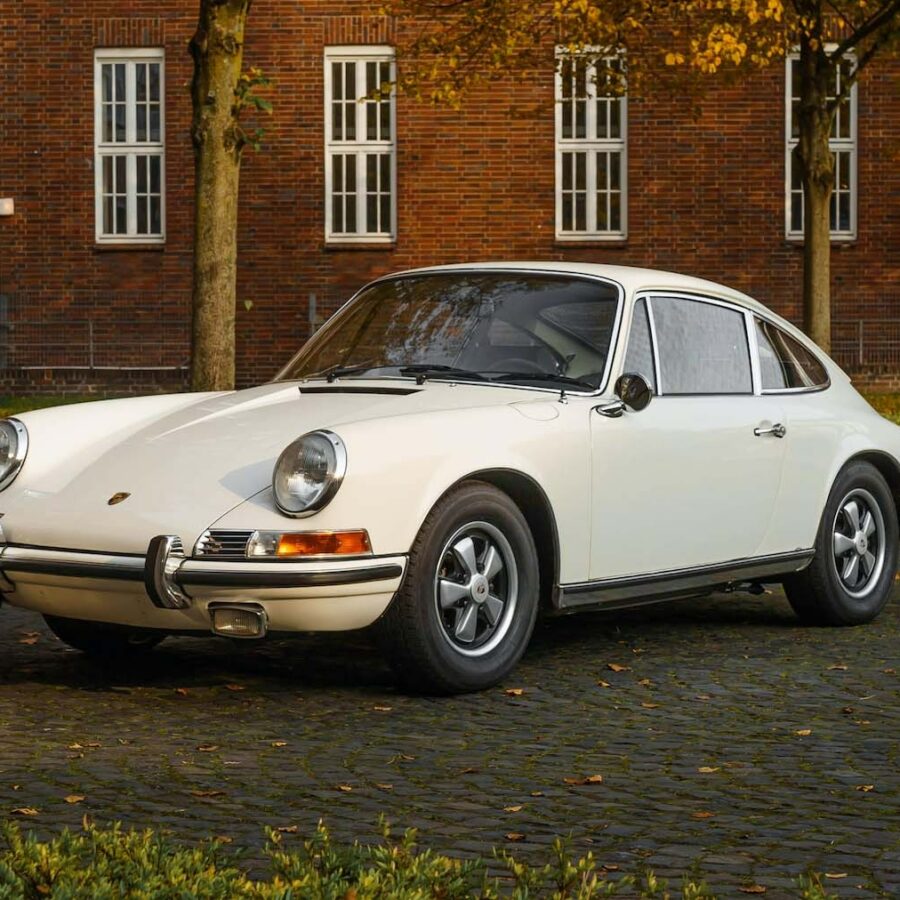
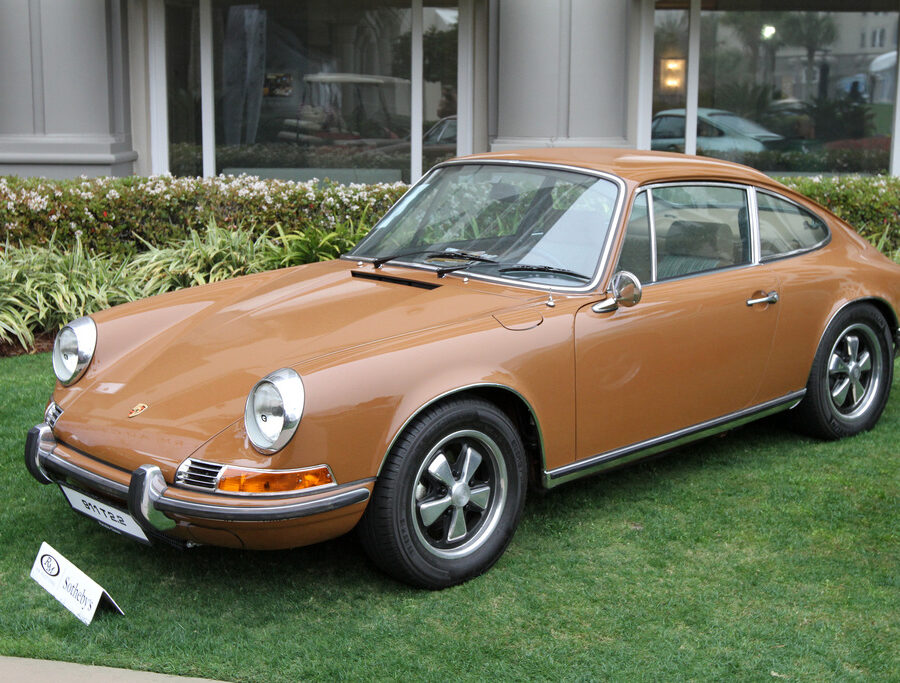
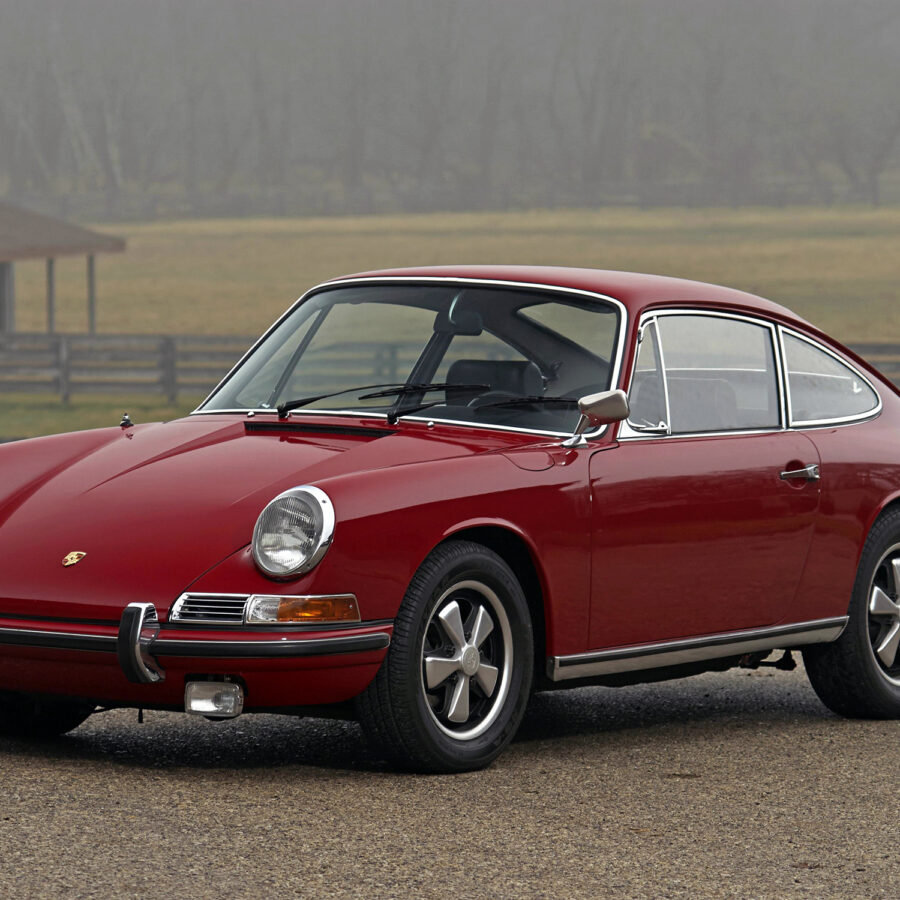
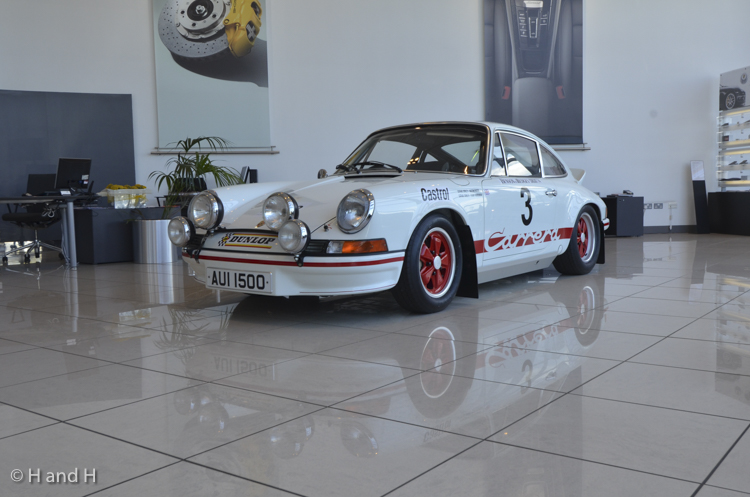
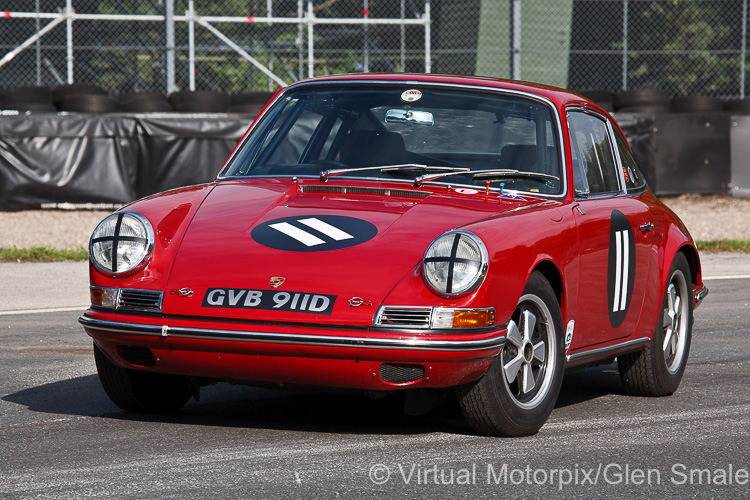
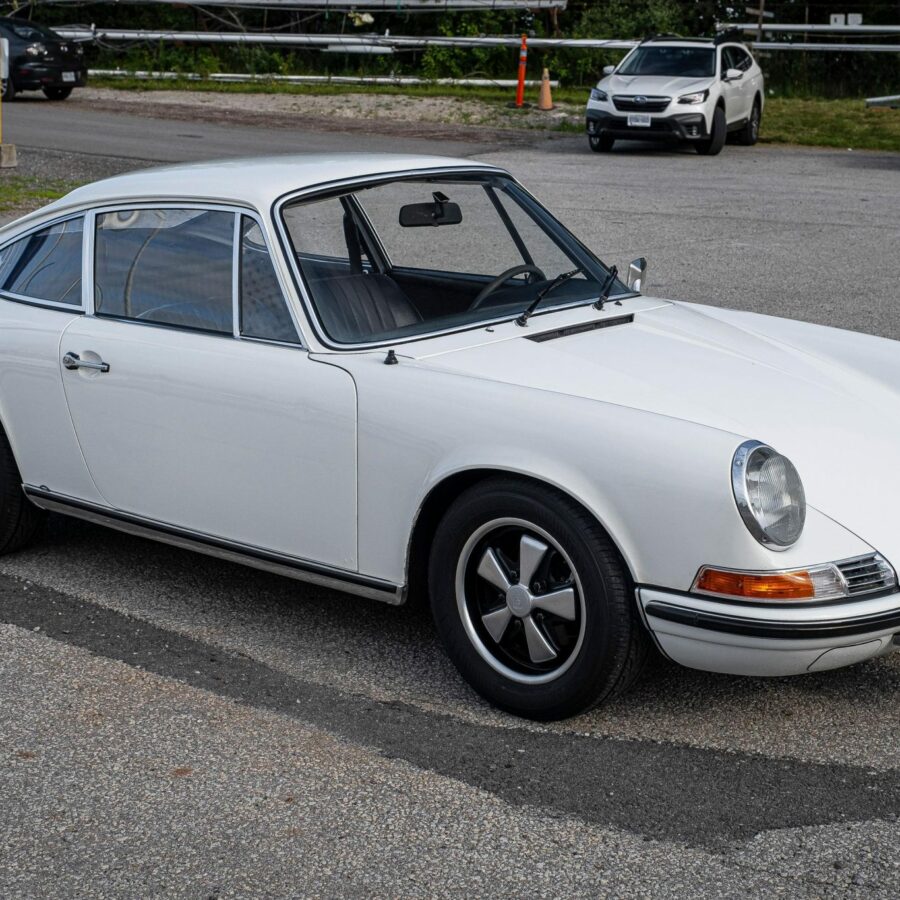
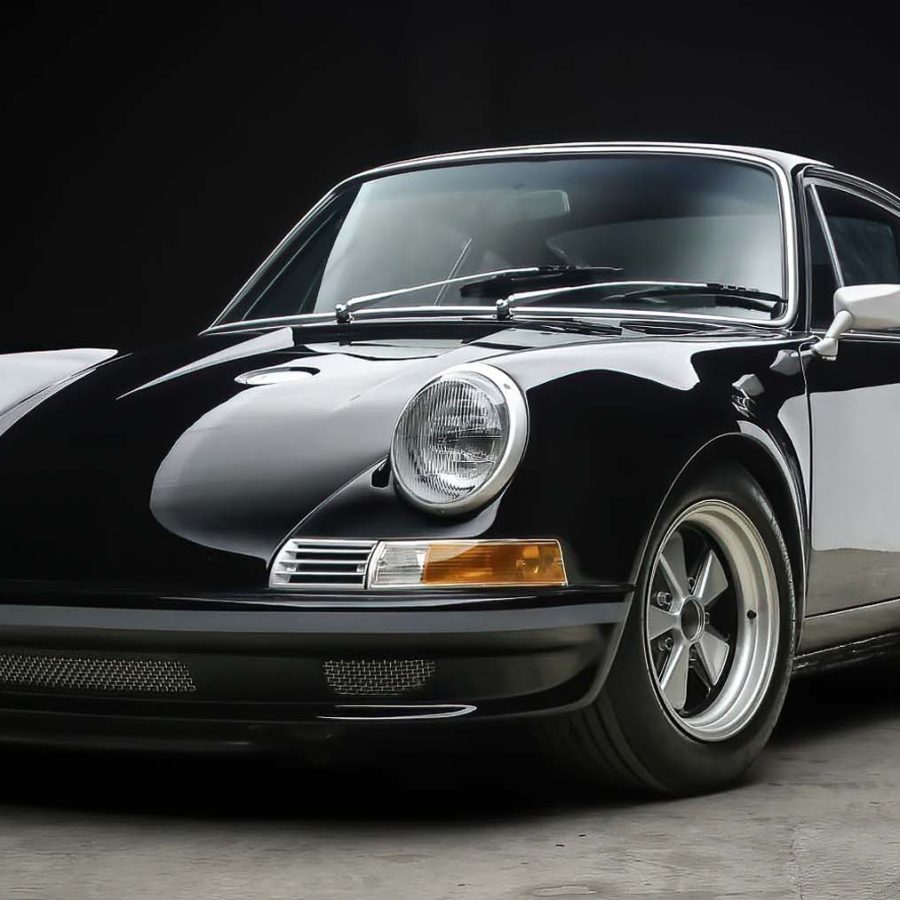
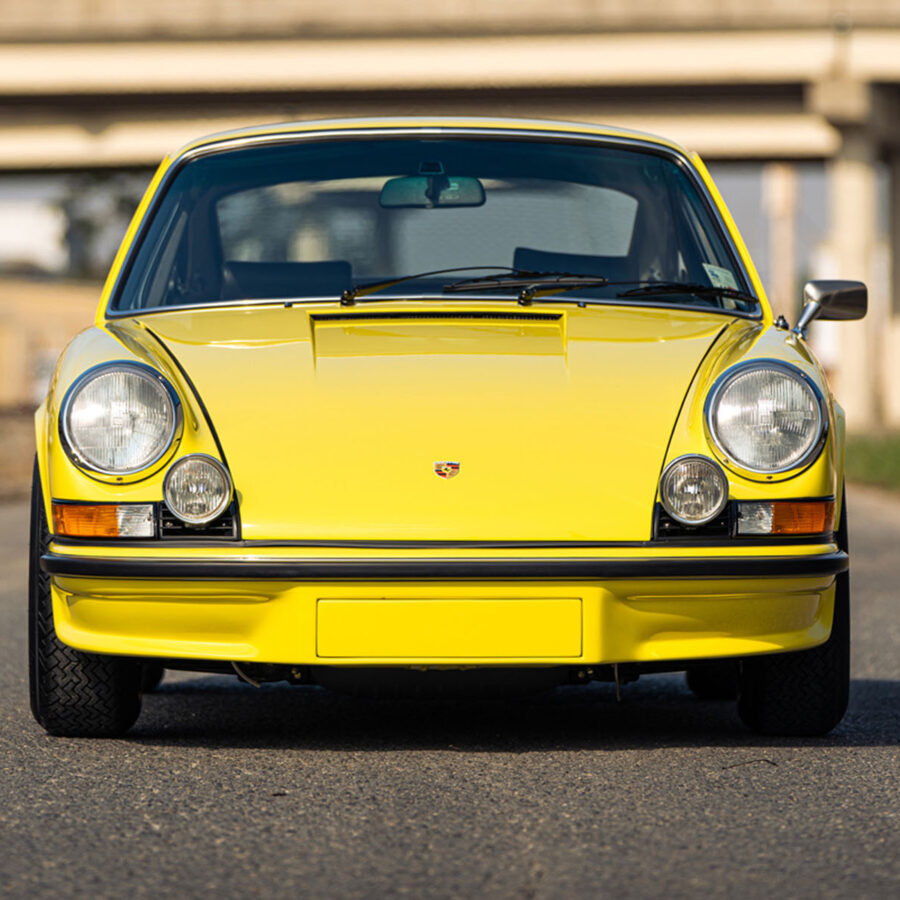
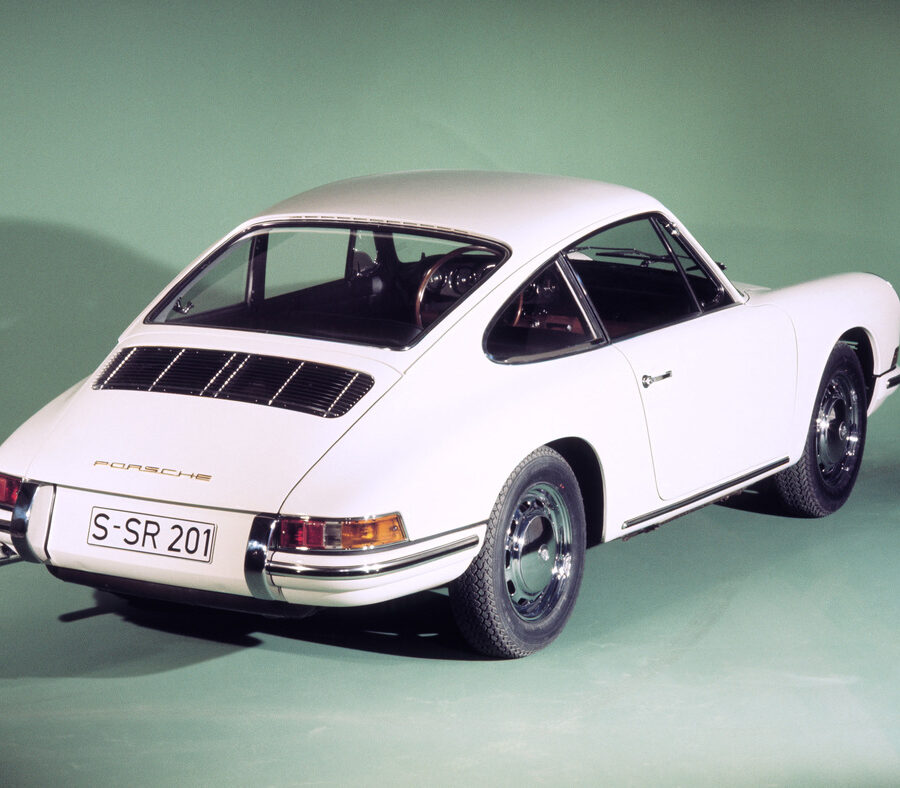
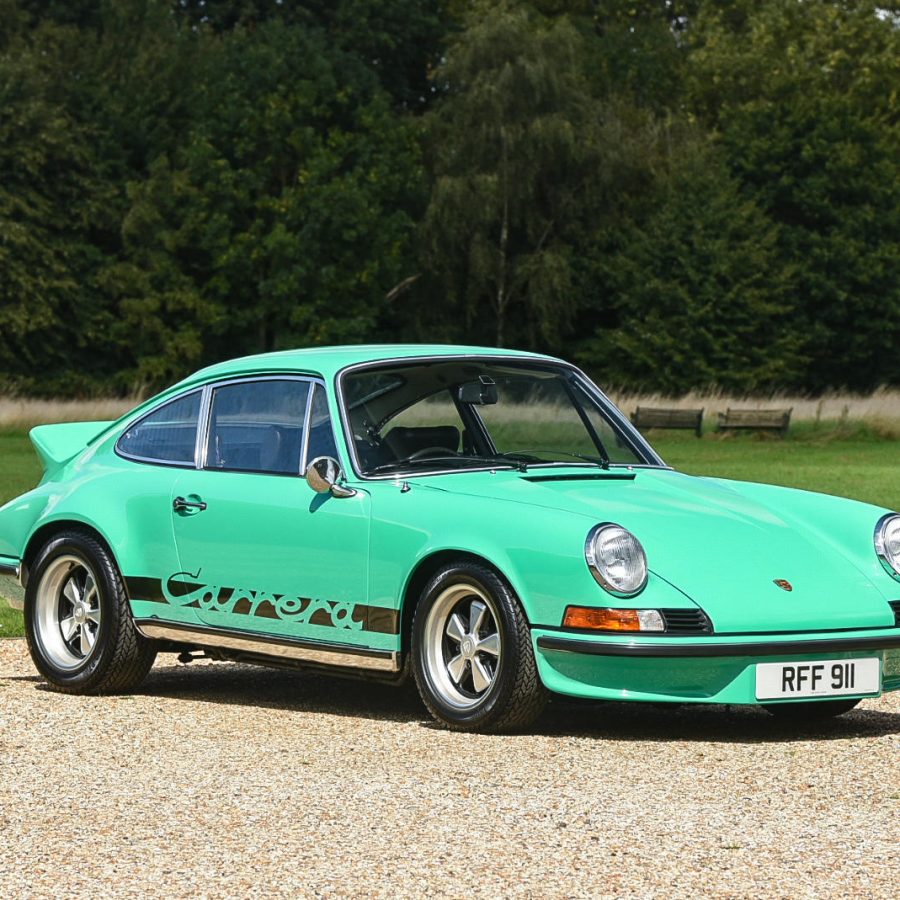
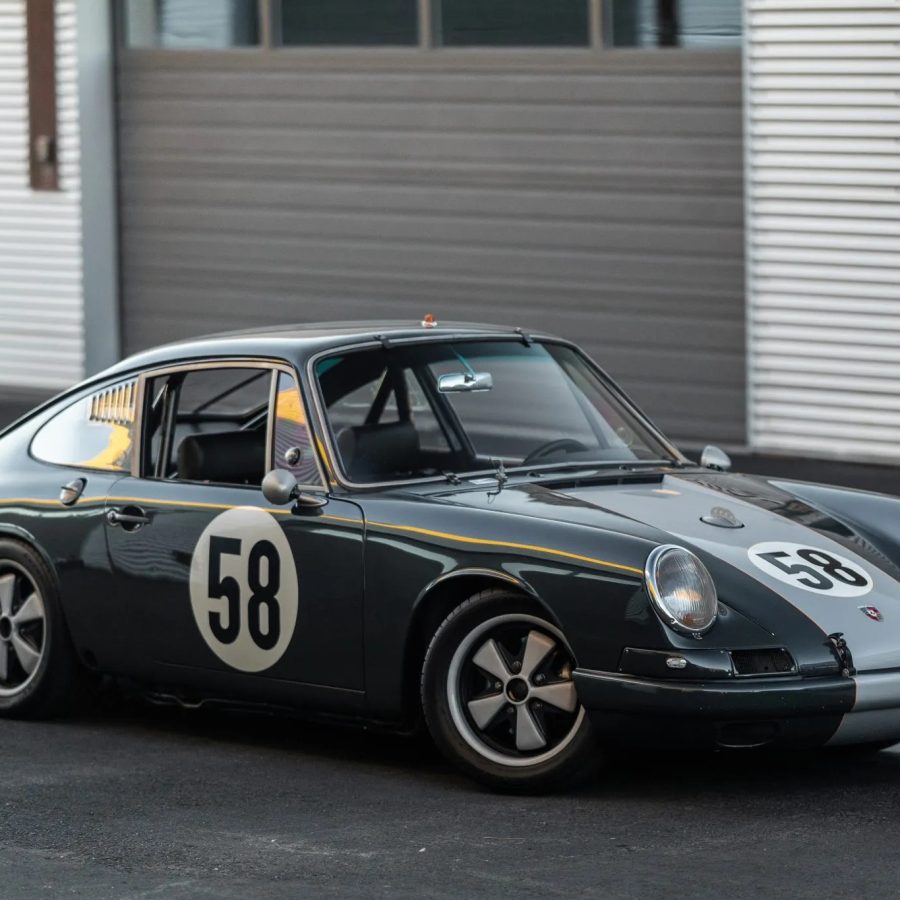
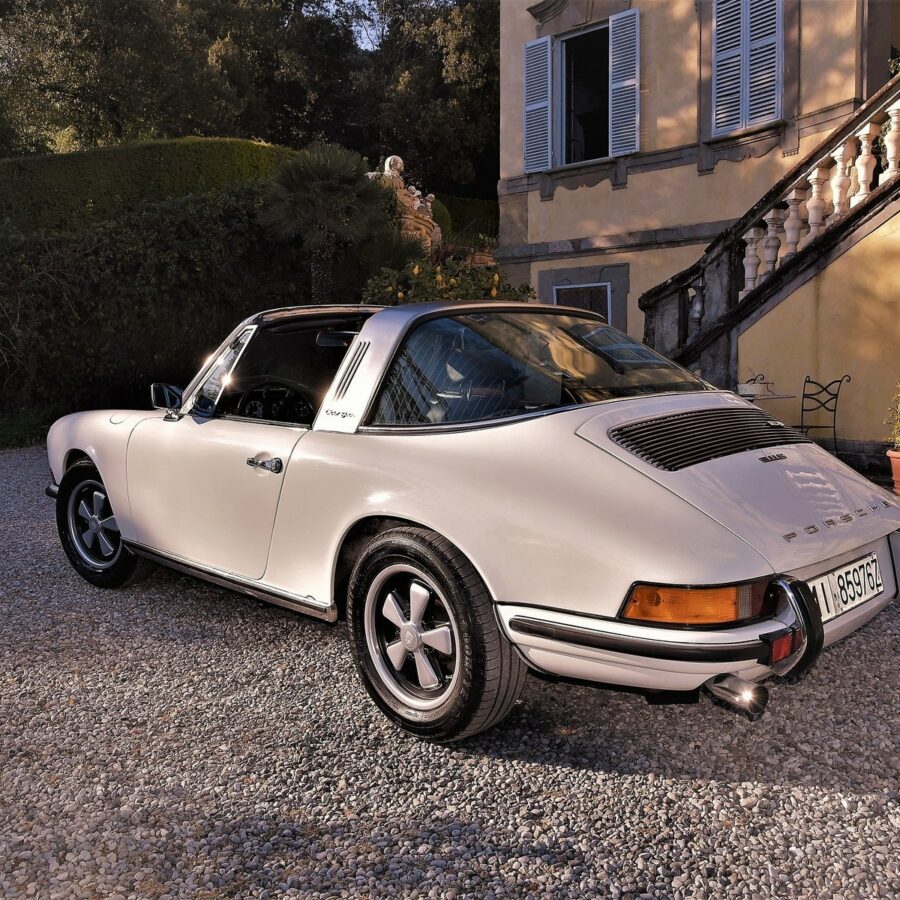
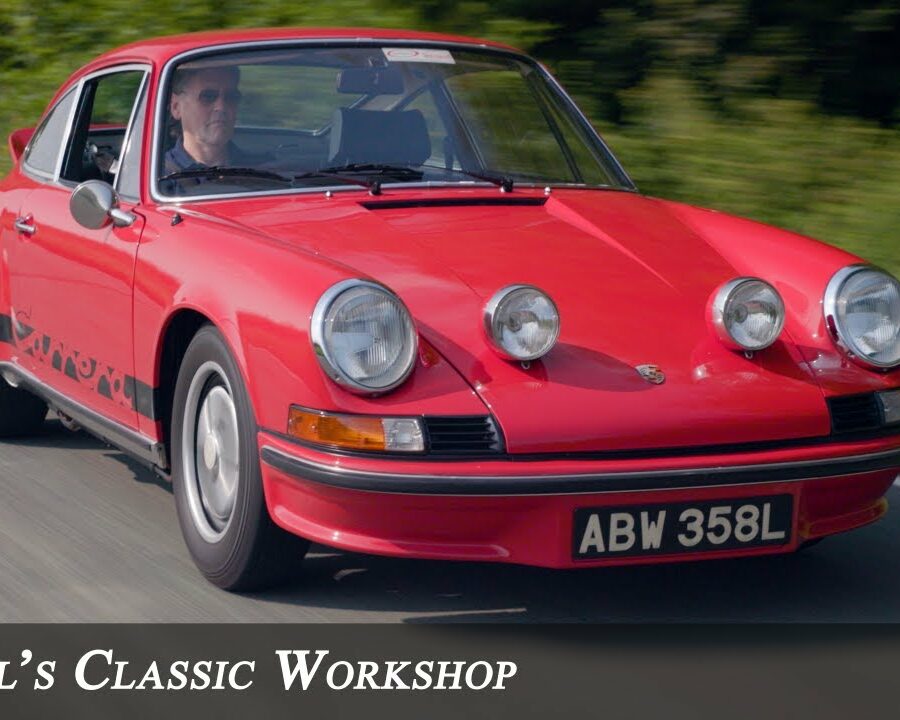
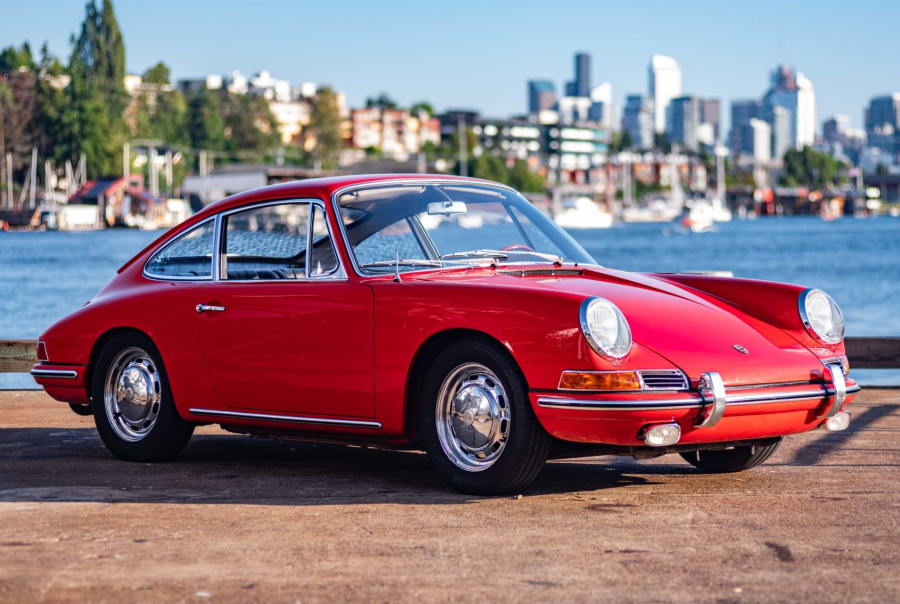
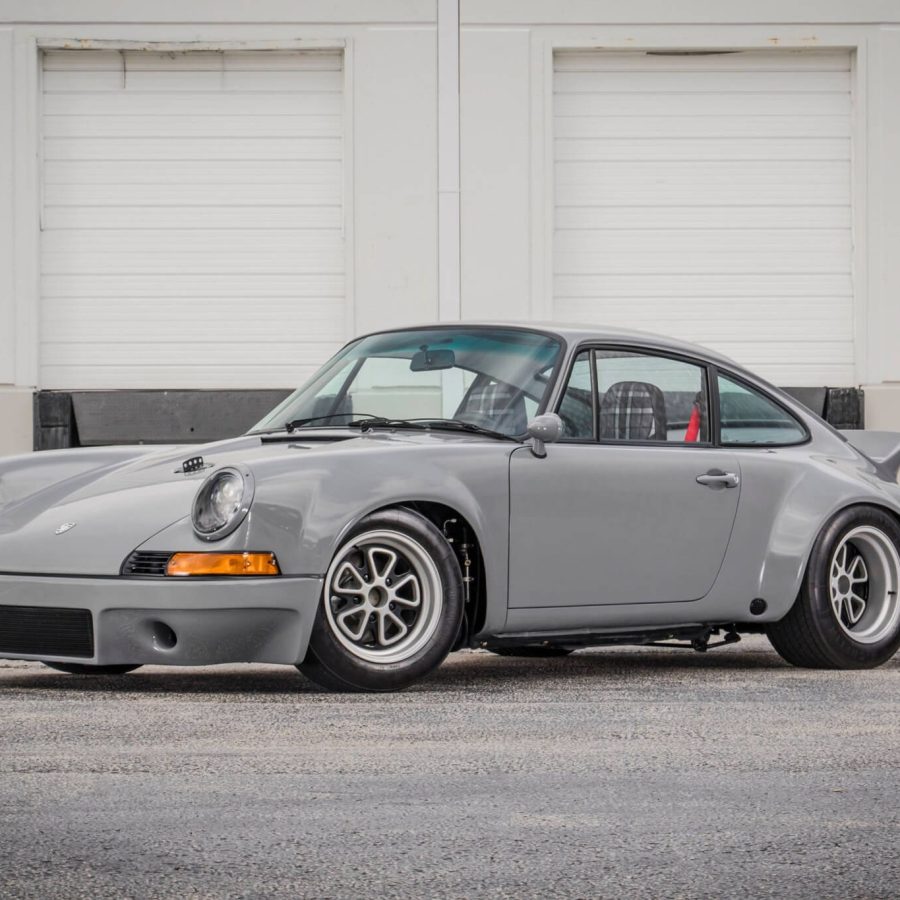
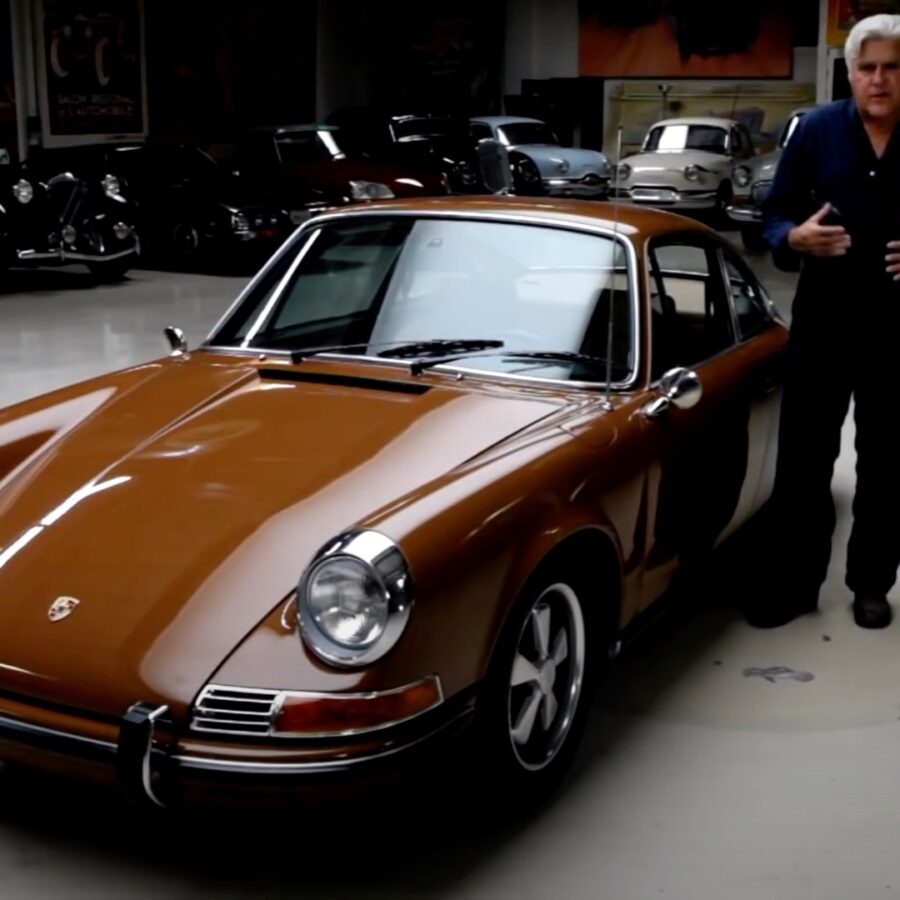
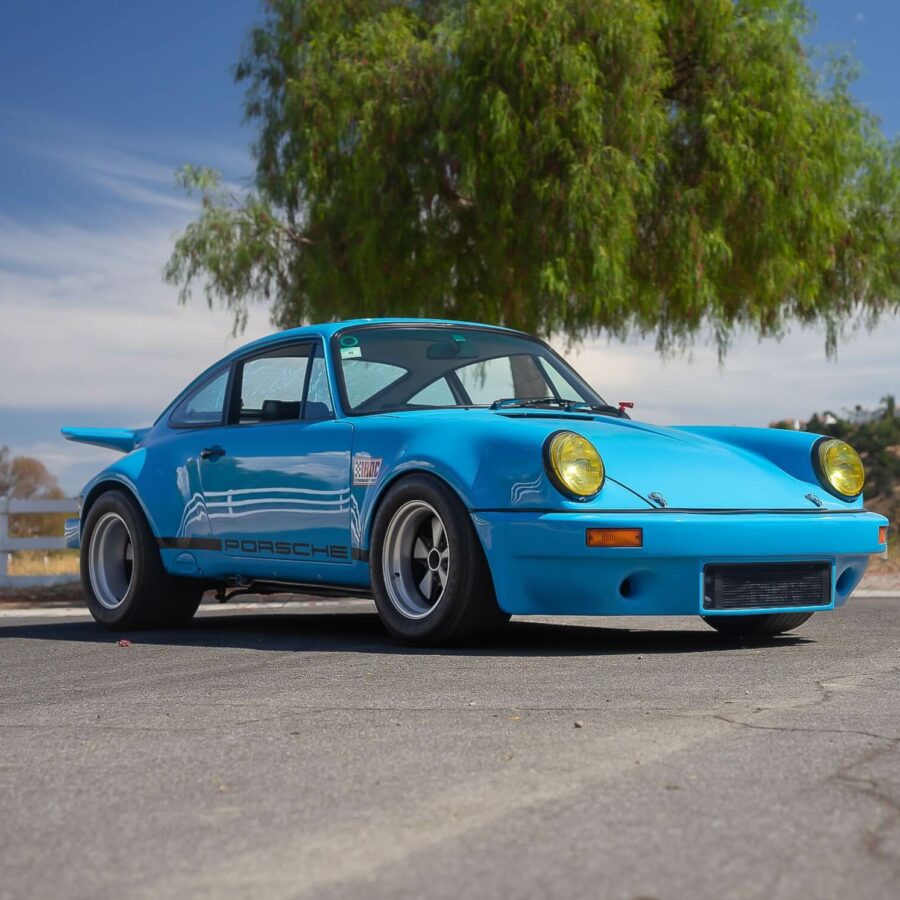
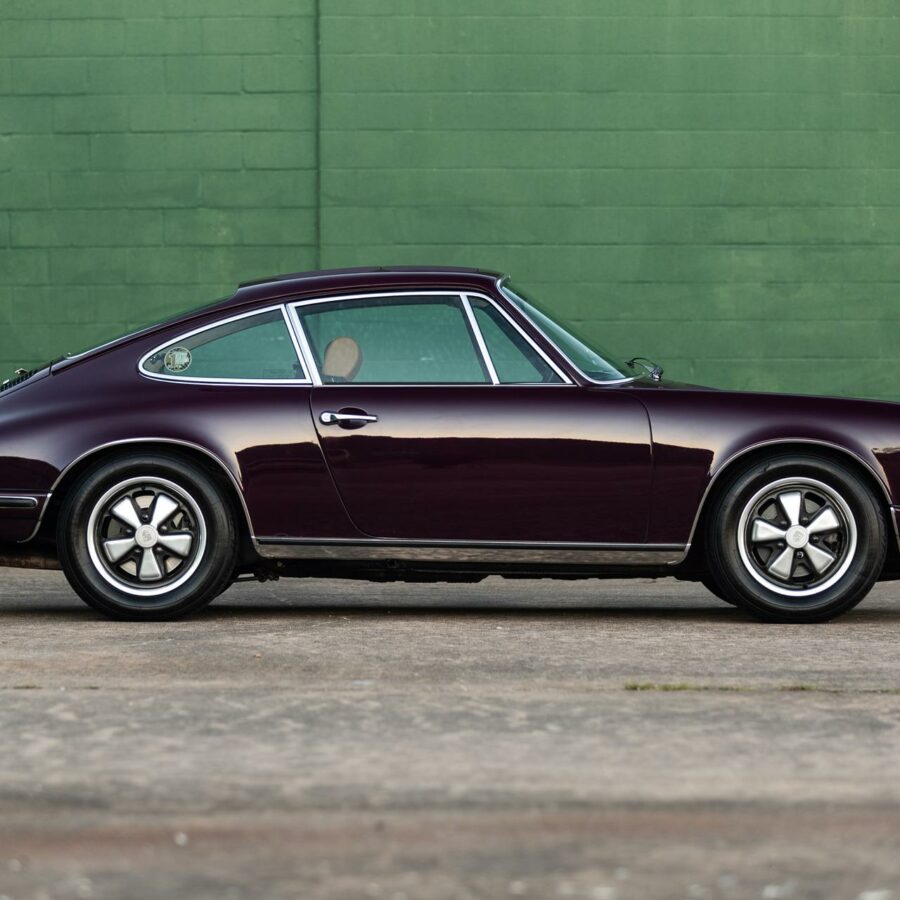
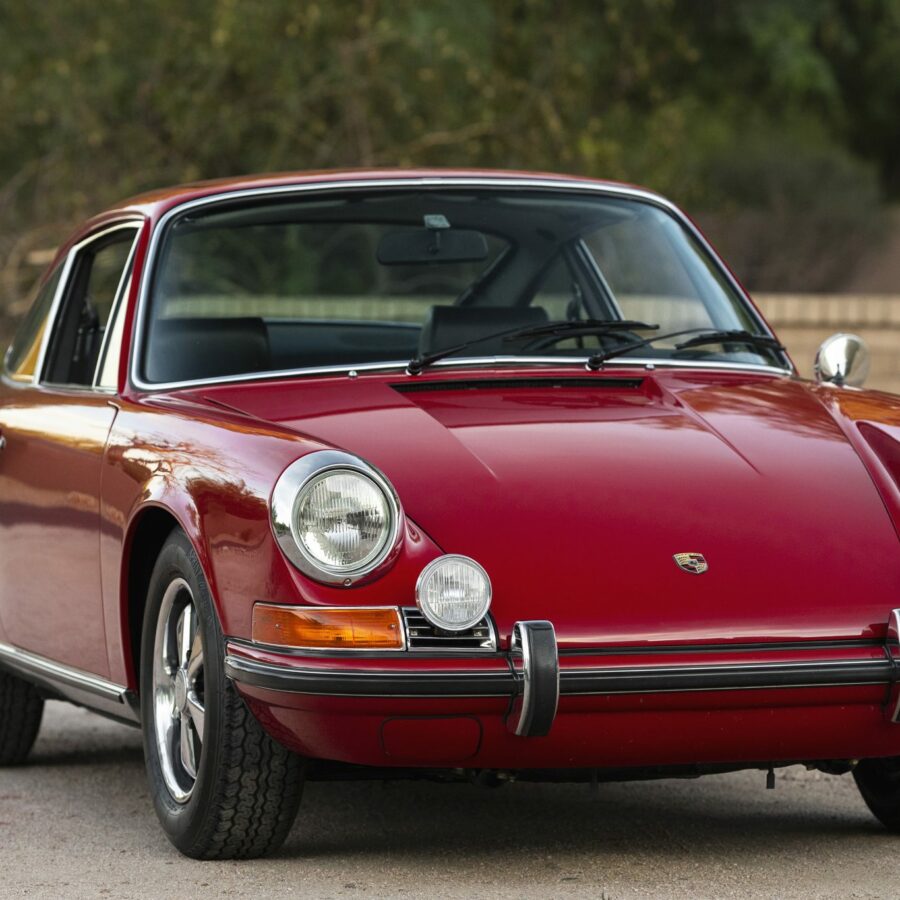
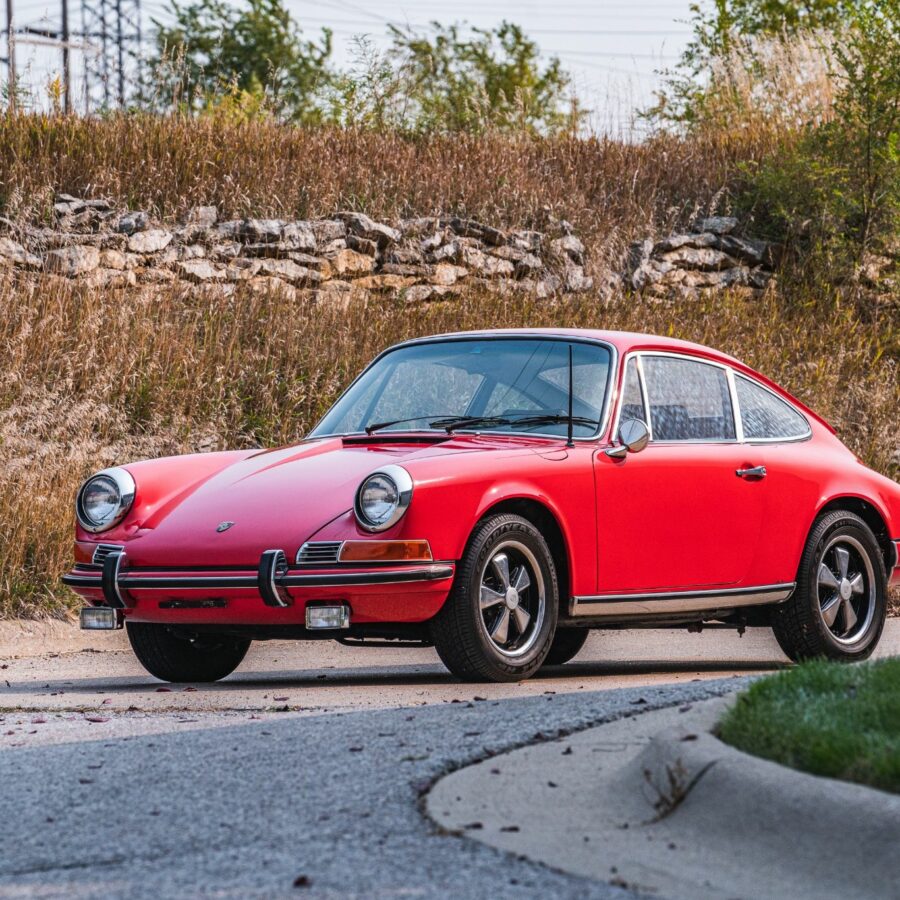
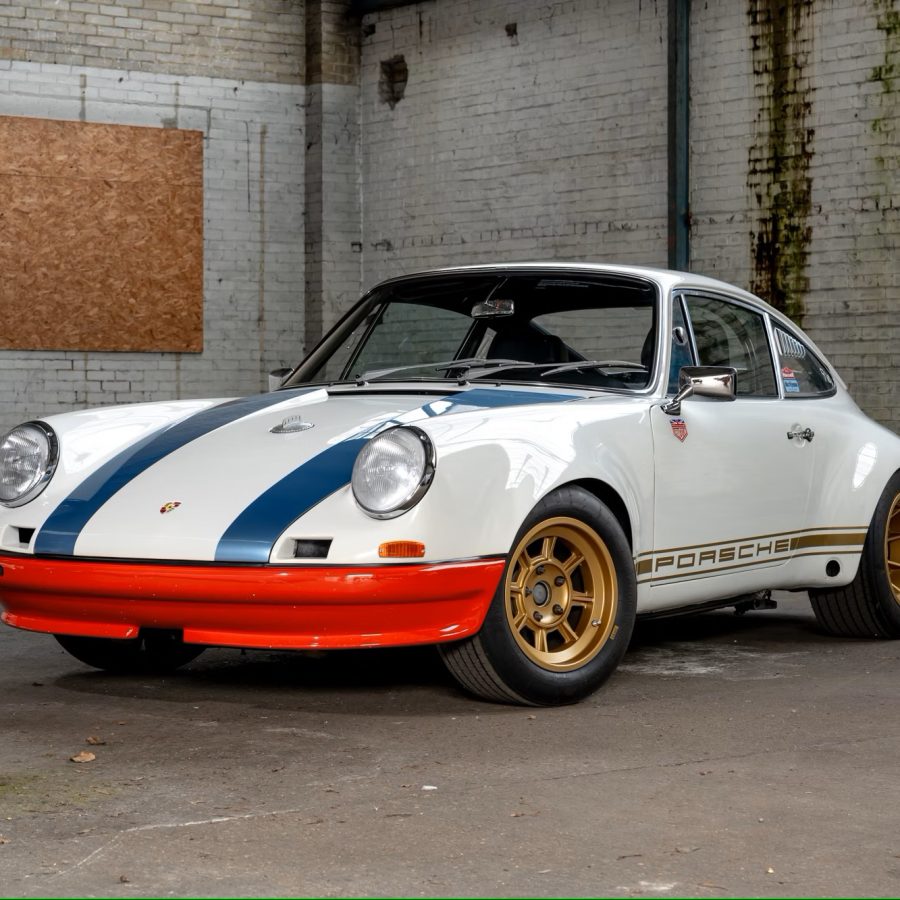
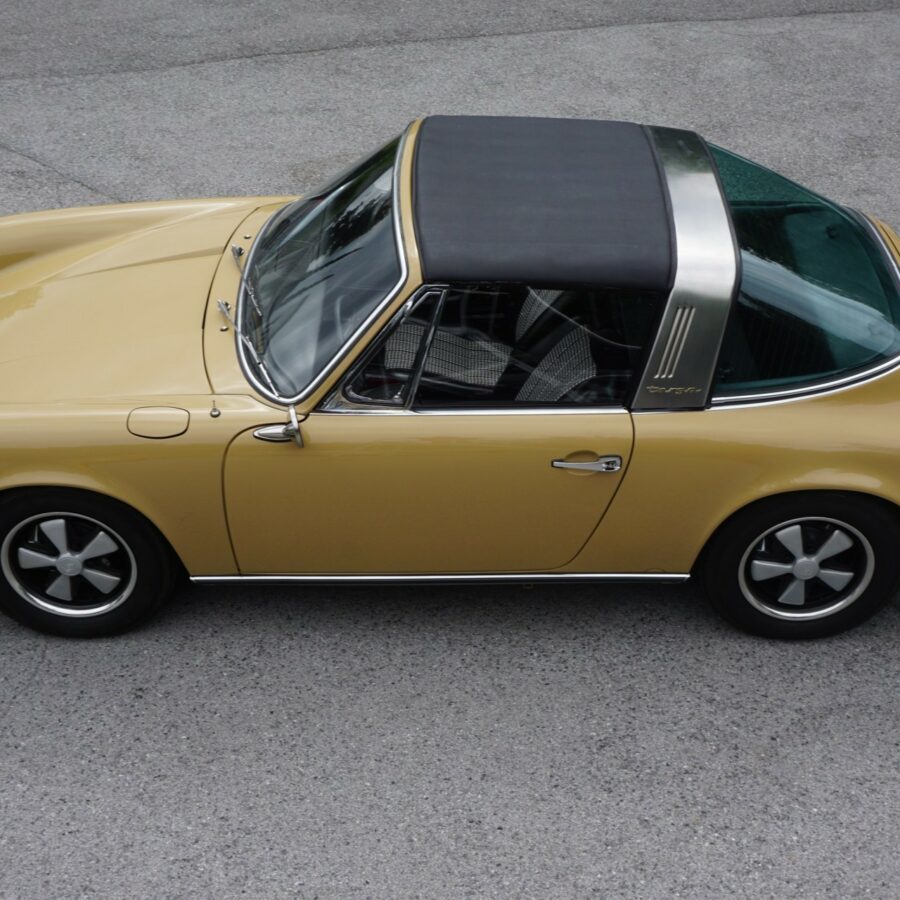
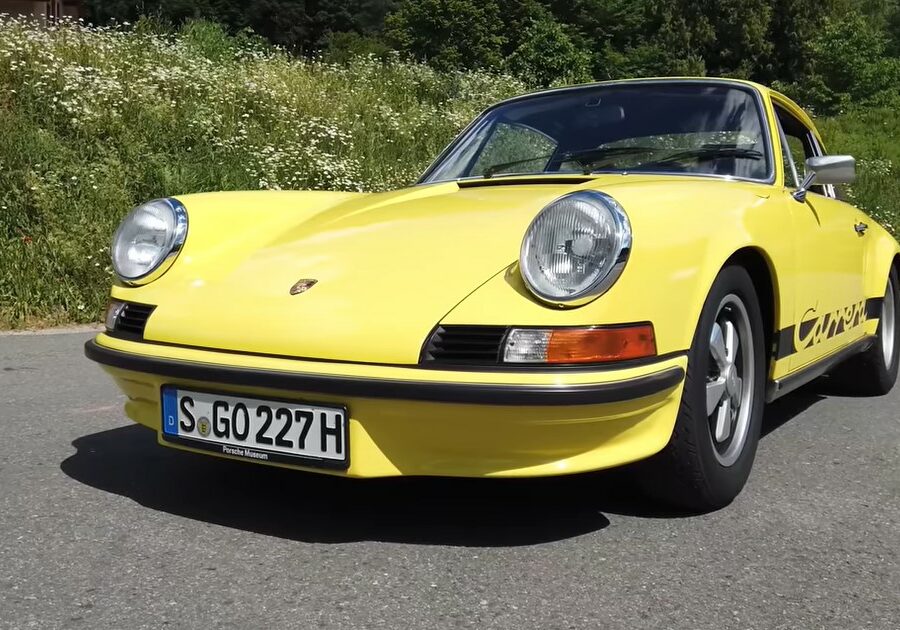
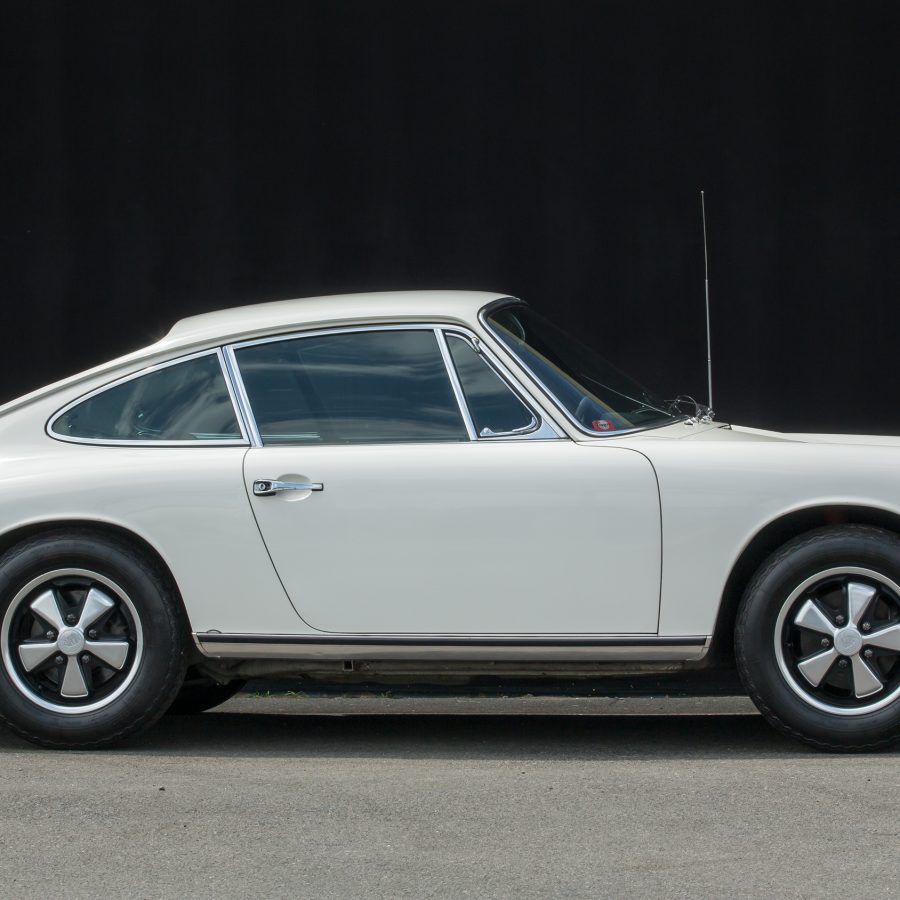
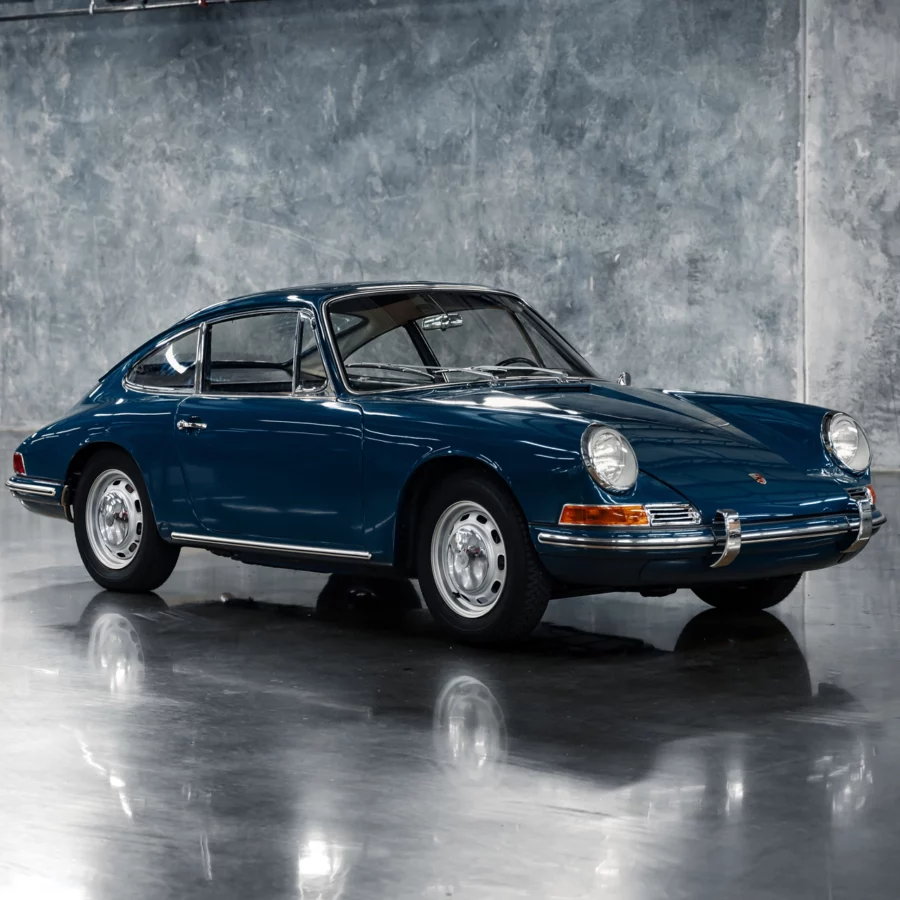
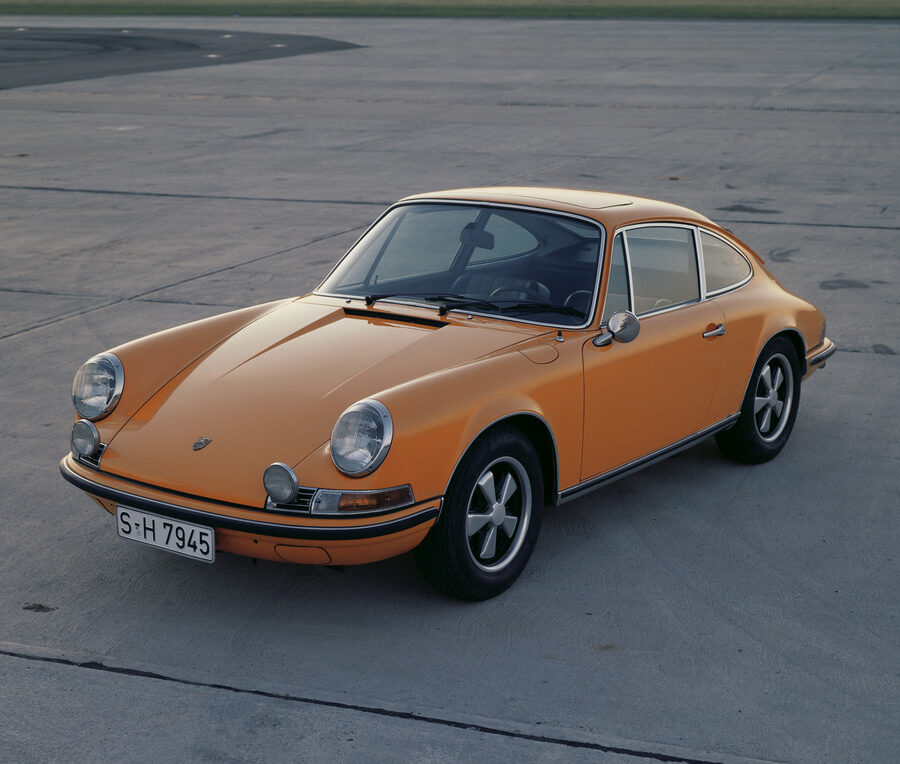
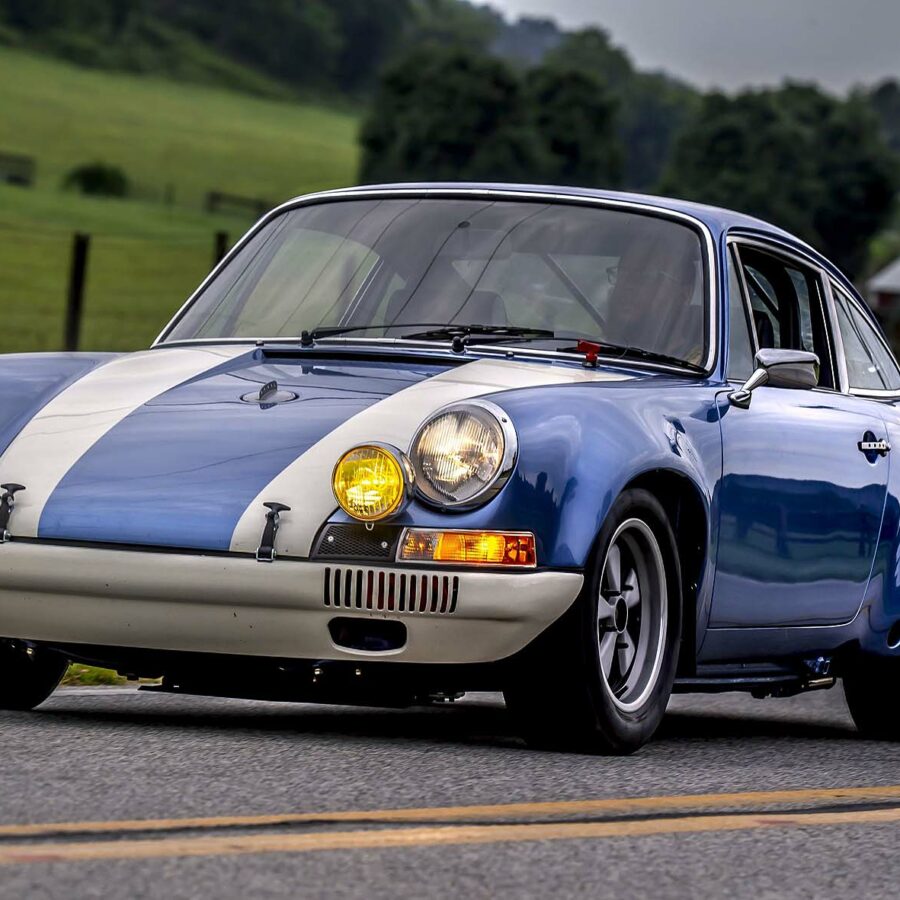
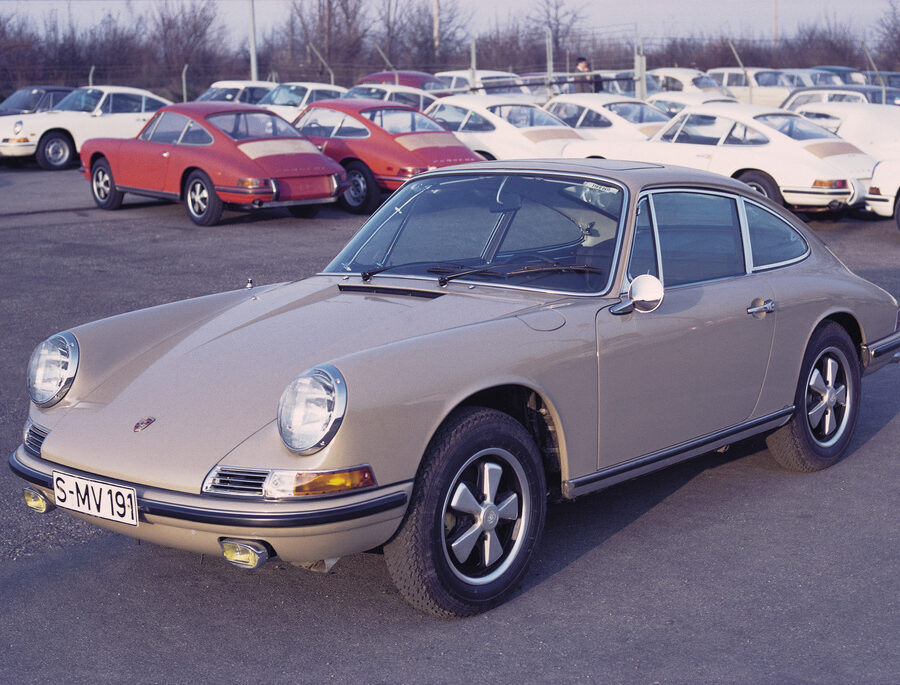
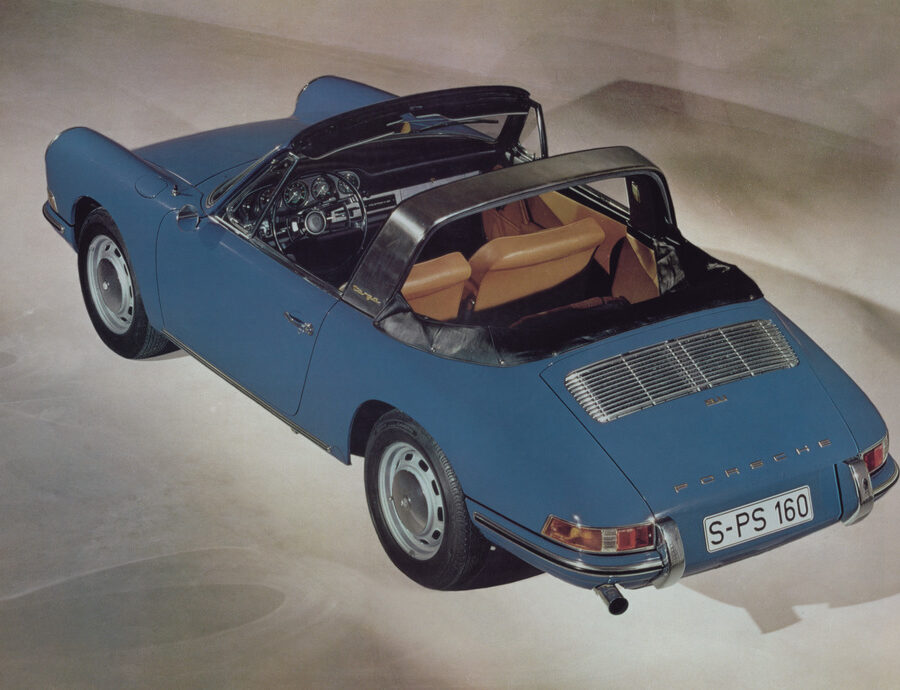
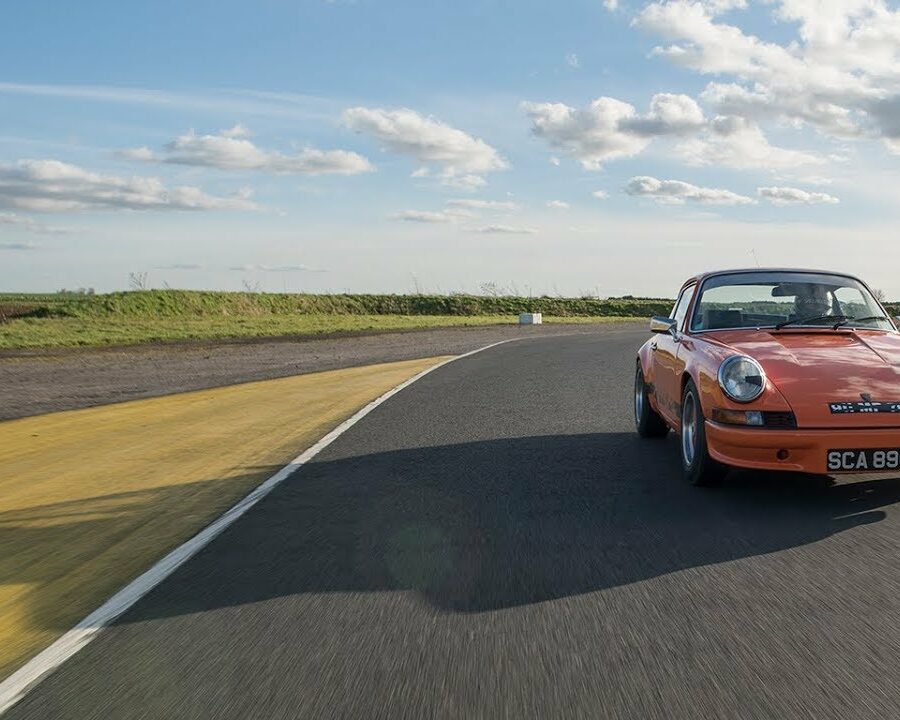
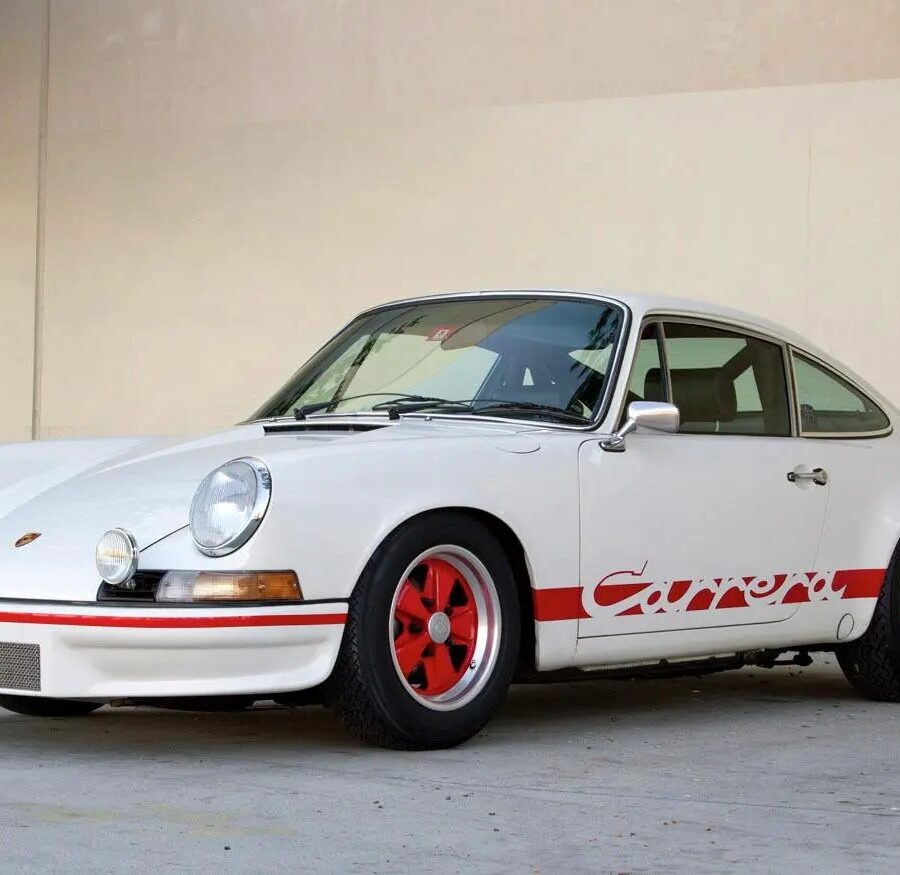
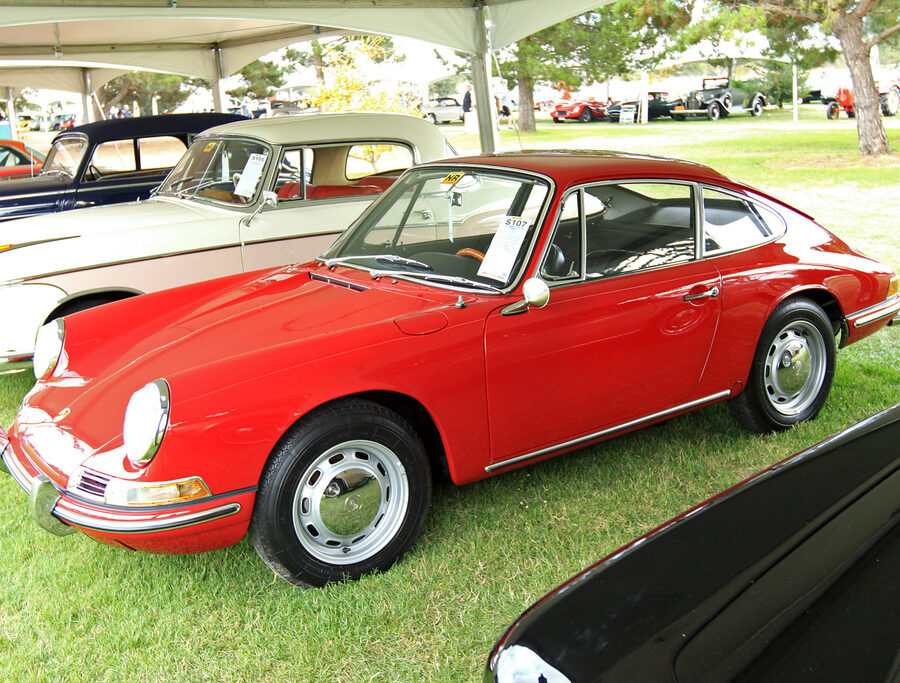
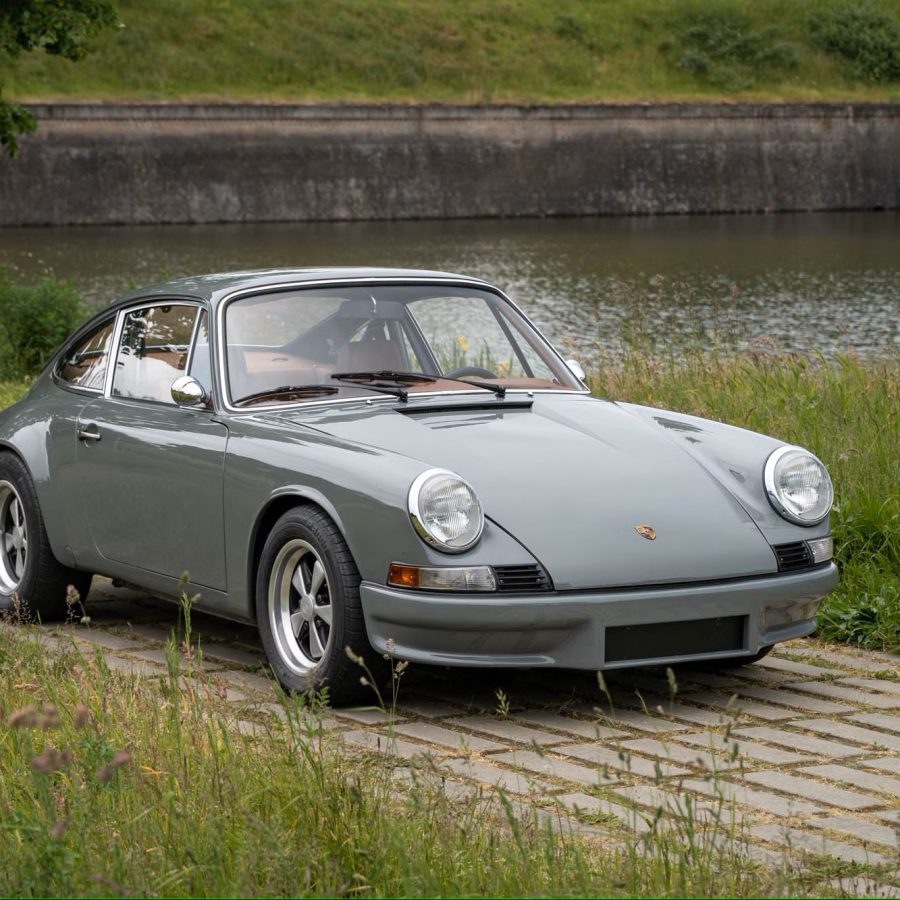
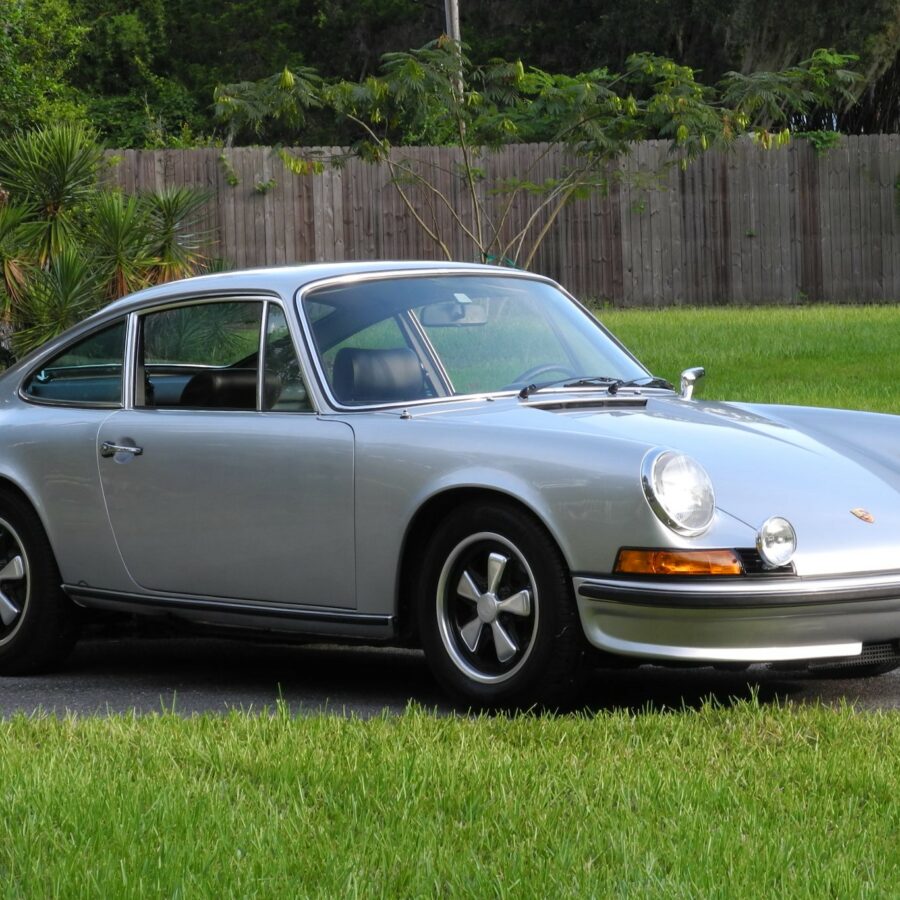
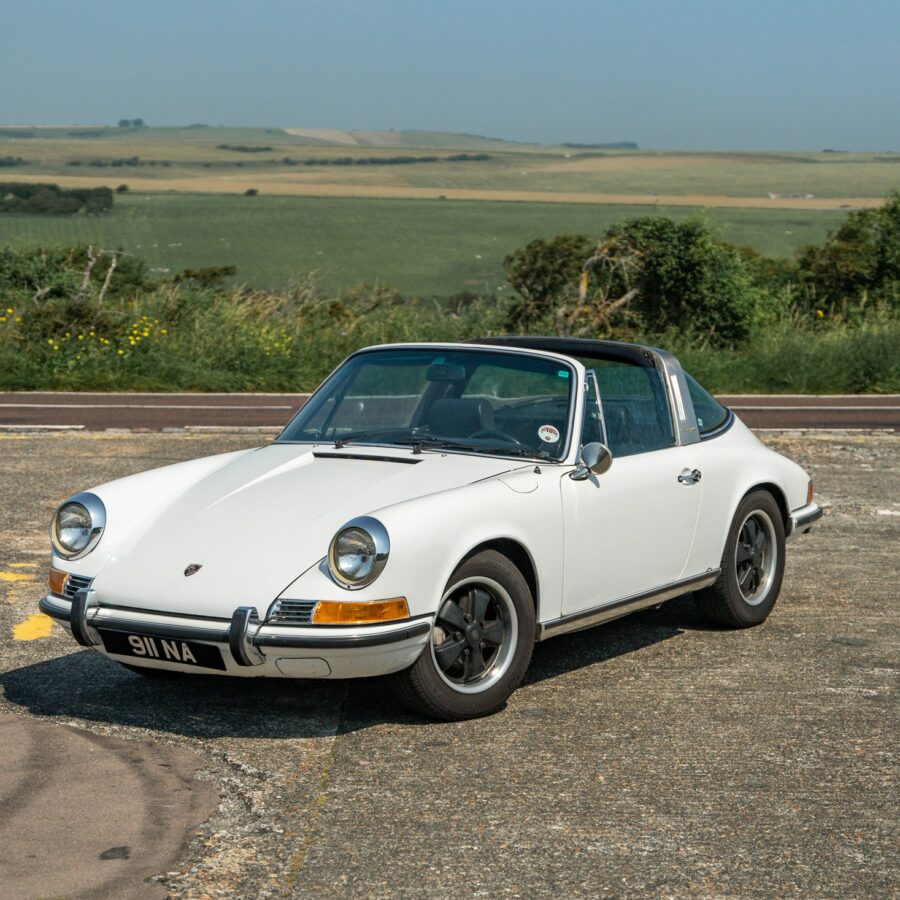
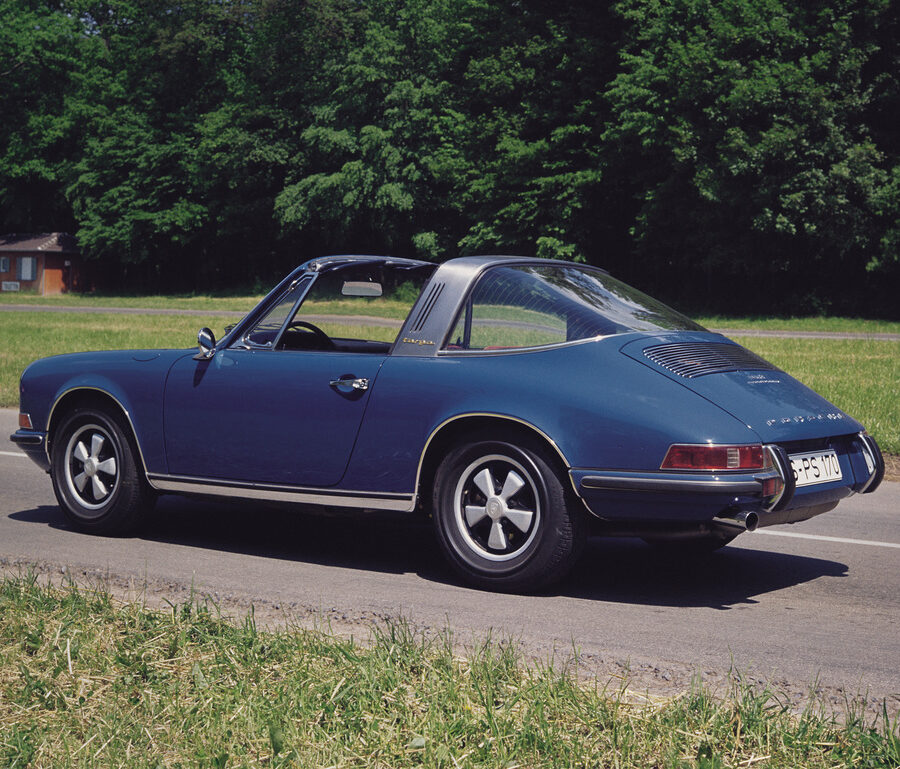
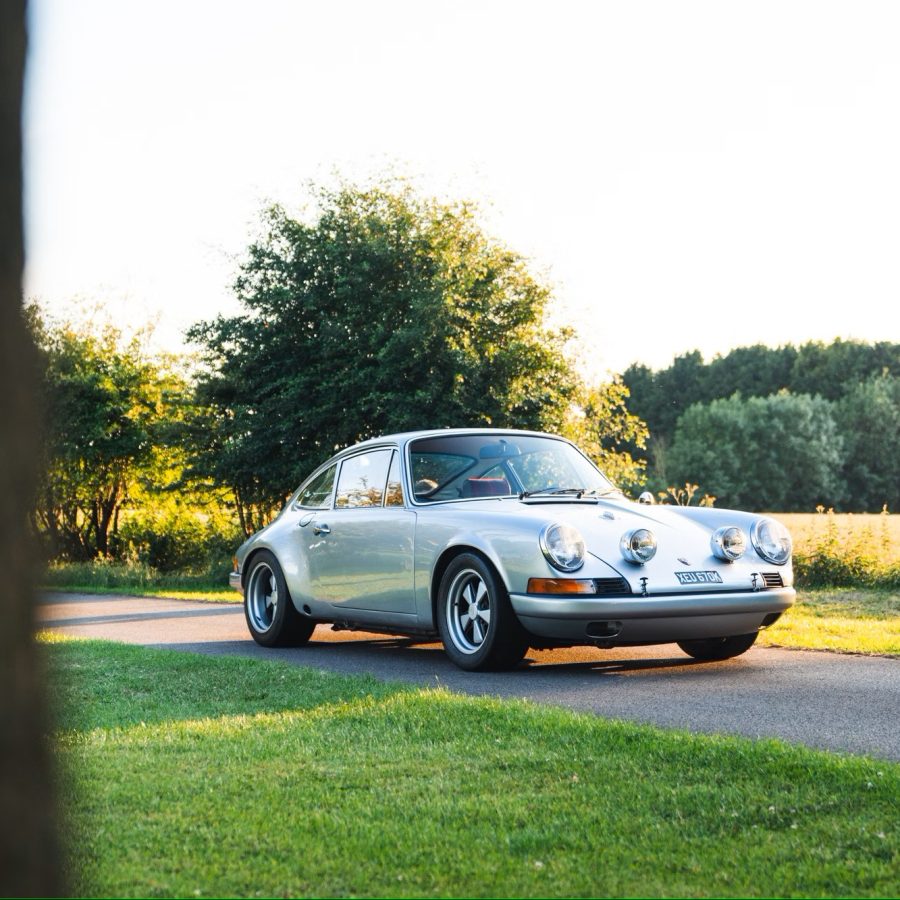
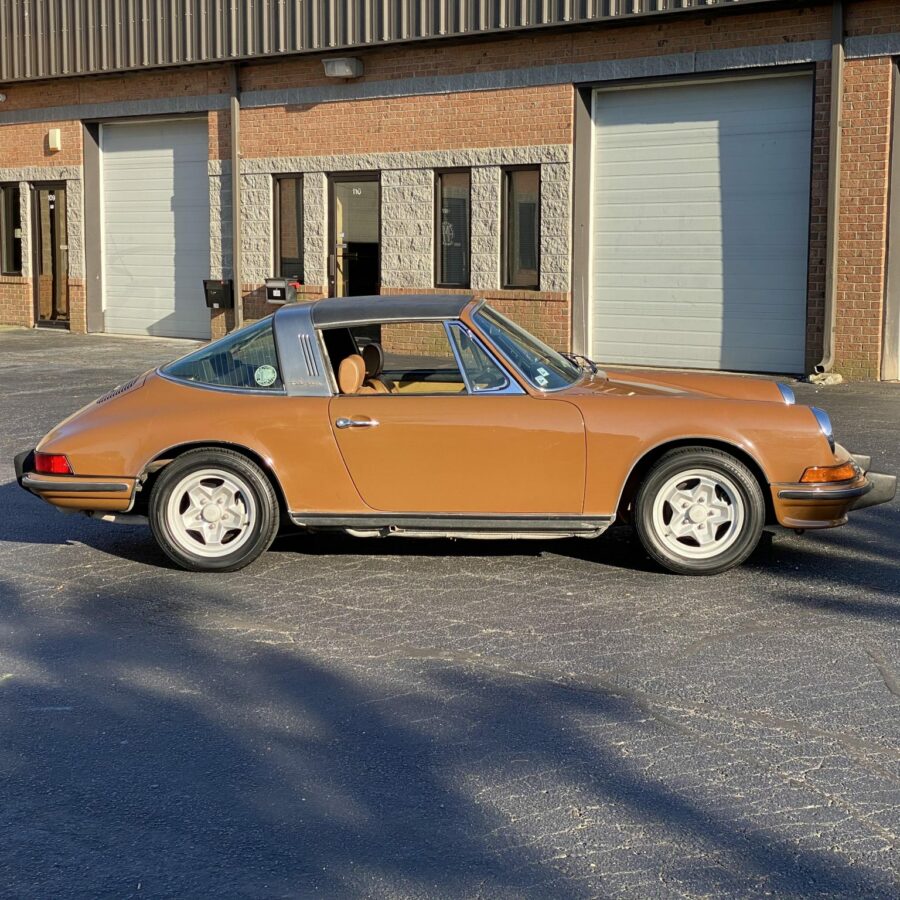
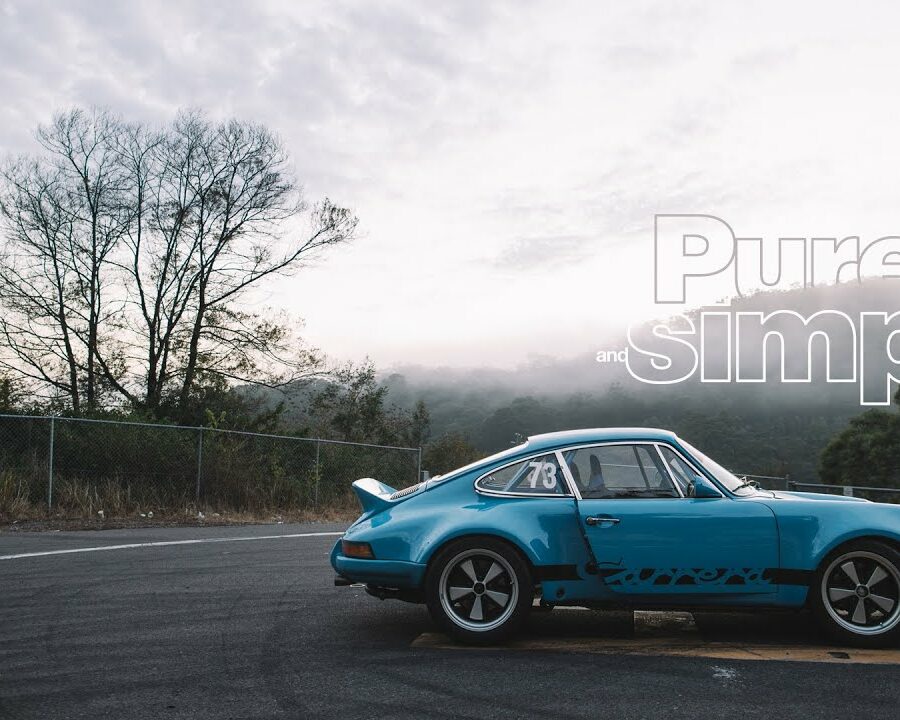
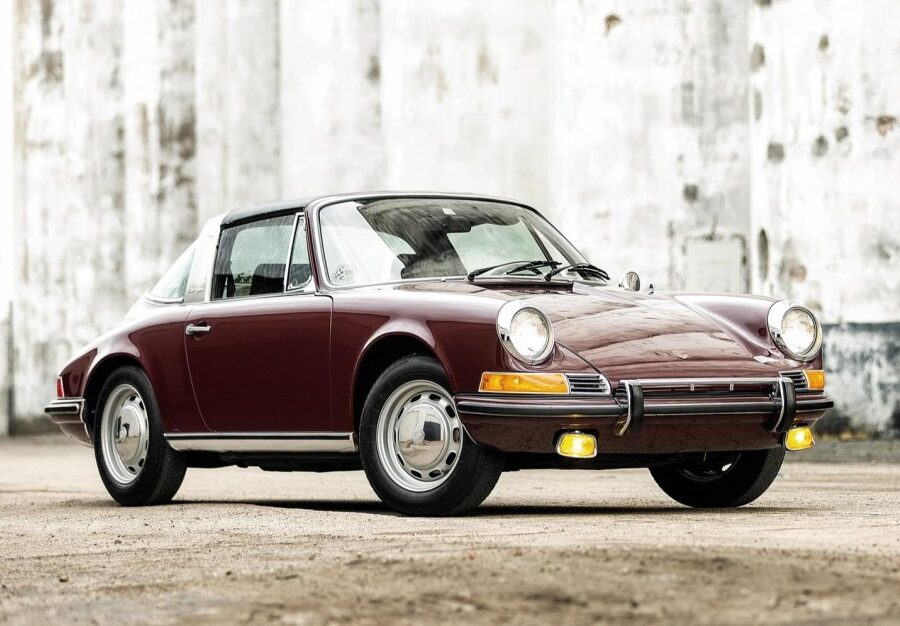
Porsche 911 (F-Series)
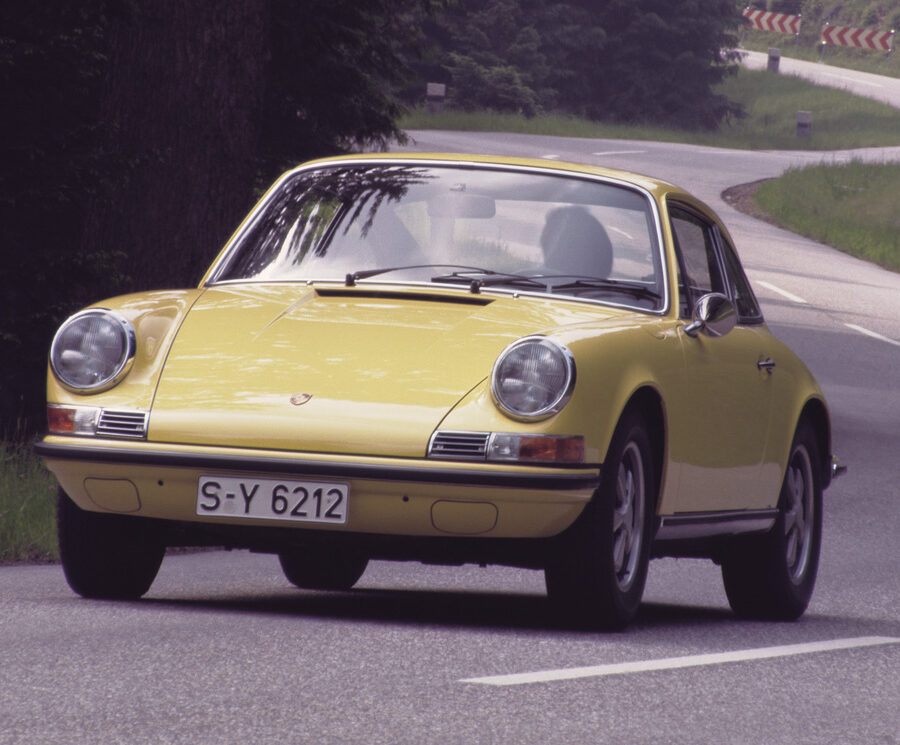
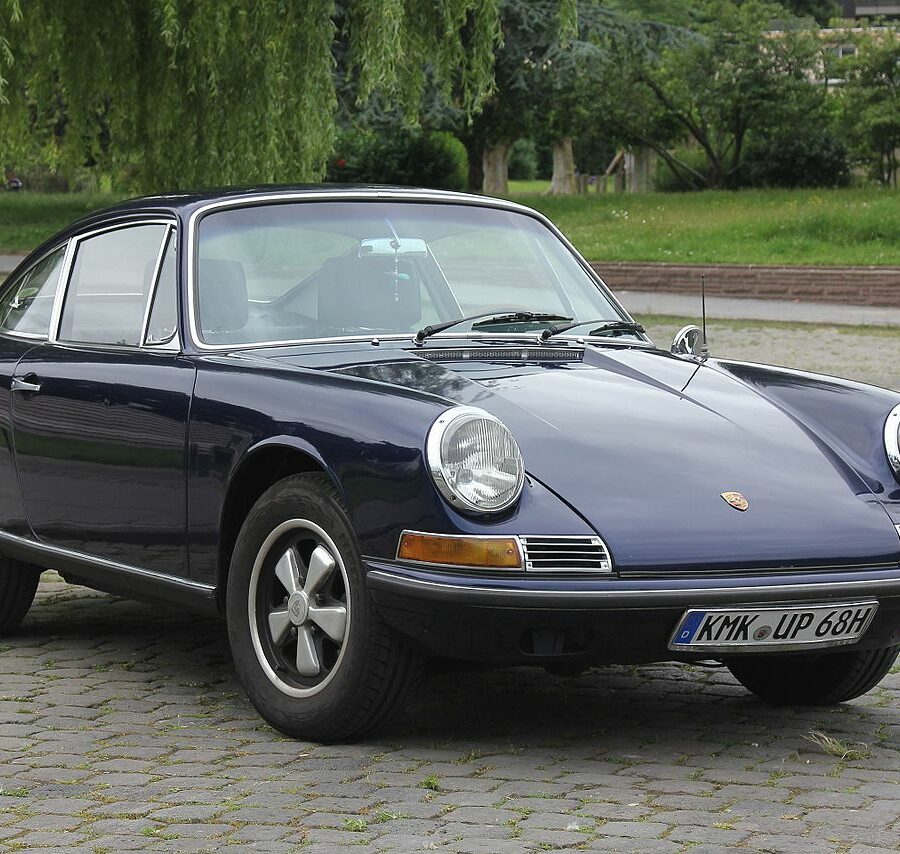
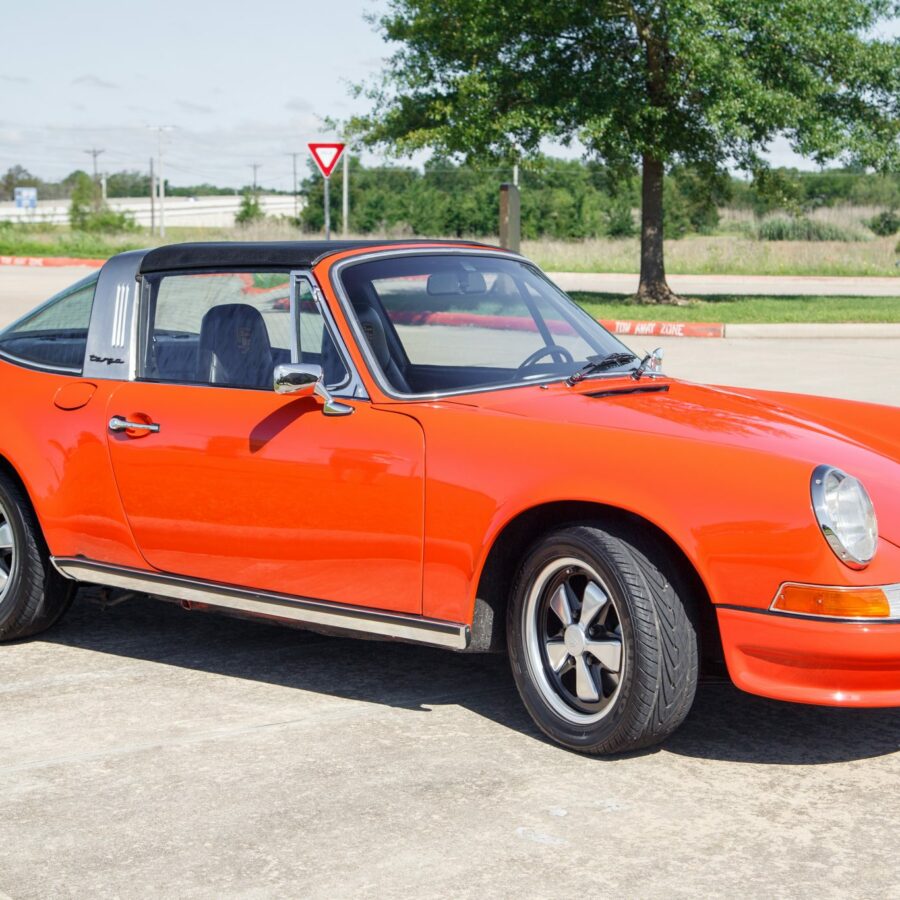
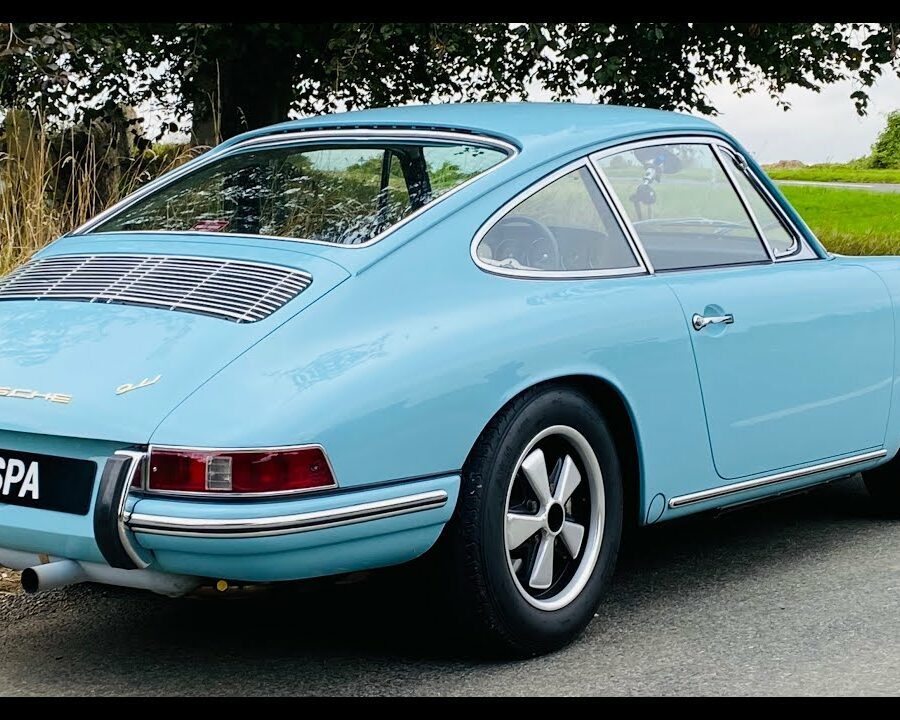
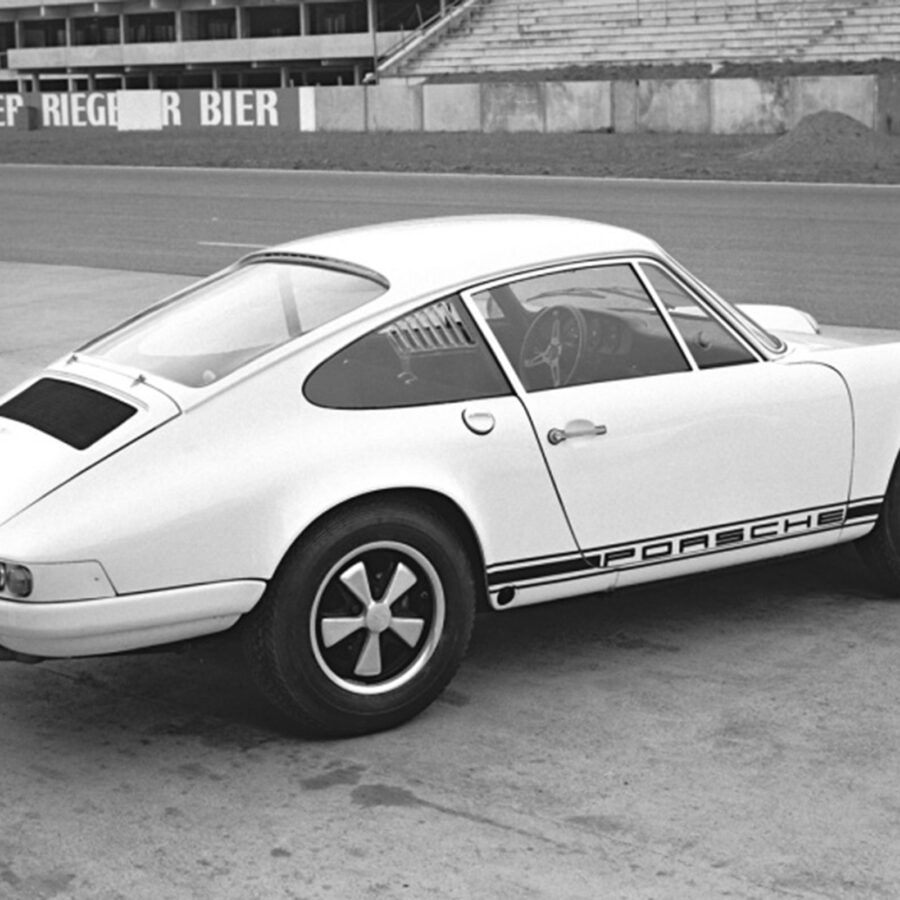
The Porsche 911 was introduced to the world in the fall of 1963 at the Frankfurt Motor Show. It was developed as a replacement for the highly successful Porsche Model 356. It was larger, more powerful, more comfortable and more competitive on the track than any other comparable car on the market at the time. The original air-cooled, boxer-engined 911 was in production from 1964 through 1989, but on this page, we are focused on the original F-Body cars. For 1969 Porsche made the single biggest change to the 911 thus far by lengthening the wheelbase 2.5 inches to reduce the oversteer characteristics inherent to rear-engined cars. Pre-1969 cars are often referred to as the short-wheel base cars (SWB) and 1969 onwards called the long-wheelbase cars (LWB). 1972 and 1973 can also be taken as one group because there were very few changes from year to year. See all of our F-Body Classic 911 Research.
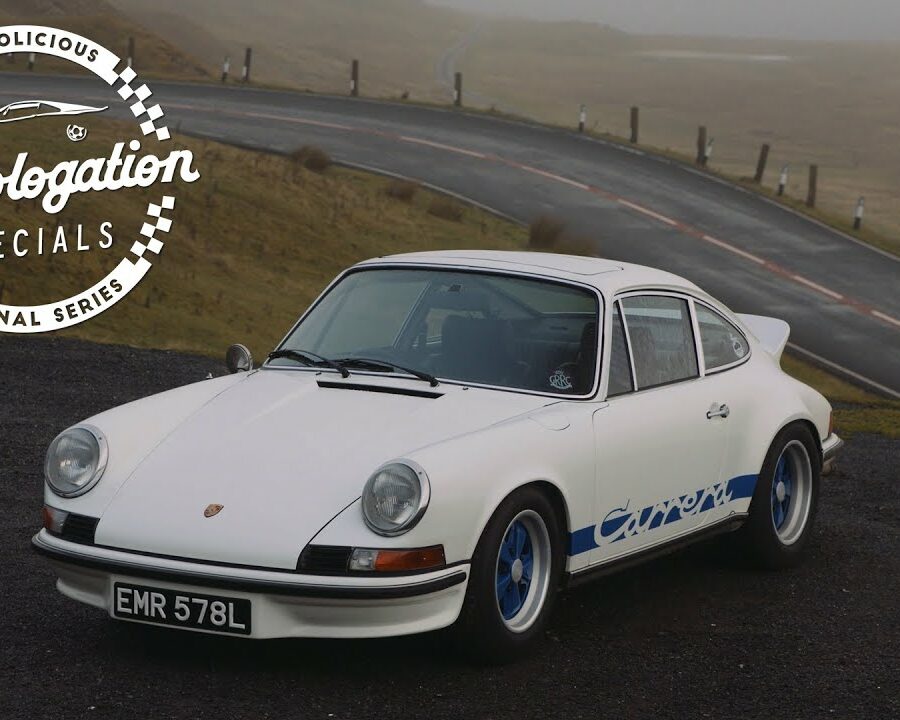
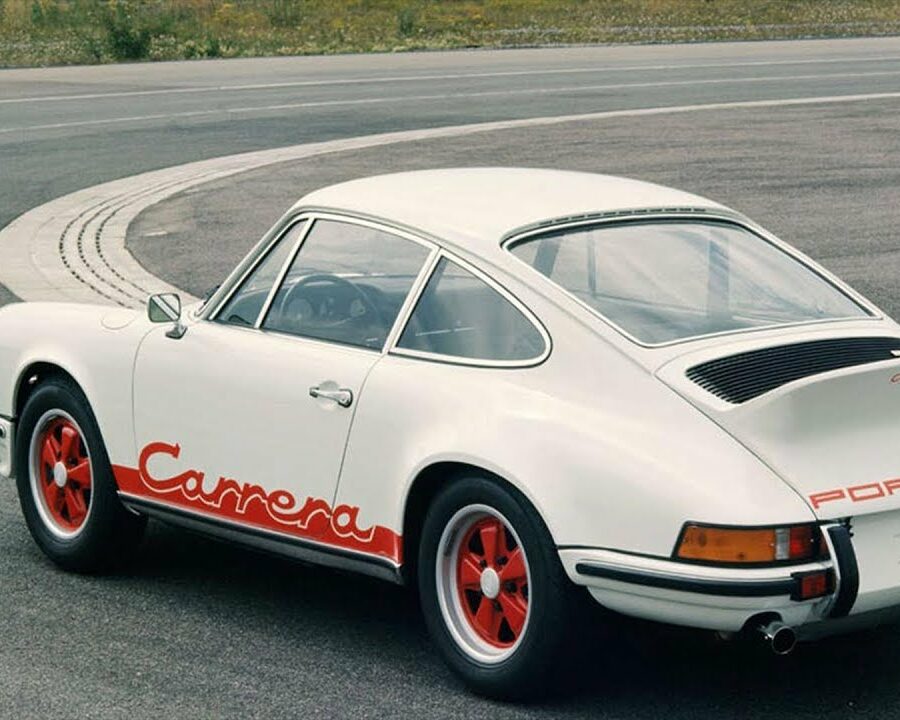
FOR SALE: 1973 Porsche 911 Carrera RS Touring
One of 1,580 built
Backdating the Porsche 911
Time travel is possible, but it comes at a price
Porsche 911 E 2.4 (1972 – 1973)
911E was the mid-range option in the E-series and F-series 911s. It benefited from the larger 2.4 engine
Significant Porsches coming to Amelia Island. Part I
Race or Street? Either will overload the senses.
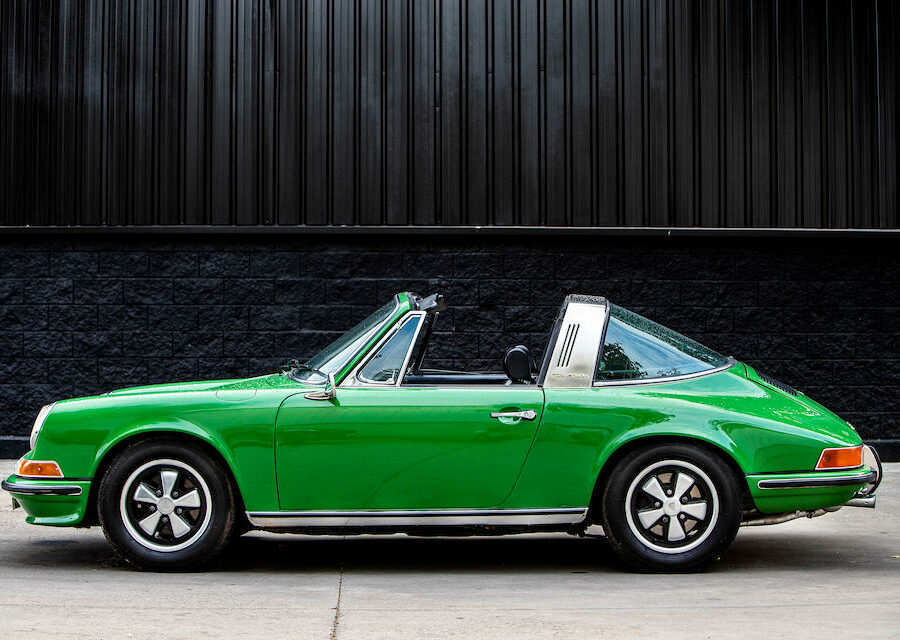
FOR SALE: 1973 Porsche 911 Carrera 2.7 RS Touring Coupé
One of only 11 examples finished in Jade Green
Porsche 911 E 2.0 (1969)
Introduced in 1969 as the midrange model for the 911, sitting between the 1969 911 T and 1969 911 S
History and future of the Porsche 911
Honoring numerous generations of the flat-6
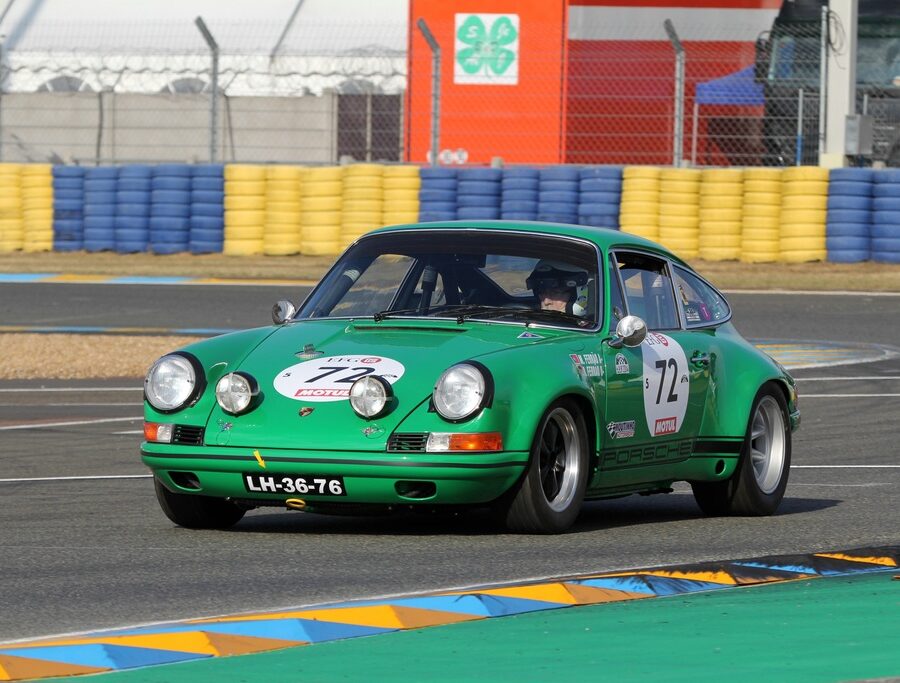
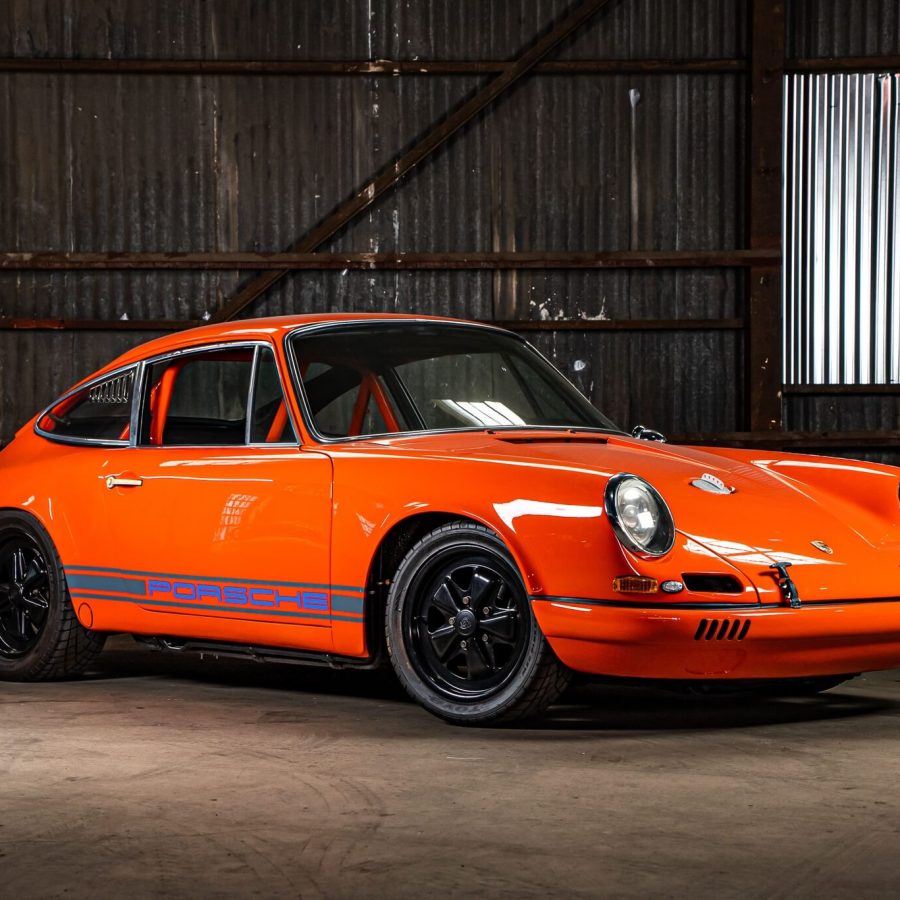
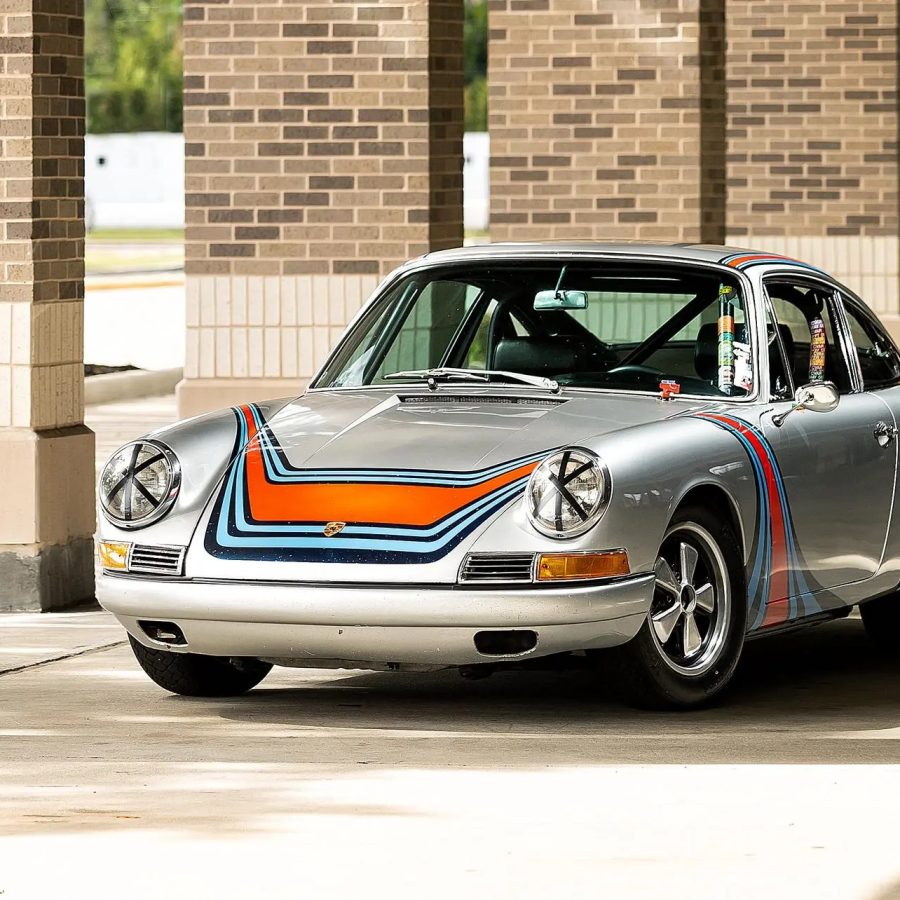
1972 Porsche 911 ST by RS-WERKS
As close to real as it gets
Porsche 911 L 2.0 (1968)
Emissions regulations meant no 911S for the U.S market. So Porsche shipped a 911S with a base 911 drivetrain and called it the 911L.
60 years of Porsche 911
Thoughts from Porsche's current chief designer
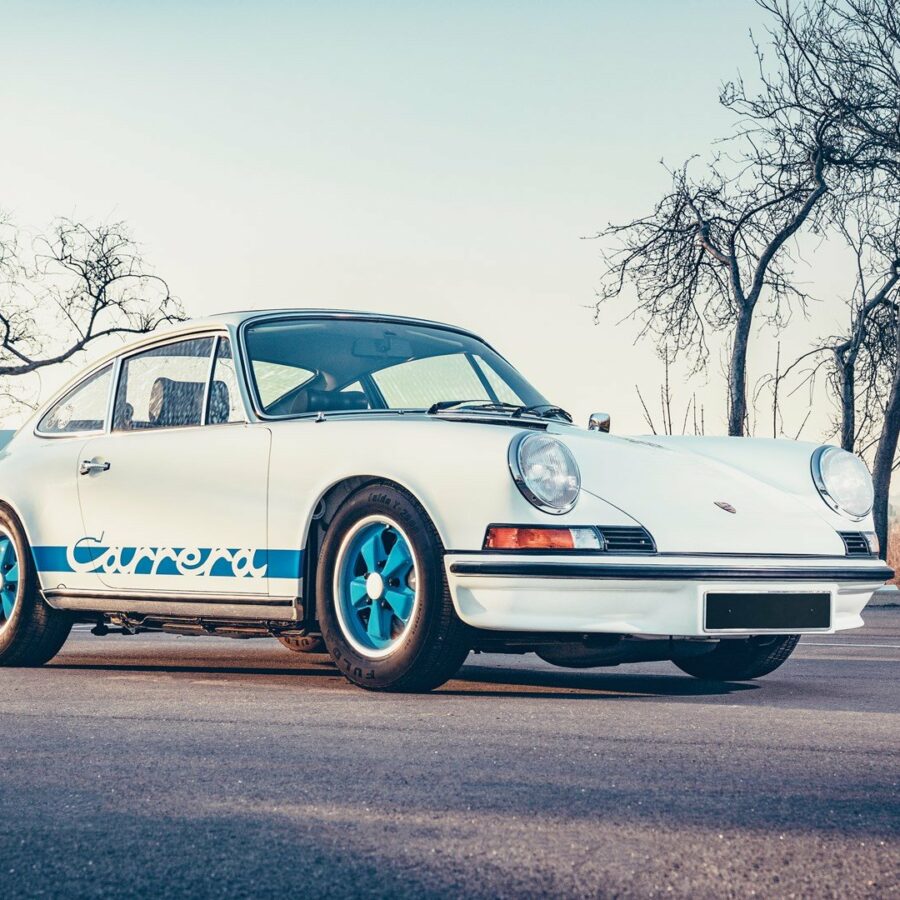
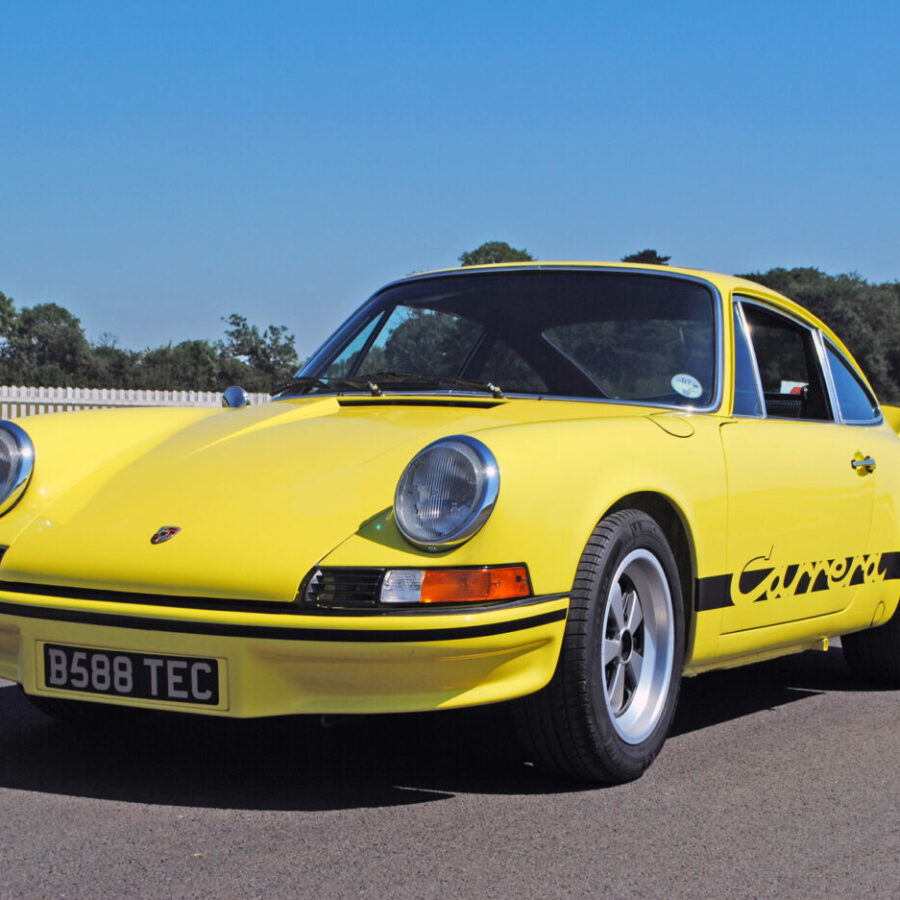
Porsche 911 Carrera RS 2.7 (1973 ) – The Deep Dive
The Story & Details Behind The Legend
FOR SALE: 1973 Porsche 911 Carrera RS 2.7 Touring
One of just 1,308 Carrera RS 2.7s built to “M472” Touring specification
The White Collection breaks $30M at auction
RM Sotheby's results show strength in Porsche collector market
Luftgekühlt in Copenhagen
Porsche culture juggernaut rolls into Scandinavia
Porsche 911 S 2.4 (1972 – 1973)
The final early 911S benefitted from Porsche's 2.4-liter engine the the long-wheel-base body
RUF-restored Porsche 901 Wins at Pebble Beach
6th 911 built earns Best in Class and Art Center Award
Porsche 911 R (1967 – 1968)
A lightweight racer designed to take the newly released 911 to its limit
Ultra-Rare ’73 Porsche 911 Carrera RS in Gulf Orange
It will be auctioned by RM Sotheby's with estimates reaching $550,000
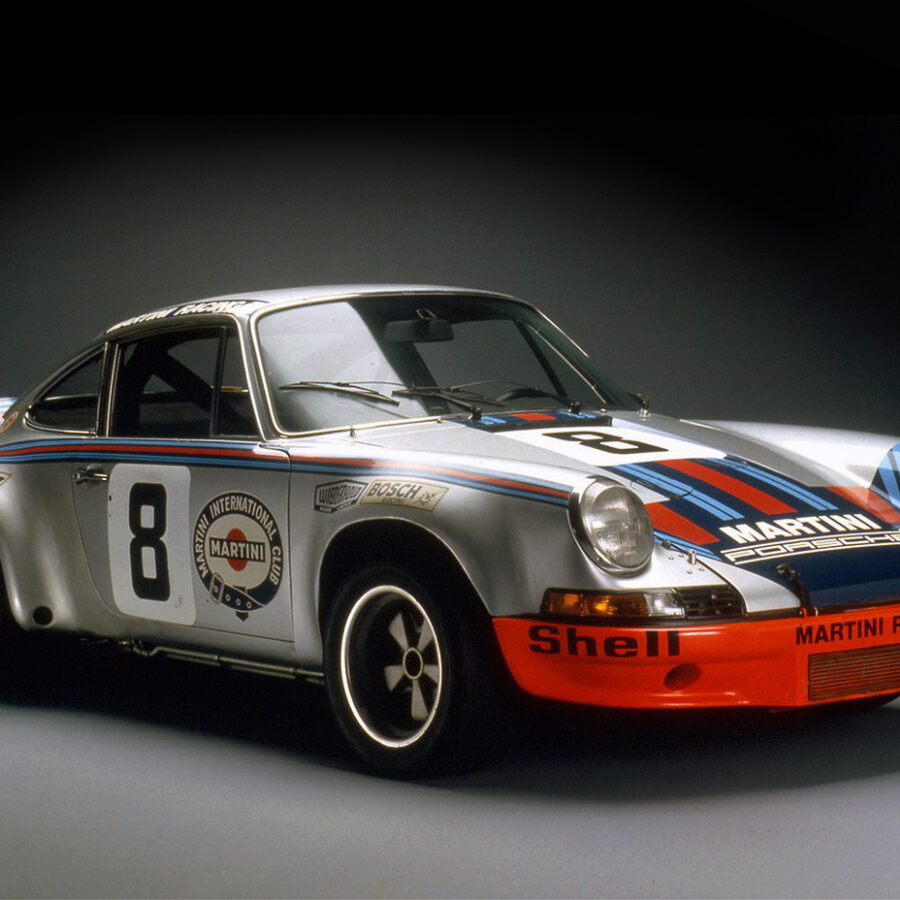
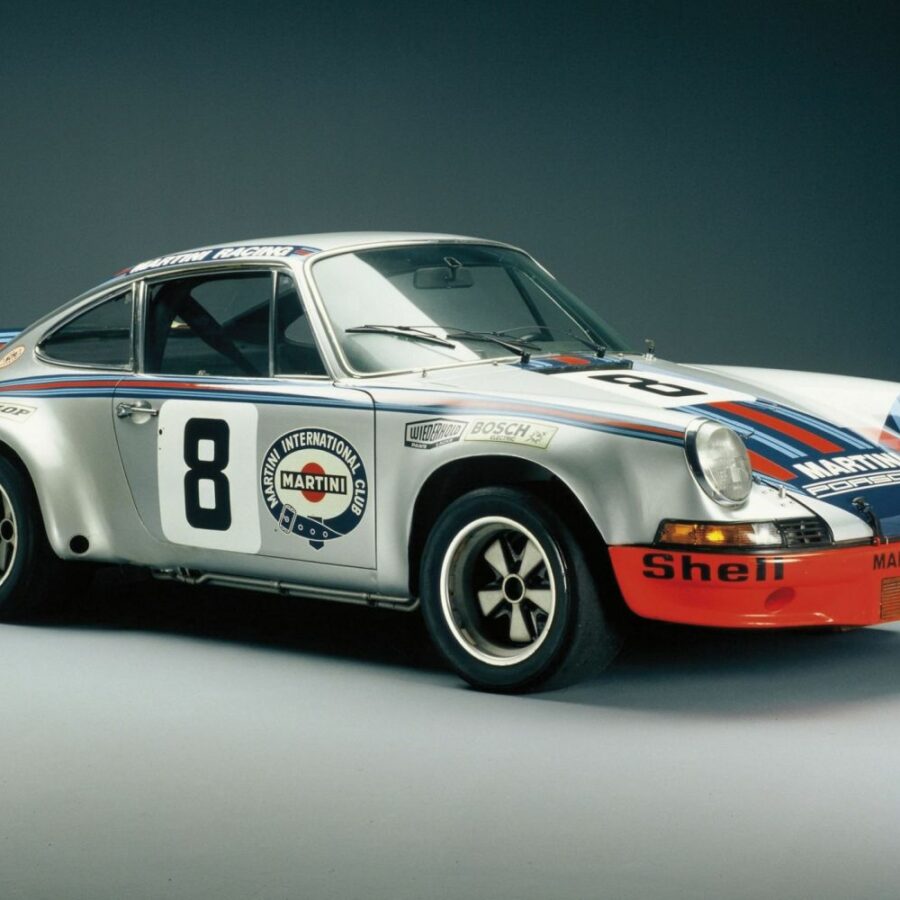
Porsche 911 Carrera RSR 2.8 (1973)
The first 911 to ever wear the RSR badge and homologated for racing by the 1973 911 Carrera RS
Porsche 911 T 2.0 (1968 – 1969)
Porsche replaced their 912 with the 911 T. Less expensive, less powerful and less stuff than the standard 911 L
Porsche 911 (MY 1970) – Equipment & Options Codes
Full list of Equipment & Option Codes Decoder for the 1970 Porsche 911
Rare and Collectible 1973 Porsche 911 Carrera RS 2.7 Lightweight Up for Auction
One of only 200 Lightweight variants produced with competition history
1973 Porsche 911 Carrera RSR 2.8L
Rarest of the rare
Signal Green 911 Outlaw checks all the boxes
Dale Christian's 73 Carrera RS build defines the modern Outlaw
Lease this 1973 Porsche 911 RS Carrera!
Stuttcars exclusive with Putnam Leasing Inc.
Ultra-Rare 1973 Porsche 911 Carrera RS 2.7 Lightweight at Mecum Kissimmee
Could fetch up to $1,300,000